H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 359
13-8
domain. An IPv6 PIM-SM domain can have only one BSR, but can have multiple
candidate-BSRs (C-BSRs). Once the BSR fails, a new BSR is automatically elected from the
C-BSRs to avoid service interruption.
z
An RP can serve IPv6 multiple multicast groups or all IPv6 multicast groups. Only one RP
can serve a given IPv6 multicast group at a time.
z
A device can server as a C-RP and a C-BSR at the same time.
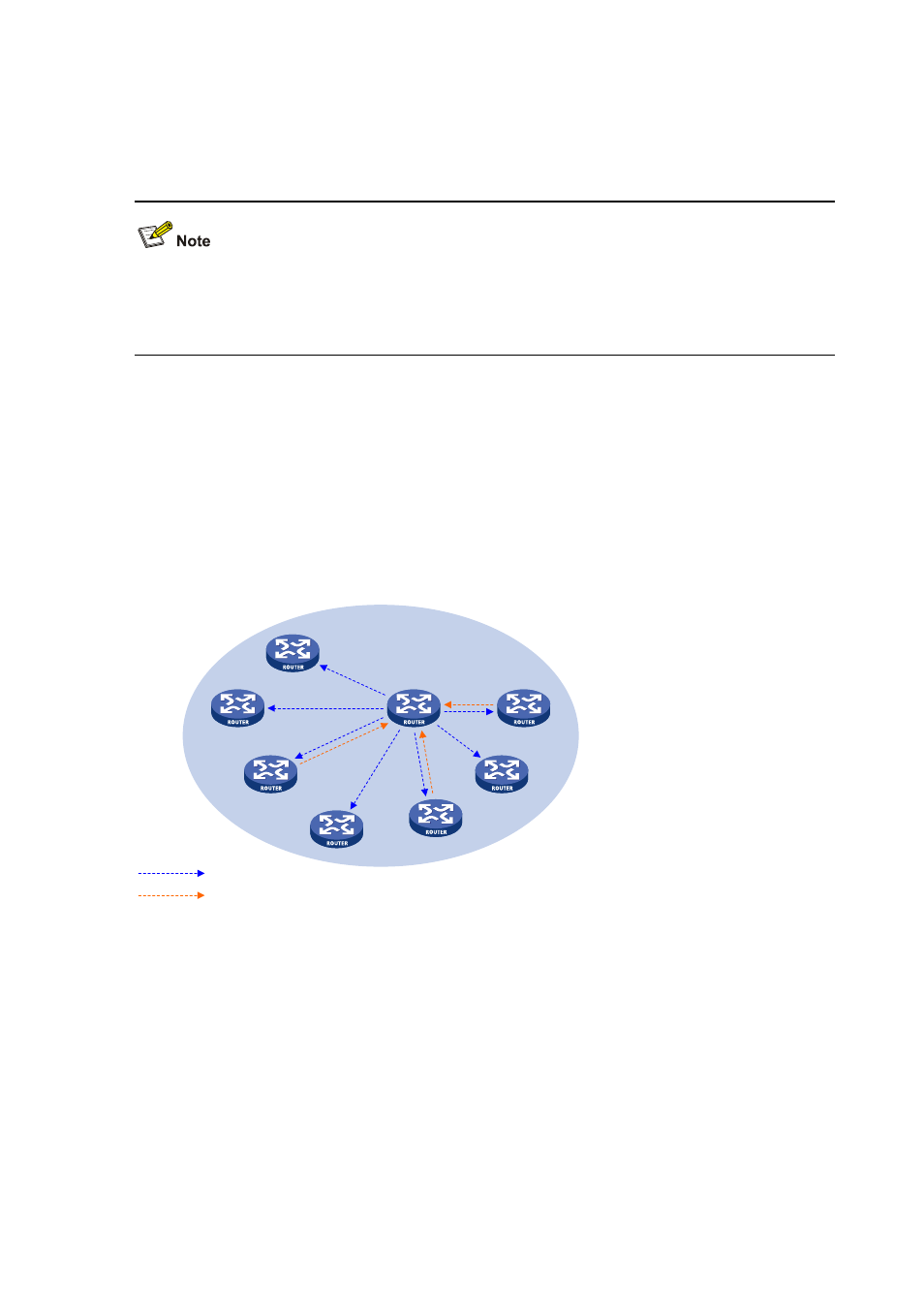
As shown in the figure below, each C-RP periodically unicasts its advertisement messages
(C-RP-Adv messages) to the BSR. A C-RP-Adv message contains the address of the
advertising C-RP and the IPv6 multicast group range it serves. The BSR collects these
advertisement messages and chooses the appropriate C-RP information for each multicast
group to form an RP-set, which is a database of mappings between IPv6 multicast groups and
RPs. The BSR then encapsulates the RP-set in the bootstrap messages it periodically
originates and floods the bootstrap messages (BSMs) to the entire IPv6 PIM-SM domain.
Figure 13-4 BSR and C-RPs
Advertisement message
Bootstrap message
IPv6 PIM-SM
BSR
C-RP
C-RP
C-RP
C-BSR
Based on the information in the RP-sets, all routers in the network can calculate the location of
the corresponding RPs based on the following rules:
The C-RP with the highest priority wins.
1) If all the C-RPs have the same priority, their hash values are calculated through the
hashing algorithm. The C-RP with the largest hash value wins.
2) If all the C-RPs have the same priority and hash value, the C-RP has the highest IP
address wins.
The hashing algorithm used for RP calculation is: Value (G, M, C
i
) = (1103515245 *
( (1103515245 * (G & M) + 12345) XOR C
i
) + 12345) mod 2
31
. The table below gives the
meanings of the values in this algorithm.