Path cost, Calculation process of the stp algorithm, Calculation process – H3C Technologies H3C S5560 Series Switches User Manual
Page 96
62
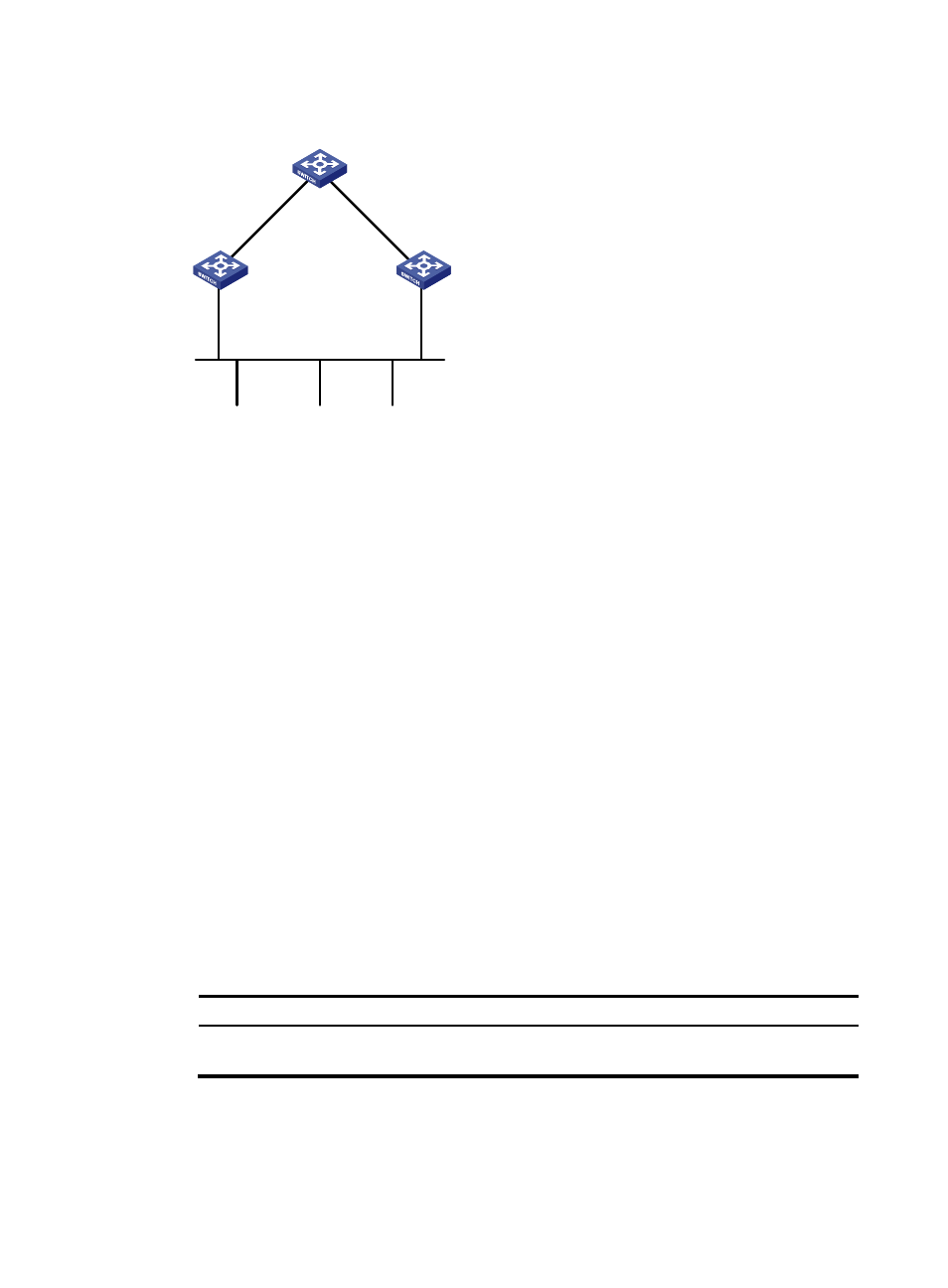
Figure 20 Designated bridges and designated ports
Path cost
Path cost is a reference value used for link selection in STP. To prune the network into a loop-free tree, STP
calculates path costs to select the most robust links and block redundant links that are less robust.
Calculation process of the STP algorithm
The spanning tree calculation process described in the following sections is an example of a simplified
process.
Calculation process
The STP algorithm uses the following calculation process:
1.
Initialize the network.
Upon initialization of a device, each port generates a BPDU with the following contents:
{
The port as the designated port.
{
The device as the root bridge.
{
0 as the root path cost.
{
The device ID as the designated bridge ID.
2.
Select the root bridge.
Initially, each STP-enabled device on the network assumes itself to be the root bridge, with its own
device ID as the root bridge ID. By exchanging configuration BPDUs, the devices compare their
root bridge IDs to elect the device with the smallest root bridge ID as the root bridge.
3.
Root port and designated ports selection on the non-root bridges.
Step
Description
1
A non-root–bridge device regards the port on which it received the optimum configuration
BPDU as the root port.
describes how the optimum configuration BPDU is selected.
Device A
Device B
Device C
Port A1
Port A2
Port B1
Port C1
Port B2
Port C2
LAN
- H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches H3C SR8800 H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module