Multicast protocols – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 426
43-9
Ethernet multicast MAC address
When a unicast IP packet is transported in an Ethernet network, the destination MAC address is the
MAC address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transported in an Ethernet network, a
multicast MAC address is used as the destination address because the destination is a group with an
uncertain number of members.
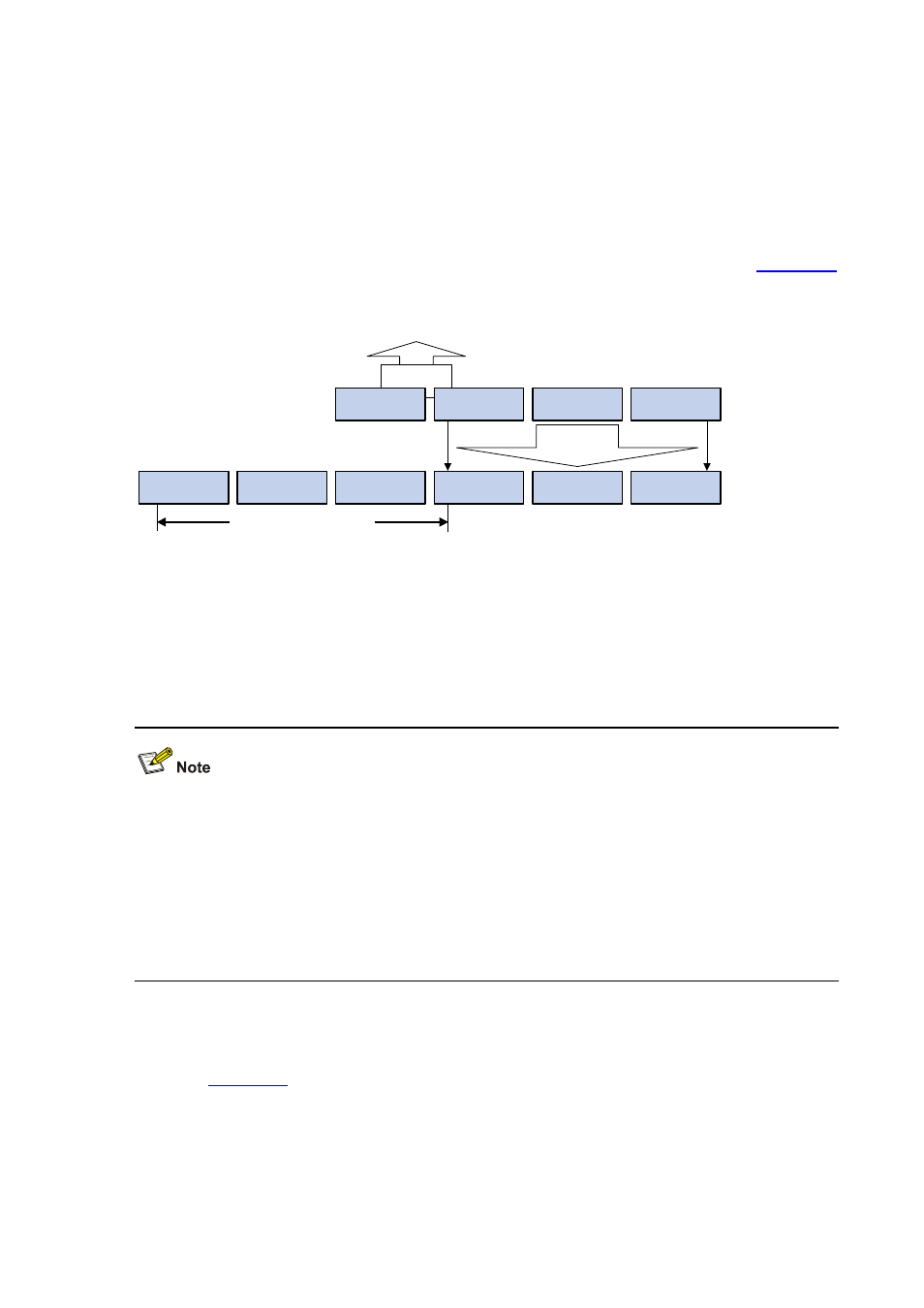
As stipulated by IANA, the high-order 24 bits of a multicast MAC address are 0x01005e, while the
low-order 23 bits of a MAC address are the low-order 23 bits of the multicast IP address.
describes the mapping relationship:
Figure 43-4
Multicast address mapping
XXXX X
X
XXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
1110 XXXX
0XXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
0000 0001
0000 0000
0101 1110
32-bit IP address
48-bit MAC address
5 bits lost
25-bit MAC address prefix
…
…
23 bits
mapped
The high-order four bits of the IP multicast address are 1110, representing the multicast ID. Only 23 bits
of the remaining 28 bits are mapped to a MAC address. Thus, five bits of the multicast IP address are
lost. As a result, 32 IP multicast addresses are mapped to the same MAC address.
Multicast Protocols
z
Generally, we refer to IP multicast working at the network layer as Layer 3 multicast and the
corresponding multicast protocols as Layer 3 multicast protocols, which include IGMP, PIM, and
MSDP; we refer to IP multicast working at the data link layer as Layer 2 multicast and the
corresponding multicast protocols as Layer 2 multicast protocols, which include IGMP Snooping.
z
This section provides only general descriptions about applications and functions of the Layer 2 and
Layer 3 multicast protocols in a network. For details about these protocols, refer to the related
chapters of this configuration guide.
Layer 3 multicast protocols
Layer 3 multicast protocols include multicast group management protocols and multicast routing
protocols.
describes where these multicast protocols are in a network.