Arp mapping table, Figure 33-2 – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 365
33-3
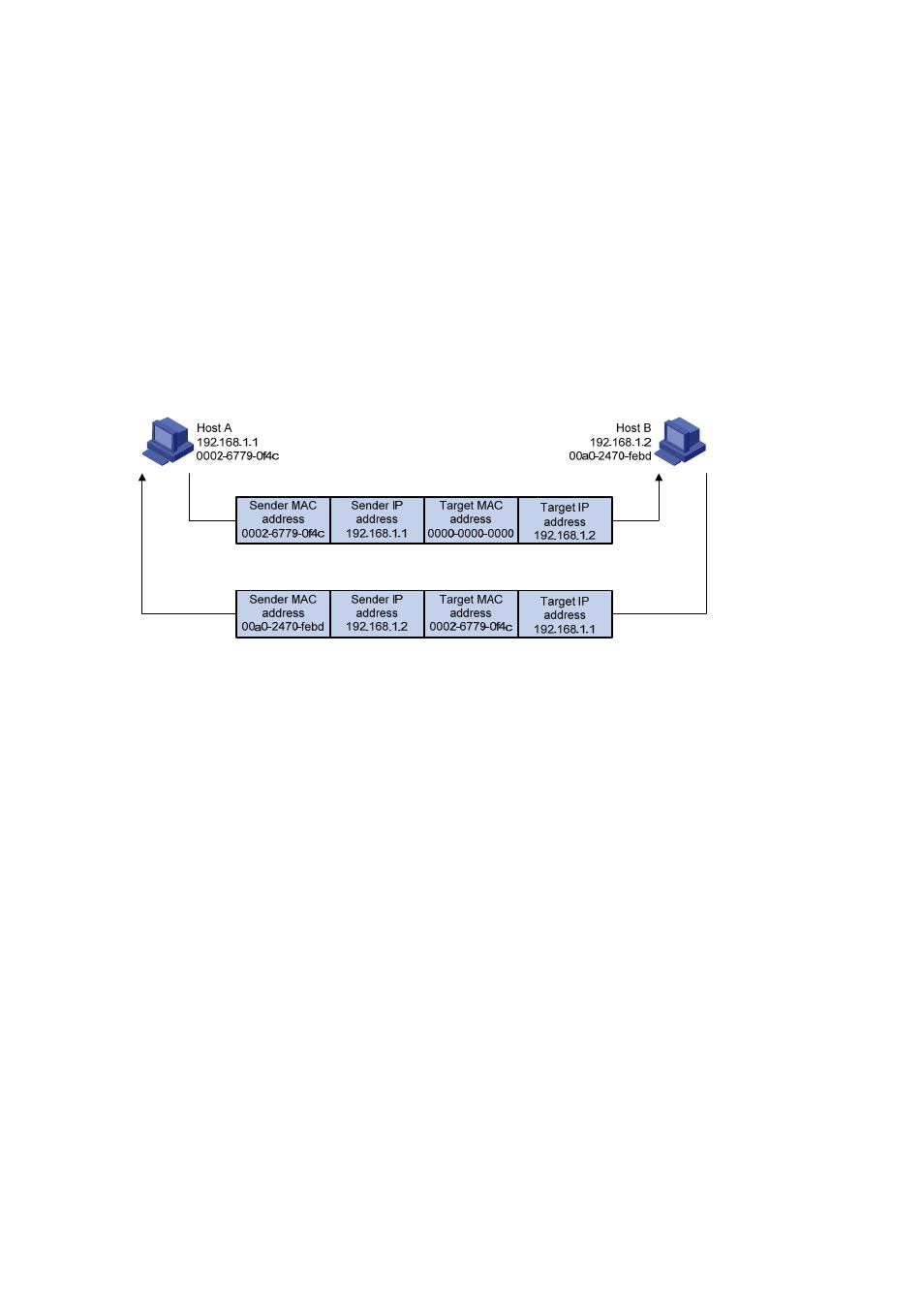
2) If Host A finds no entry for Host B, Host A buffers the packet and broadcasts an ARP request, in
which the source IP address and source MAC address are respectively the IP address and MAC
address of Host A and the destination IP address and MAC address are respectively the IP
address of Host B and an all-zero MAC address. Because the ARP request is sent in broadcast
mode, all hosts on this subnet can receive the request, but only the requested host (namely, Host B)
will process the request.
3) Host B compares its own IP address with the destination IP address in the ARP request. If they are
the same, Host B saves the source IP address and source MAC address into its ARP mapping
table, encapsulates its MAC address into an ARP reply, and unicasts the reply to Host A.
4) After receiving the ARP reply, Host A adds the MAC address of Host B into its ARP mapping table
for subsequent packet forwarding. Meanwhile, Host A encapsulates the IP packet and sends it out.
Figure 33-2
ARP address resolution process
When Host A and Host B are not on the same subnet, Host A first sends an ARP request to the gateway.
The destination IP address in the ARP request is the IP address of the gateway. After obtaining the MAC
address of the gateway from an ARP reply, Host A encapsulates the packet and sends it to the gateway.
Subsequently, the gateway broadcasts the ARP request, in which the destination IP address is the one
of Host B. After obtaining the MAC address of Host B from another ARP reply, the gateway sends the
packet to Host B.
ARP Mapping Table
After obtaining the destination MAC address, the device adds the IP-to-MAC mapping into its own ARP
mapping table. This mapping is used for forwarding packets with the same destination in future.
An ARP mapping table contains ARP entries, which fall into two categories: dynamic and static.
1) A dynamic entry is automatically created and maintained by ARP. It can get aged, be updated by a
new ARP packet, or be overwritten by a static ARP entry. When the aging timer expires or the port
goes down, the corresponding dynamic ARP entry will be removed.
2) A static ARP entry is manually configured and maintained. It cannot get aged or be overwritten by a
dynamic ARP entry. It can be permanent or non-permanent.
z
A permanent static ARP entry can be directly used to forward packets. When configuring a
permanent static ARP entry, you must configure a VLAN and outbound port for the entry besides
the IP address and MAC address.