Regional root, Common root bridge, Port roles – H3C Technologies H3C S5560 Series Switches User Manual
Page 106
72
Regional root
The root bridge of the IST or an MSTI within an MST region is the regional root of the IST or MSTI. Based
on the topology, different spanning trees in an MST region might have different regional roots, as shown
in MST region 3 in
:
•
The regional root of MSTI 1 is Device B.
•
The regional root of MSTI 2 is Device C.
•
The regional root of MSTI 0 (also known as the IST) is Device A.
Common root bridge
The common root bridge is the root bridge of the CIST.
In
, the common root bridge is a device in MST region 1.
Port roles
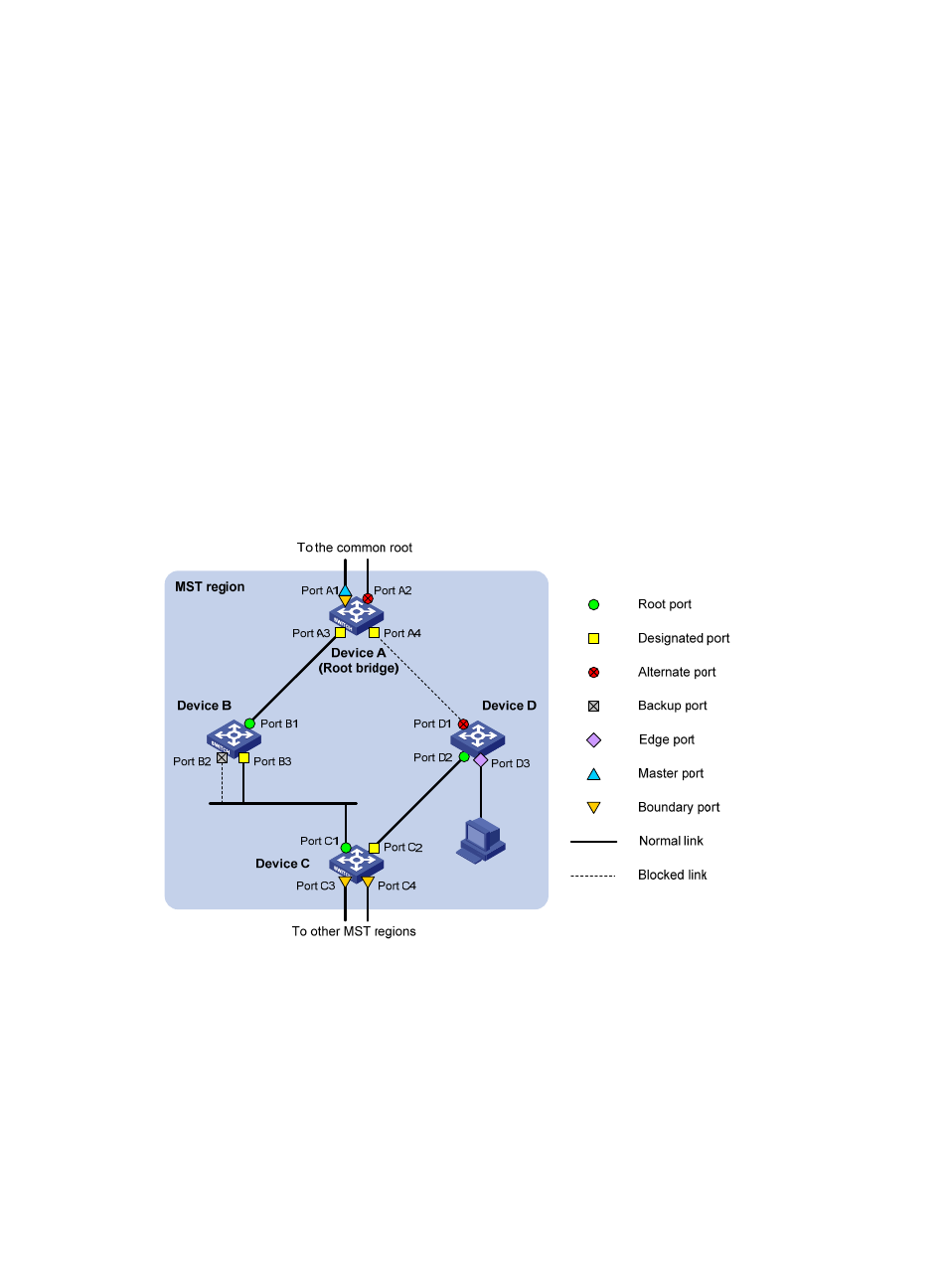
A port can play different roles in different MSTIs. As shown in
, an MST region comprises
Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D. Port A1 and port A2 of Device A connect to the common
root bridge. Port B2 and Port B3 of Device B form a loop. Port C3 and Port C4 of Device C connect to
other MST regions. Port D3 of Device D directly connects to a host.
Figure 25 Port roles
MSTP calculation involves the following port roles:
•
Root port—Forwards data for a non-root bridge to the root bridge. The root bridge does not have
any root port.
•
Designated port—Forwards data to the downstream network segment or device.
•
Alternate port—Acts as the backup port for a root port or master port. When the root port or master
port is blocked, the alternate port takes over.
•
Backup port—Acts as the backup port of a designated port. When the designated port is invalid,
the backup port becomes the new designated port. A loop occurs when two ports of the same