Security mode of voice vlan – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 123
1-6
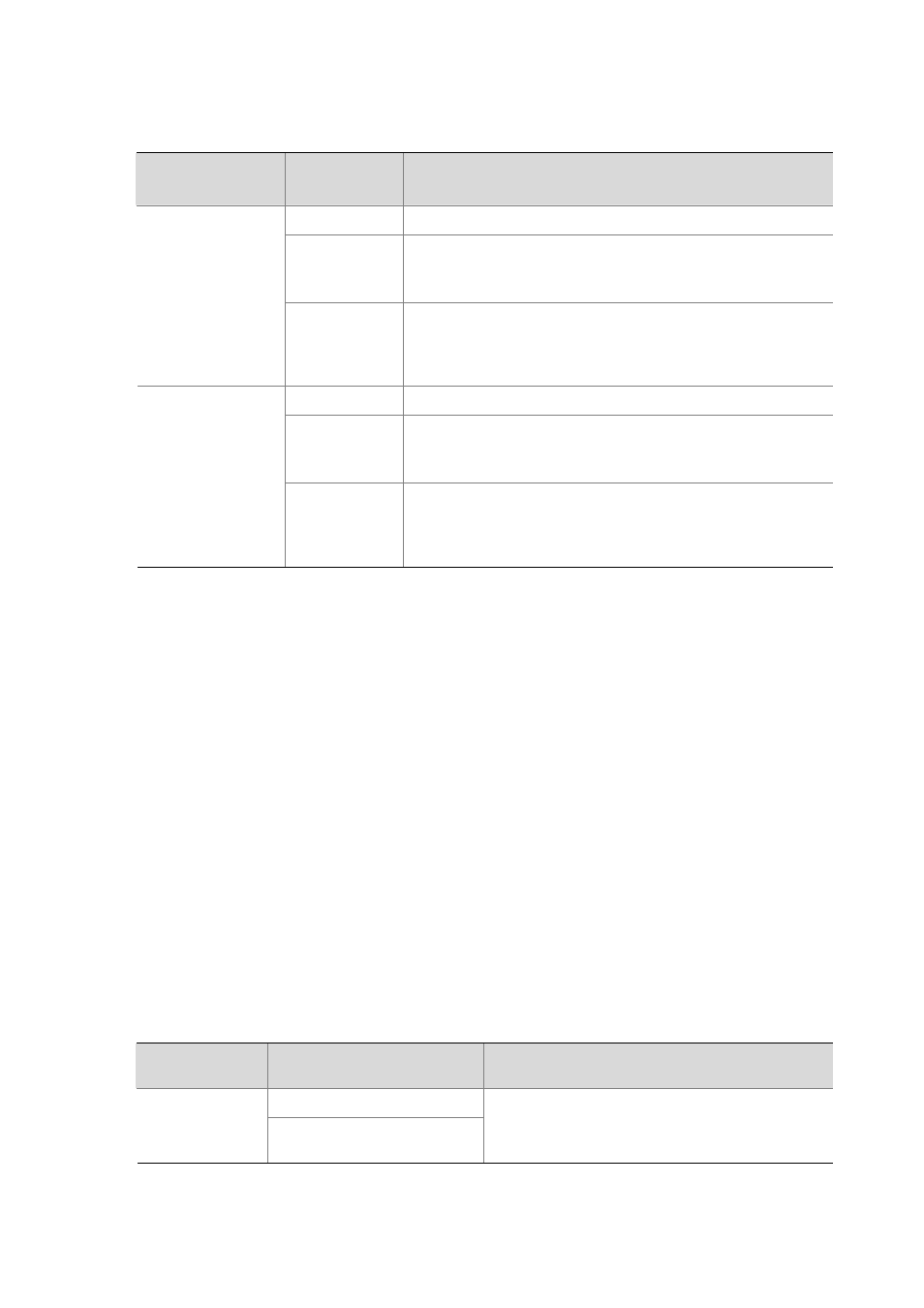
Table 1-3 Matching relationship between port types and voice devices acquiring voice VLAN through
manual configuration
Voice VLAN
assignment mode
Port type
Supported or not
Access Not
supported
Trunk
Supported
Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice
VLAN, and the access port permits the traffic of the default VLAN.
Automatic
Hybrid
Supported
Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice
VLAN, and the default VLAN is in the list of the tagged VLANs
whose traffic is permitted by the access port.
Access
Not supported
Trunk
Supported
Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice
VLAN, and the access port permits the traffic of the default VLAN.
Manual
Hybrid
Supported
Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice
VLAN, and the default VLAN and the voice VLAN is in the list of the
tagged VLANs whose traffic is permitted by the access port.
Security Mode of Voice VLAN
The automatic mode and manual mode described earlier only apply to the process of assigning a port to
the voice VLAN. After a port is assigned to the voice VLAN, the switch receives and forwards all voice
VLAN-tagged traffic without matching the source MAC address of each received packet against its OUI
list. For a port in the manual mode with the default VLAN as the voice VLAN, any untagged packet can
be transmitted in the voice VLAN. This makes the voice VLAN vulnerable to flow attacks, because
malicious users can create a large amount of voice VLAN-tagged packets to consume the voice VLAN
bandwidth, affecting normal voice communication.
H3C series switches provide the security mode for voice VLAN to address this problem. When the voice
VLAN works in security mode, the switch checks the source MAC address of each packet to enter the
voice VLAN and drops the packets whose source MAC addresses do not match the OUI list. However,
checking packets occupies lots of system resources. Therefore, in a relatively safe network, you can
configure the voice VLAN to operate in normal mode.
The following table presents how a packet is handled when the voice VLAN is operating in security
mode and normal mode.
Table 1-4 How a packet is handled when the voice VLAN is operating in different modes
Voice VLAN
Mode
Packet Type
Processing Method
Untagged packet
Security
Packet carrying the voice VLAN
tag
If the source MAC address of the packet matches the
OUI list, the packet is transmitted in the voice VLAN.
Otherwise, the packet is dropped.