Port-based multicast vlan, Figure 3-2 – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 73
3-2
Figure 3-2 Sub-VLAN-based multicast VLAN
Source
Router A
IGMP querier
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
VLAN 4
Switch A
Receiver
Host A
Receiver
Host B
Receiver
Host C
Multicast packets
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
VLAN 4
VLAN 10 (Multicast VLAN)
After the configuration, IGMP Snooping manages router ports in the multicast VLAN and
member ports in the sub-VLANs. When forwarding multicast data to Switch A, Router A needs
to send only one copy of multicast traffic to Switch A in the multicast VLAN, and Switch A
distributes the traffic to the multicast VLAN’s sub-VLANs that contain receivers.
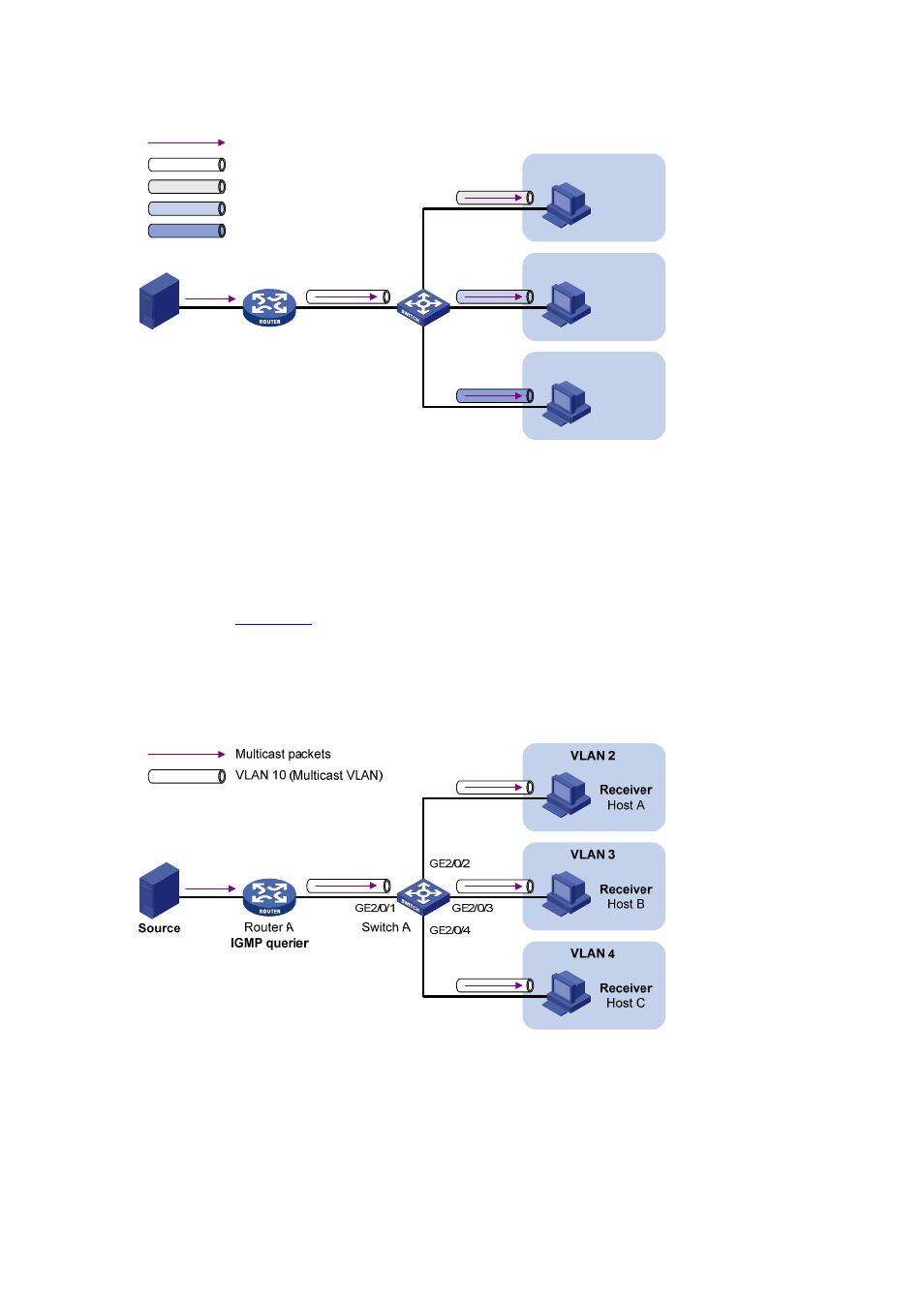
Port-based multicast VLAN
As shown in
, Host A, Host B and Host C are in three different user VLANs. All the
user ports (ports with attached hosts) on Switch A are hybrid ports. On Switch A, configure
VLAN 10 as a multicast VLAN, assign all the user ports to this multicast VLAN, and enable
IGMP Snooping in the multicast VLAN and all the user VLANs.
Figure 3-3 Port-based multicast VLAN
After the configuration, upon receiving an IGMP message on a user port, Switch A tags the
message with the multicast VLAN ID and relays it to the IGMP querier, so that IGMP Snooping
can uniformly manage the router ports and member ports in the multicast VLAN. When
forwarding multicast data to Switch A, Router A needs to send only one copy of multicast traffic
to Switch A in the multicast VLAN, and Switch A distributes the traffic to all the member ports in
the multicast VLAN.