Configuring vlans, Overview, Vlan frame encapsulation – H3C Technologies H3C S5560 Series Switches User Manual
Page 154
120
Configuring VLANs
Overview
Ethernet is a family of shared-media LAN technologies based on the CSMA/CD mechanism. An Ethernet
LAN is both a collision domain and a broadcast domain. Because the medium is shared, collisions and
broadcasts are common in an Ethernet LAN. Typically, bridges and Layer 2 switches can reduce
collisions in an Ethernet LAN. To confine broadcasts, a Layer 2 switch must use the Virtual Local Area
Network (VLAN) technology.
VLANs enable a Layer 2 switch to break a LAN down into smaller broadcast domains, as shown
in
.
Figure 38 A VLAN diagram
A VLAN is logically divided on an organizational basis rather than on a physical basis. For example, you
can assign all workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup to the same VLAN, regardless of
their physical locations. Hosts in the same VLAN can directly communicate with one another. You need
a router or a Layer 3 switch for hosts in different VLANs to communicate with one another.
All these VLAN features reduce bandwidth waste, improve LAN security, and enable flexible virtual
group creation.
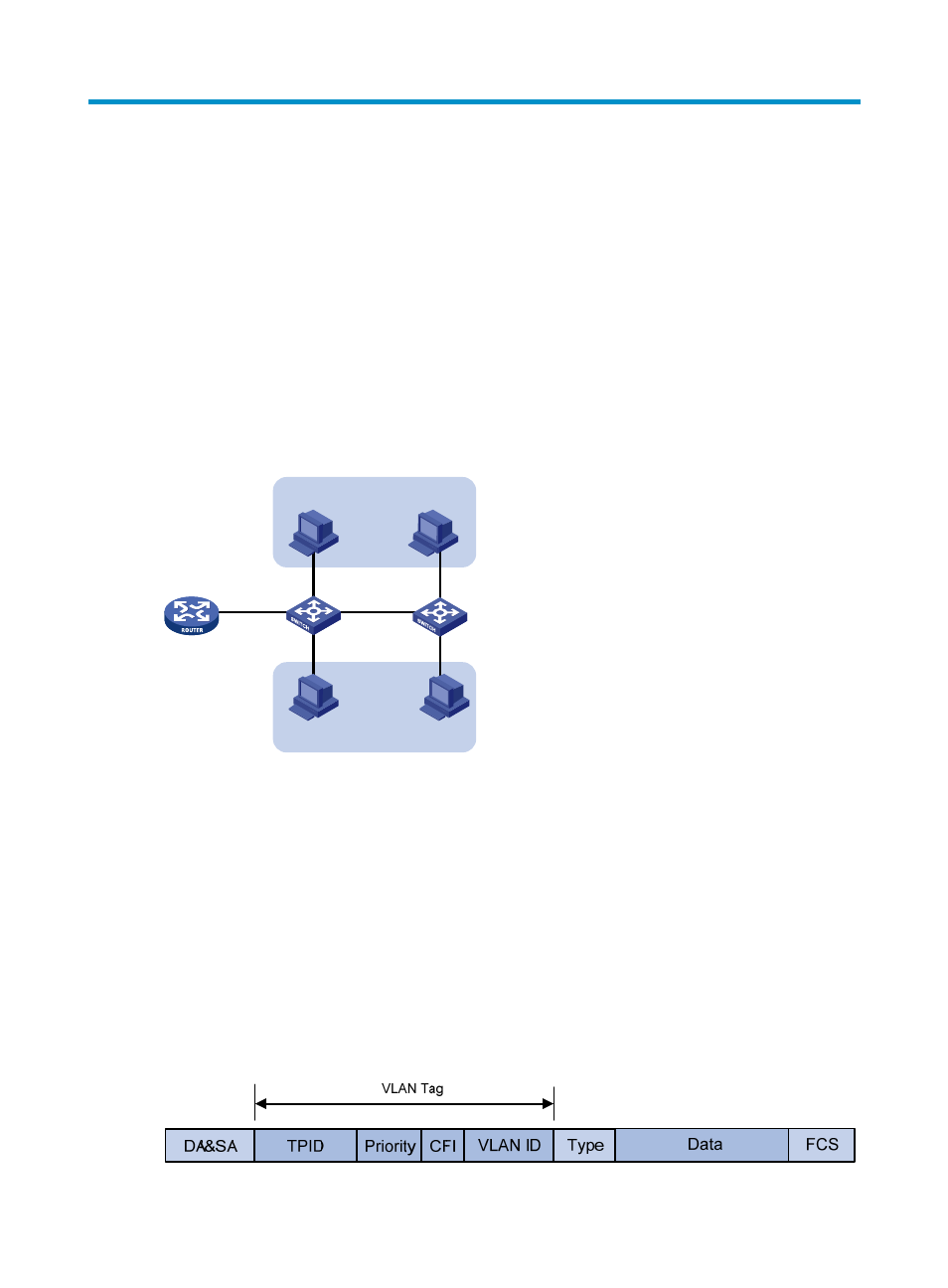
VLAN frame encapsulation
To identify Ethernet frames from different VLANs, IEEE 802.1Q inserts a four-byte VLAN tag between the
destination and source MAC address (DA&SA) field and Type field.
Figure 39 VLAN tag placement and format
VLAN 2
VLAN 5
Switch B
Switch A
Router