Multicast static routes, Changing an rpf route – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 88
4-4
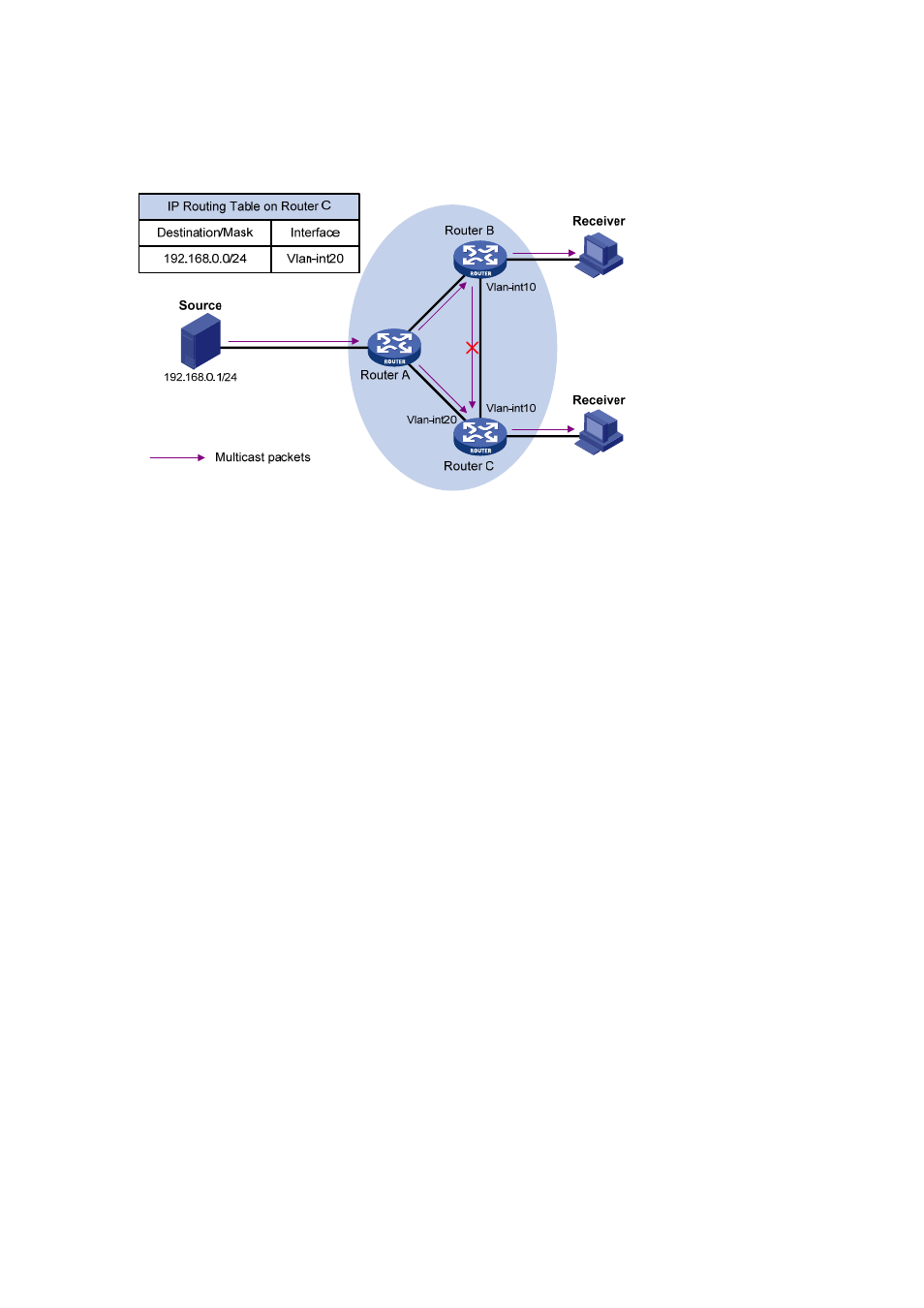
forwarding table on Router C contains the (S, G) entry, with Vlan-interface20 as the RPF
interface.
Figure 4-1 RPF check process
z
When a multicast packet arrives on Vlan-interface20 of Router C, as the interface is the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet to all outgoing
interfaces.
z
When a multicast packet arrives on Vlan-interface10 of Router C, as the interface is not the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet: The
router searches its unicast routing table and finds that the outgoing interface to Source (the
RPF interface) is Vlan-interface20. This means the (S, G) entry is correct and packet
arrived along a wrong path. The RPF check fails and the packet is discarded.
Multicast Static Routes
A multicast static route is an important basis for RPF check. Depending on the application
environment, a multicast static route has the following two functions:
Changing an RPF route
Typically, the topology structure of a multicast network is the same as that of a unicast network,
and multicast traffic follows the same transmission path as unicast traffic does. By configuring a
multicast static route for a given multicast source, you can change the RPF route so as to
create a transmission path for multicast traffic different from that for unicast traffic.