Dldp introduction, N in, Figure 27-1 – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 294: Figure 27-2
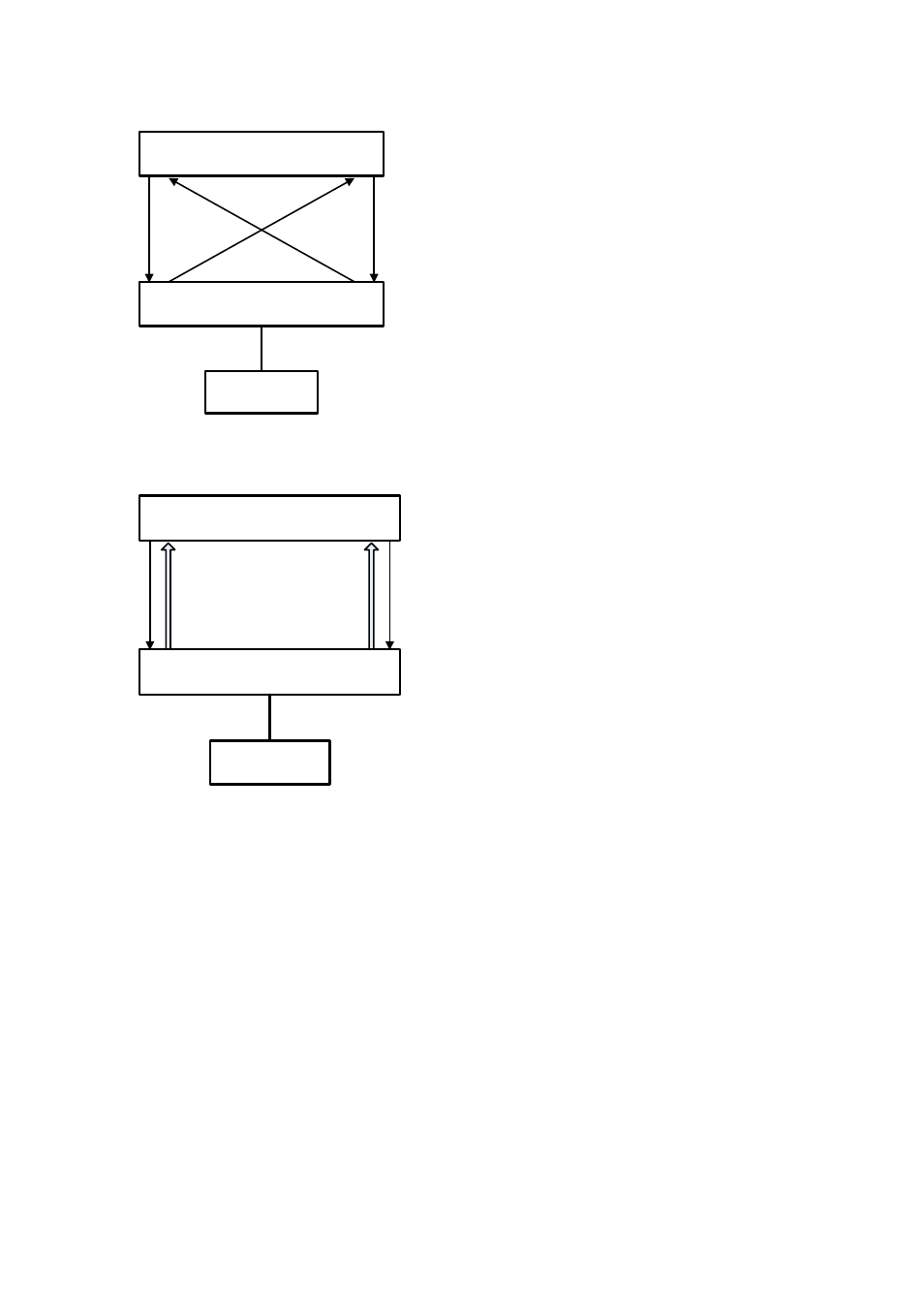
27-2
Figure 27-1
Unidirectional fiber link: cross-connected fiber
Device A
GE1/0/50
GE1/0/51
Device B
PC
GE1/0/50
GE1/0/51
Figure 27-2
Unidirectional fiber link: fiber not connected or disconnected
Device A
Device B
PC
GE1/0/50
GE1/0/50
GE1/0/51
GE1/0/51
DLDP Introduction
Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) can detect the link status of a fiber cable or twisted pair. On
detecting a unidirectional link, DLDP can shut down the related port automatically or prompt users to
take measures as configured to avoid network problems.
As a data link layer protocol, DLDP cooperates with physical layer protocols to monitor the link status of
a device. The auto-negotiation mechanism provided by physical layer protocols detects physical signals
and faults. DLDP, however, performs operations such as identifying peer devices, detecting
unidirectional links, and shutting down unreachable ports. The cooperation of physical layer protocols
and DLDP ensures that physical/logical unidirectional links be detected and shut down. For a link with
the devices on the both sides of it operating properly, DLDP checks to see if the cable is connected
correctly and if packets can be exchanged between the two devices. Note that DLDP is not
implemented through auto-negotiation.