Mac address-based vlan configuration, Introduction to mac address-based vlan, Mac address-based vlan implementation – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 64
7-9
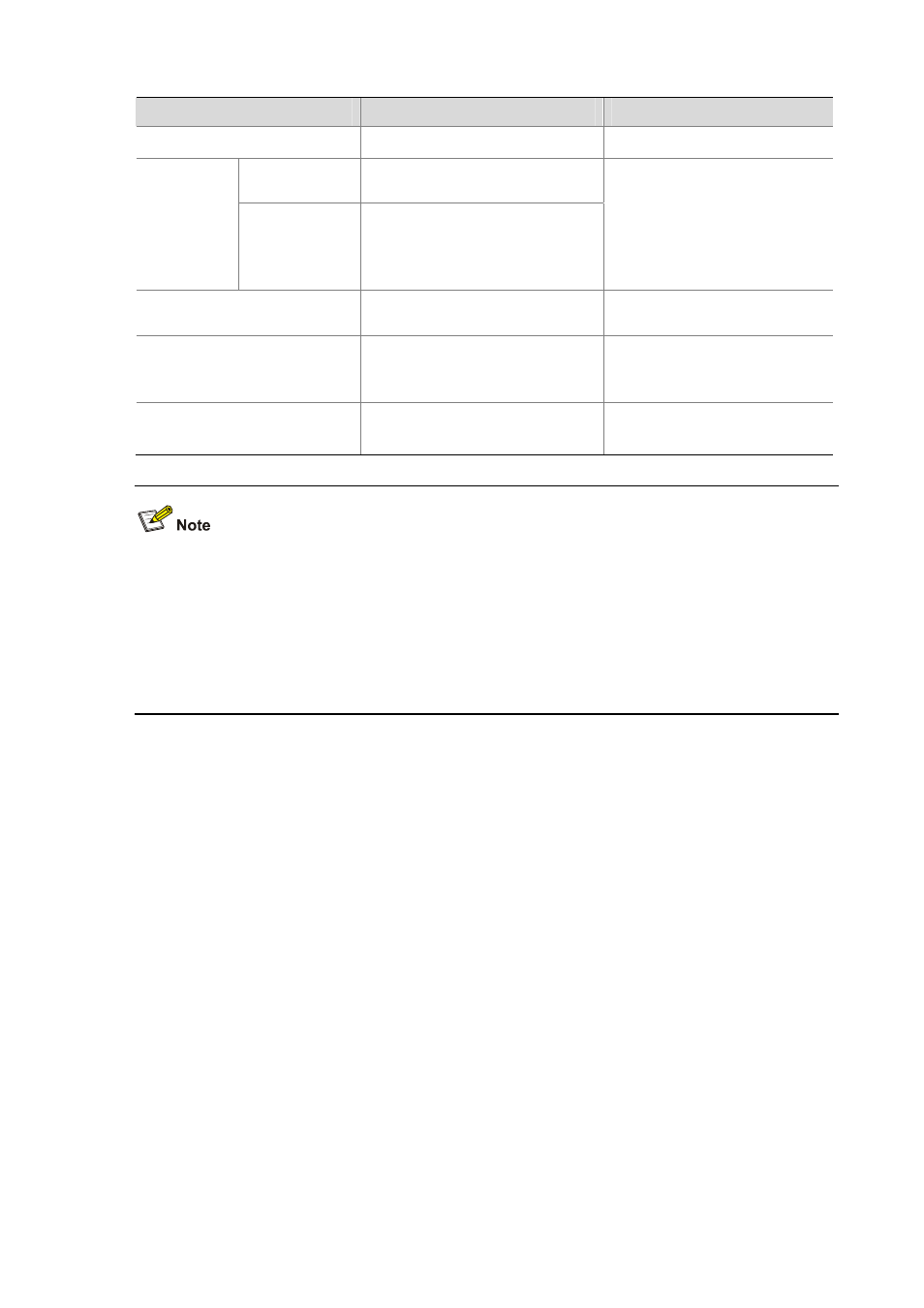
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enter Ethernet
port view
interface interface-type
interface-number
Enter
Ethernet port
view or port
group view
Enter port group
view
port-group
{ manual
port-group-name
| aggregation
agg-id
}
Use either command;
In Ethernet port view, the
subsequent configurations only
apply to the current port; in port
group view, the subsequent
configurations apply to all ports in
the port group
Configure the port link type as
Hybrid
port link-type
hybrid Required
Allow the specified VLANs to
pass through the current Hybrid
port
port hybrid
vlan vlan-id-list
{ tagged | untagged }
Required
By default, all Hybrid ports only
allow packets of VLAN 1 to pass.
Configure the default VLAN of the
Hybrid port
port hybrid pvid vlan vlan-id
Optional
VLAN 1 is the default by default
z
To configure a Trunk port into a Hybrid port (or vice versa), you need to use the Access port as a
medium. For example, the Trunk port has to be configured as an Access port first and then a Hybrid
port.
z
Ensure that the VLANs already exist before configuring them to pass through a Hybrid port.
z
The default VLAN IDs of the Hybrid ports on the local and the peer devices must be the same.
Otherwise, packets cannot be transmitted properly.
MAC Address-Based VLAN Configuration
Introduction to MAC Address-Based VLAN
With MAC address-based VLANs created, the VLAN to which a packet belongs is determined by its
source MAC address, and packets in a MAC address-based VLAN are forwarded after being tagged
with the tag of the VLAN. This function is usually coupled with the security technologies (such as 802.1X)
to provide secure and flexible network accesses for terminal devices.
MAC address-based VLAN implementation
With MAC address-based VLANs created on a port, the port operates as follows:
z
If an untagged packet is received, the port checks its MAC address VLAN entries for the one that
matches the source MAC address of the packet. If the entry exists, the packet is forwarded based
on the matched VLAN ID and the precedence value; otherwise, the packet is forwarded based on
the default VLAN of the port.
z
If a tagged packet is received, the port processes the packet in the same way as it processes
port-based VLAN packets, that is, forwards the packet if the VLAN corresponding to the VLAN tag
is permitted by the port or drops the packet if the VLAN corresponding to the VLAN tag is not
permitted by the port.