Dldp fundamentals, Dldp status – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 155
20-2
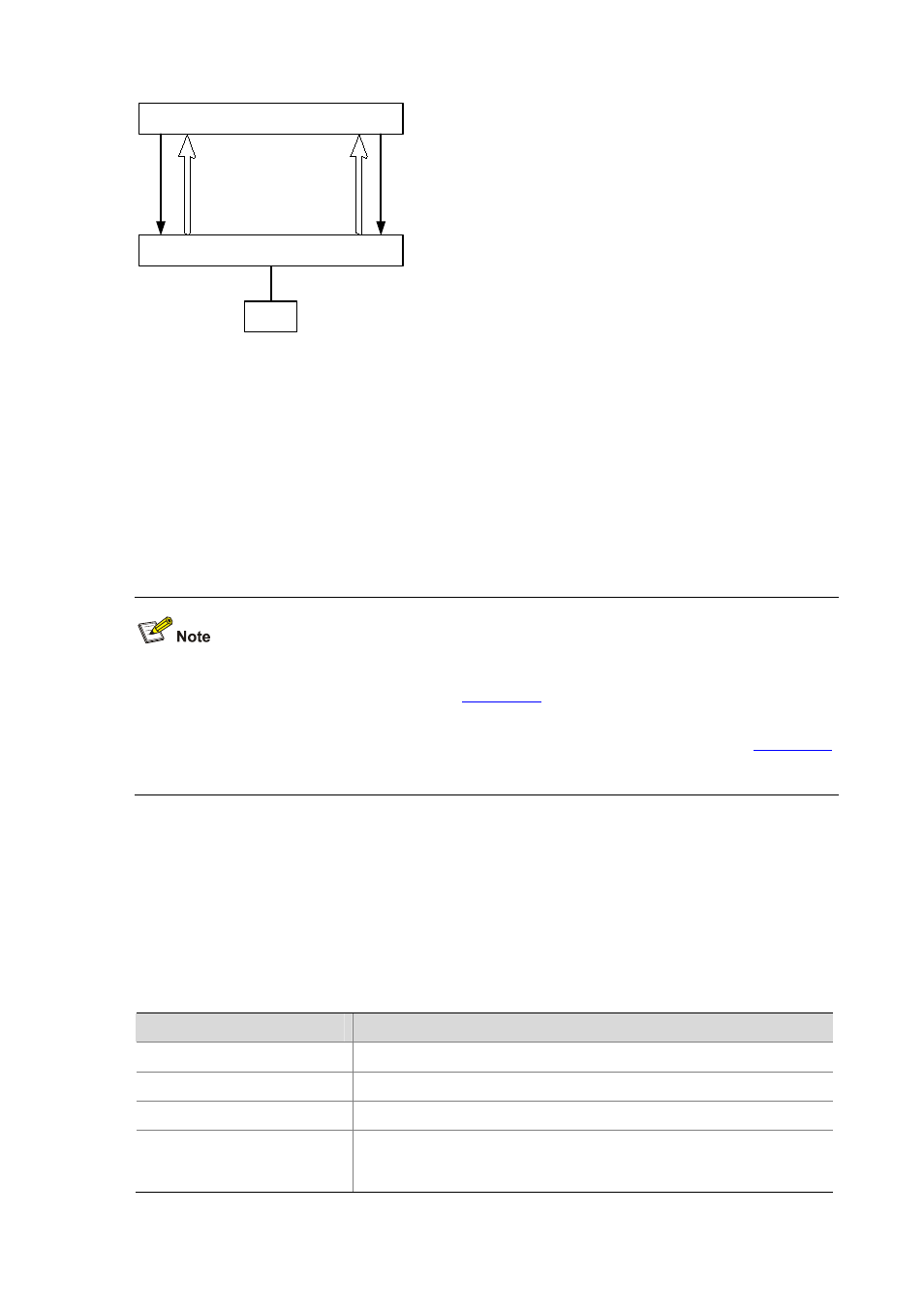
Figure 20-2
Fiber correct connection/disconnection in one direction
GE1/0/10 SwitchA GE1/0/11
GE1/0/10 SwitchB GE1/0/11
PC
DLDP provides the following features:
z
As a link layer protocol, it works together with the physical layer protocols to monitor the link status
of a device. While the auto-negotiation mechanism on the physical layer detects physical signals
and faults; DLDP identifies peer devices and unidirectional links, and disables unreachable ports.
z
Even if the links of both ends can normally operate individually on the physical layer, DLDP can
detect (at the link layer) whether these links are connected correctly and packets can be
exchanged normally between the two ends. This detection cannot be implemented by the
auto-negotiation mechanism.
z
When the port works in mandatory full duplex mode and the mandatory rate, DLDP can detect fiber
disconnection in one direction as shown in
z
When the port works in auto-negotiation duplex mode and auto-negotiation rate, even if DLDP is
enabled, it does not take effect when fiber in one direction is disconnected as shown in
,
in that case, it considers that the port is down.
DLDP Fundamentals
DLDP status
A link can be in one of these DLDP states: initial, inactive, active, advertisement, probe, disable, and
delaydown.
Table 20-1
DLDP status
Status
Description
Initial
DLDP is not enabled.
Inactive
DLDP is enabled but the corresponding link is down
Active
DLDP is enabled and the link is up, or an neighbor entry is cleared
Advertisement
All neighbors communicate normally in both direction, or DLDP remains in
active status for more than five seconds and enters this status. It is a stable
status when no unidirectional link is found