H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 443
46-3
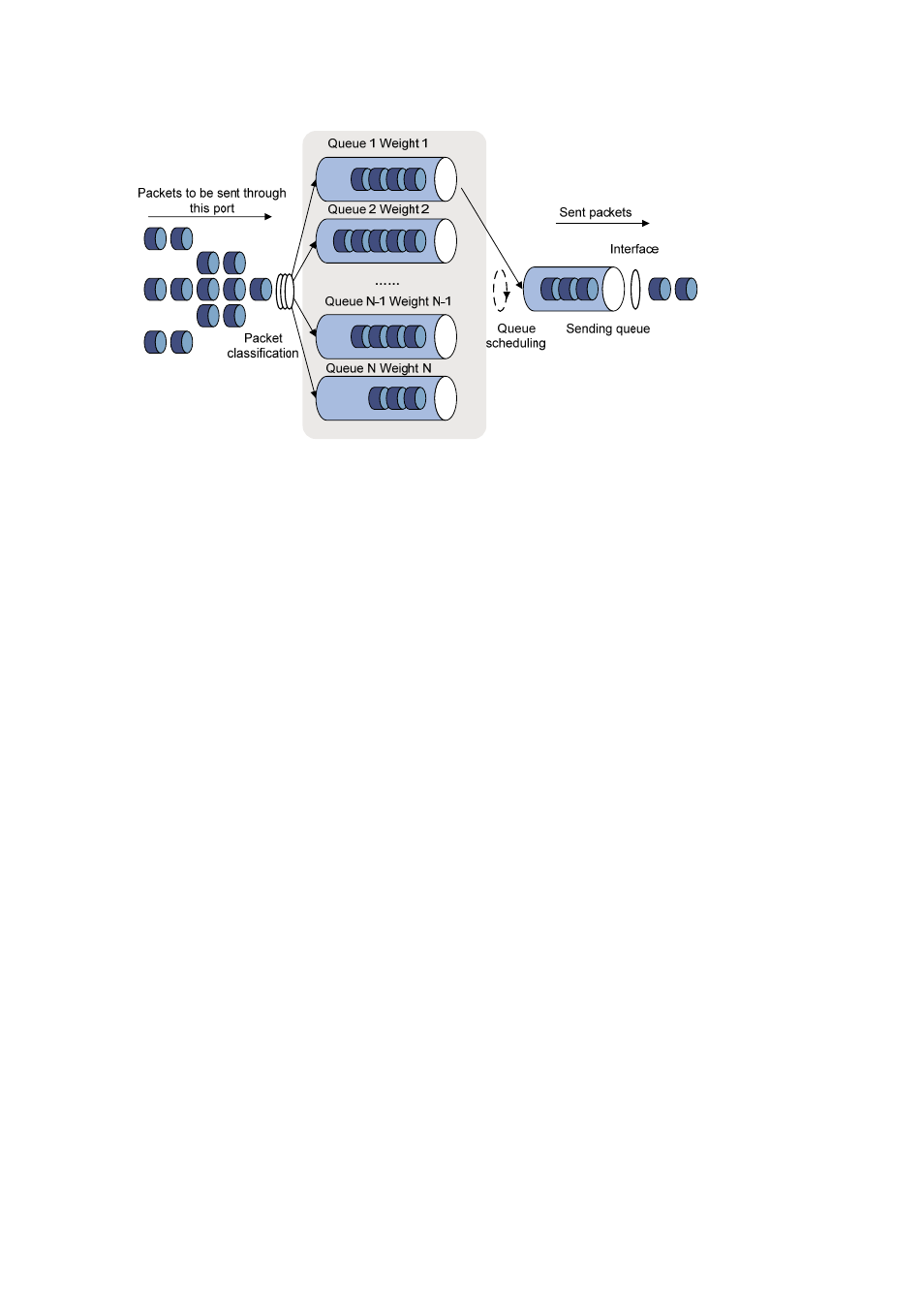
Figure 46-2
Diagram for WRR queuing
A port of the switch supports eight outbound queues. The WRR queue-scheduling algorithm schedules
all the queues in turn to ensure that every queue can be assigned a certain service time. Assume there
are eight output queues on the port. The eight weight values (namely, w 7, w 6, w 5, w 4, w 3, w 2, w 1,
and w 0) indicating the proportion of assigned resources are assigned to the eight queues respectively.
On a 100M port, you can configure the weight values of WRR queue-scheduling algorithm to 50, 30, 10,
10, 50, 30, 10, and 10 (corresponding to w7, w6, w5, w4, w3, w2, w1, and w0 respectively). In this way,
the queue with the lowest priority can be assured of 5 Mbps of bandwidth at least, thus avoiding the
disadvantage of SP queue-scheduling algorithm that packets in low-priority queues are possibly not to
be served for a long time. Another advantage of WRR queue-scheduling algorithm is that though the
queues are scheduled in turn, the service time for each queue is not fixed, that is to say, if a queue is
empty, the next queue will be scheduled immediately. In this way, the bandwidth resources are fully
utilized.
The H3C WX6103 access controller switch interface boards support the following three queue
scheduling algorithms:
z
All the queues are scheduled through the SP algorithm.
z
All the queues are scheduled through the WRR algorithm.
z
Some queues are scheduled through the SP algorithm, while other queues are scheduled through
the WRR algorithm.