Ipv6 multicast addresses, Ethernet multicast mac addresses – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 314
28-8
Address
Description
224.0.0.18 Virtual
Router
Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
IPv6 Multicast Addresses
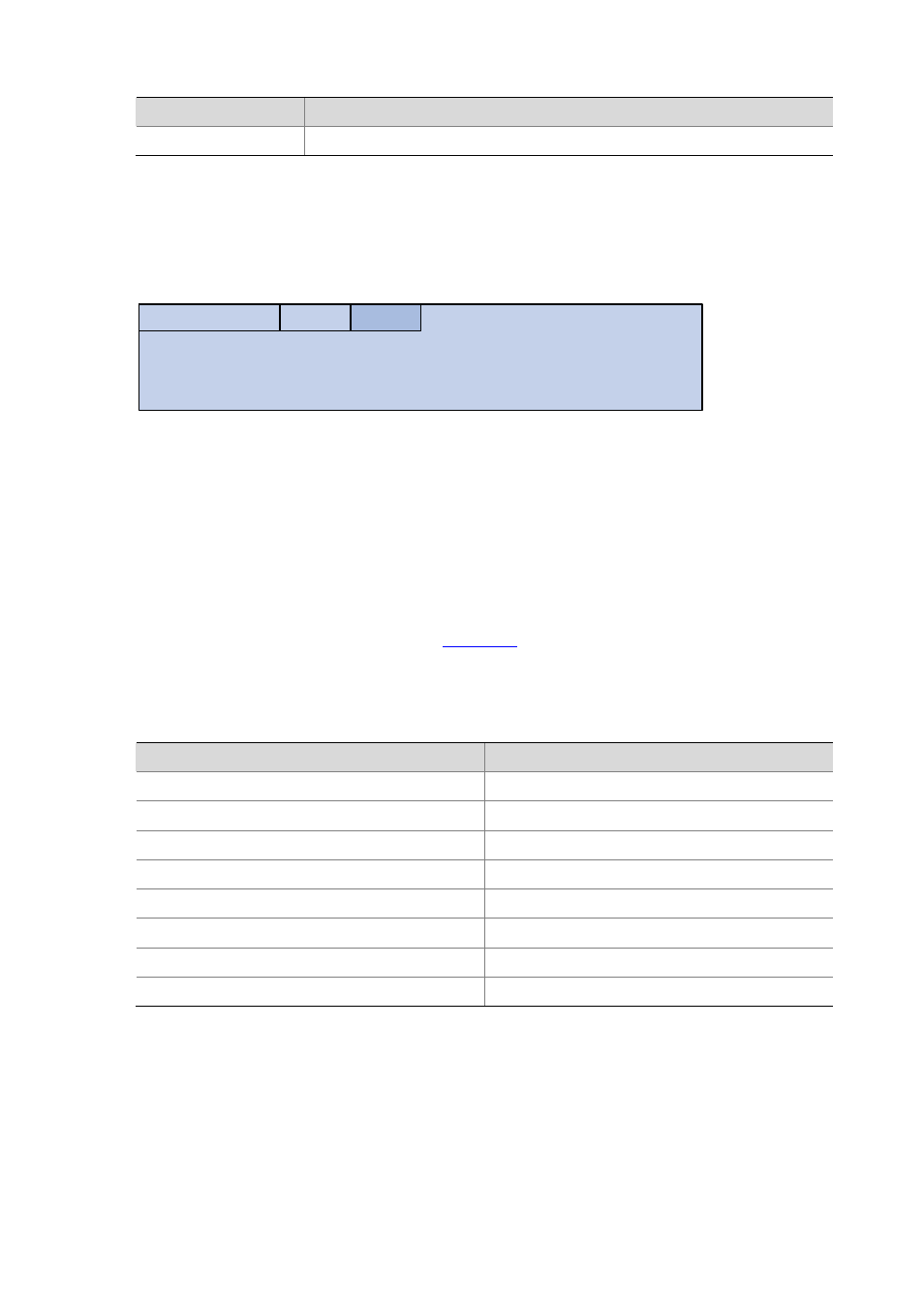
As defined in RFC 4291, the format of an IPv6 multicast is as follows:
Figure 28-4
IPv6 multicast format
Group ID (112 bits)
0xFF
Flags
Scope
0
7
11
15
31
z
0xFF: 8 bits, indicating that this address is an IPv6 multicast address.
z
Flags: 4 bits, of which the high-order flag is reserved and set to 0; the definition and usage of the
second bit can be found in RFC 3956; and definition and usage of the third bit can be found in RFC
3306; the low-order bit is the Transient (T) flag. When set to 0, the T flag indicates a
permanently-assigned multicast address assigned by IANA; when set to 1, the T flag indicates a
transient, or dynamically assigned multicast address.
z
Scope: 4 bits, indicating the scope of the IPv6 internetwork for which the multicast traffic is intended.
Possible values of this field are given in
z
Reserved: 80 bits, all set to 0 currently.
z
Group ID: 112 bits, identifying the multicast group. For details about this field, refer to RFC 3306.
Table 28-4
Values of the Scope field
Value
Meaning
0, 3, F
Reserved
1 Node-local
scope
2 Link-local
scope
4 Admin-local
scope
5
Site-local scope
6, 7, 9 through D
Unassigned
8 Organization-local
scope
E Global
scope
Ethernet multicast MAC addresses
When a unicast IP packet is transmitted over Ethernet, the destination MAC address is the MAC
address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transmitted over Ethernet, however, the destination
address is a multicast MAC address because the packet is directed to a group formed by a number of
receivers, rather than to one specific receiver.
1) IPv4 multicast MAC addresses