H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 171
22-2
Upon network convergence, the root bridge generates and sends out configuration BPDUs periodically.
Other devices just forward the configuration BPDUs received. This mechanism ensures the topological
stability.
2) Root
port
On a non-root bridge device, the root port is the port with the lowest path cost to the root bridge. The
root port is used for communicating with the root bridge. A non-root-bridge device has one and only one
root port. The root bridge has no root port.
3) Designated bridge and designated port
Refer to the following table for the description of designated bridge and designated port.
Table 22-1
Designated bridge and designated port
Classification
Designated bridge
Designated port
For a device
A designated bridge is a device that is directly
connected to a WX3000 series device and is
responsible for forwarding BPDUs to the device.
The port through which the
designated bridge forwards
BPDUs to this device
For a LAN
A designated bridge is a device responsible for
forwarding BPDUs to this LAN segment.
The port through which the
designated bridge forwards
BPDUs to this LAN segment
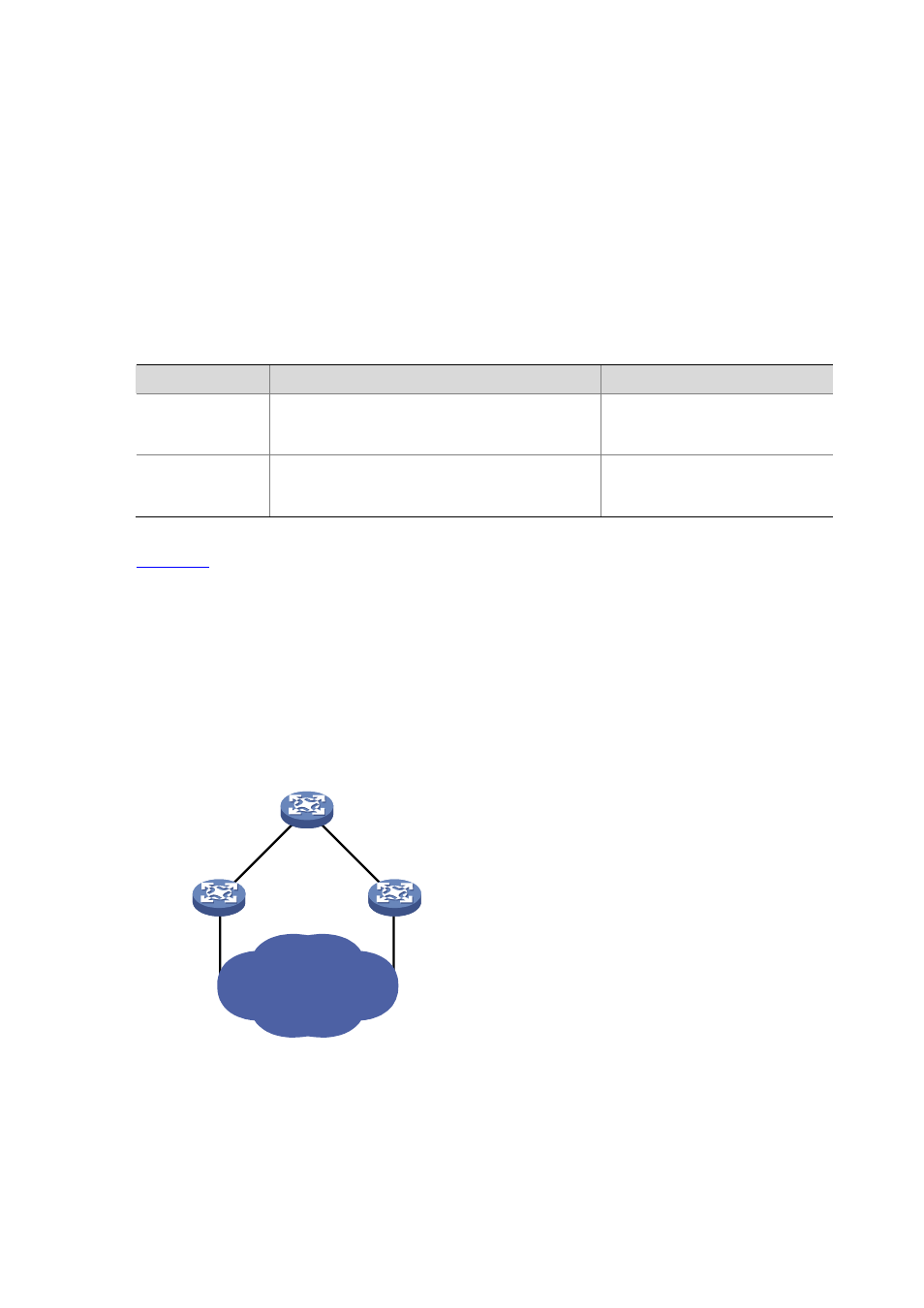
shows designated bridges and designated ports. In the figure, AP1 and AP2, BP1 and BP2,
and CP1 and CP2 are ports on Device A, Device B, and Device C respectively.
z
If Device A forwards BPDUs to Device B through AP1, the designated bridge for Device B is Device
A, and the designated port is the port AP1 on Device A.
z
Two devices are connected to the LAN: Device B and Device C. If Device B forwards BPDUs to the
LAN, the designated bridge for the LAN is Device B, and the designated port is the port BP2 on
Device B.
Figure 22-1
A schematic diagram of designated bridges and designated ports
LAN
AP1
AP2
Device A
Device B
Device C
BP1
BP2
CP1
CP2