Dldp authentication mode – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 297
27-5
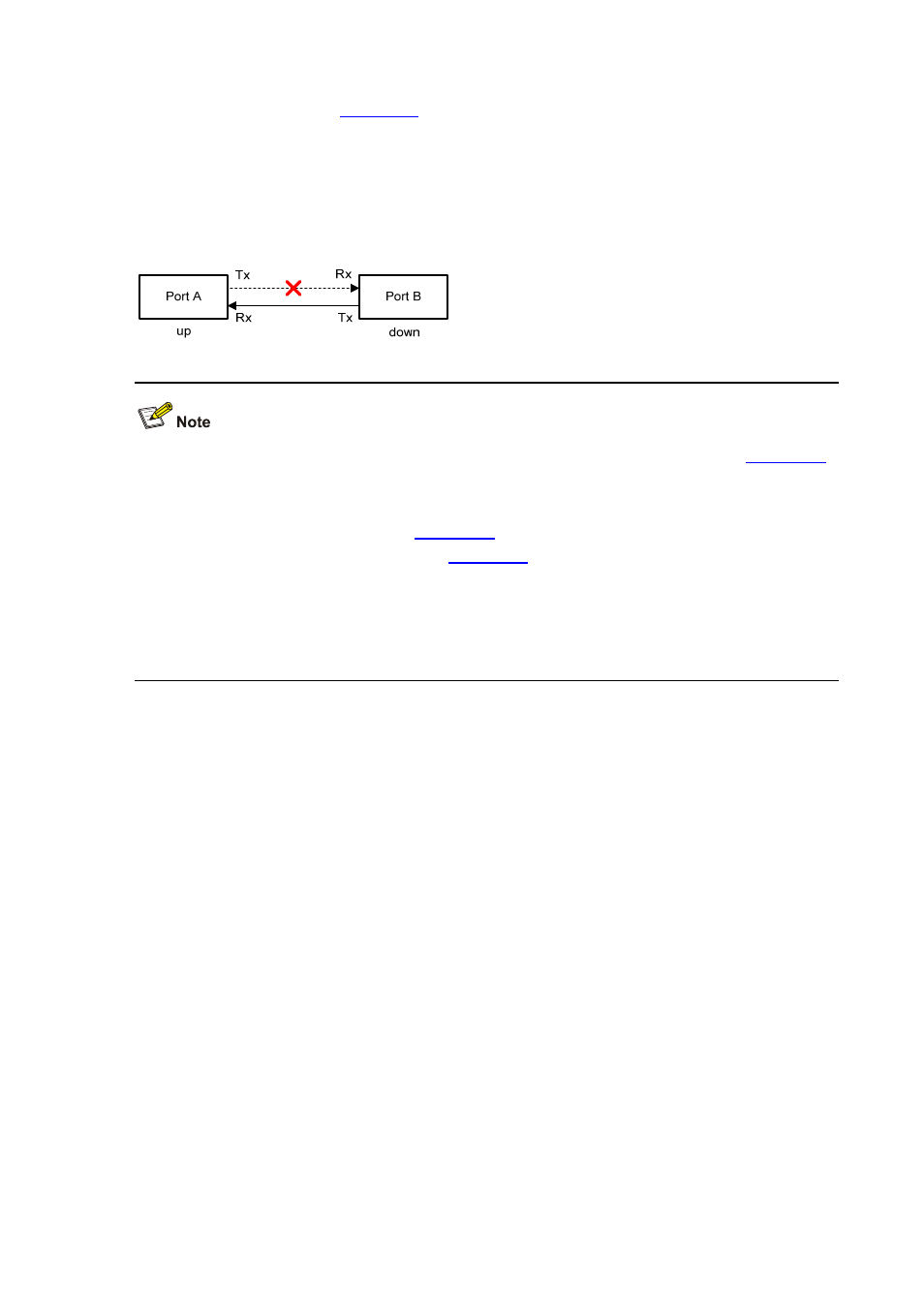
device, the situation shown in
may occur, where Port B is actually down but the state of Port
B cannot be detected by common data link protocols, so Port A is still up. In enhanced DLDP mode,
however, Port A tests Port B after the Entry timer concerning Port B expires. Port A then transits to the
Disable state if it receives no Echo packet from Port A when the Echo timer expires. As Port B is
physically down, it is in the Inactive DLDP state.
Figure 27-3
A case for Enhanced DLDP mode
z
In normal DLDP mode, only fiber cross-connected unidirectional links (as shown in
)
can be detected.
z
In enhanced DLDP mode, two types of unidirectional links can be detected. One is fiber
cross-connected links (as shown in
). The other refers to fiber pairs with one fiber not
connected or disconnected (as shown in
). To detect unidirectional links that are of the
latter type, you need to configure the ports to operate at specific speed and in full duplex mode.
Otherwise, DLDP cannot take effect. When a fiber of a fiber pair is not connected or gets
disconnected, the port that can receive optical signals is in Disable state; the other port is in
Inactive state.
DLDP authentication mode
You can prevent network attacks and illegal detect through DLDP authentication. Three DLDP
authentication modes exist, as described below.
z
Non-authentication. In this mode, the sending side sets the Authentication field and the
Authentication type field of DLDP packets to 0. The receiving side checks the values of the two
fields of received DLDP packets and drops the packets with the two fields conflicting with the
corresponding local configuration.
z
Plain text authentication. In this mode, before sending a DLDP packet, the sending side sets the
Authentication field to the password configured in plain text and sets the Authentication type field to
1. The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received DLDP packets and drops the
packets with the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local configuration.
z
MD5 authentication. In this mode, before sending a packet, the sending side encrypts the user
configured password using MD5 algorithm, assigns the digest to the Authentication field, and sets
the Authentication type field to 2. The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received
DLDP packets and drops the packets with the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local
configuration.