Configuring qinq, Overview, How qinq works – H3C Technologies H3C S5560 Series Switches User Manual
Page 235: Configuring, Qinq
201
Configuring QinQ
This document uses the following terms:
•
CVLAN—Customer network VLANs, also called inner VLANs, refer to VLANs that a customer uses
on the private network.
•
SVLAN—Service provider network VLANs, also called outer VLANs, refer to VLANs that a service
provider uses to transmit VLAN tagged traffic for customers.
Overview
802.1Q-in-802.1Q (QinQ) adds an 802.1Q tag to 802.1Q tagged customer traffic. It enables a service
provider to extend Layer 2 connections across an Ethernet network between customer sites.
QinQ provides the following benefits:
•
Enables a service provider to use a single SVLAN to convey multiple CVLANs for a customer.
•
Enables customers to plan CVLANs without conflicting with SVLANs.
•
Enables customers to keep their VLAN assignment schemes unchanged when the service provider
changes its VLAN assignment scheme.
•
Allows customers to use overlapping CVLAN IDs. Devices in the service provider network make
forwarding decisions based on SVLAN IDs instead of CVLAN IDs.
How QinQ works
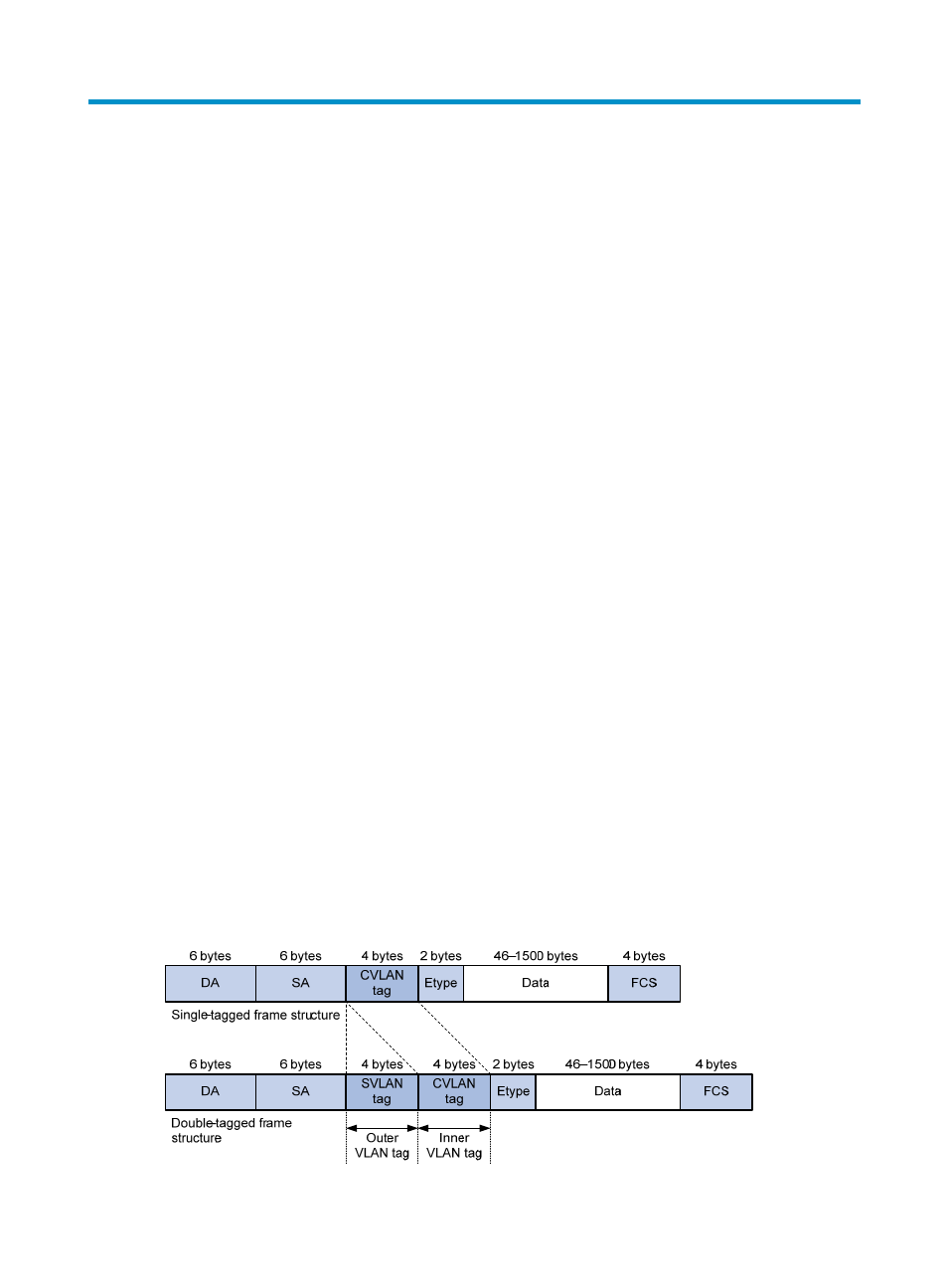
As shown in
, a QinQ frame transmitted over the service provider network carries the following
tags:
•
CVLAN tag—Identifies the VLAN to which the frame belongs when it is transmitted in the customer
network.
•
SVLAN tag—Identifies the VLAN to which the QinQ frame belongs when it is transmitted in the
service provider network. The service provider allocates the SVLAN tag to the customer.
The devices in the service provider network forward a tagged frame based on its SVLAN tag. The
CVLAN tag is transmitted as part of the frame's payload.
Figure 58 Single-tagged Ethernet frame header and double-tagged Ethernet frame header