Unicast address, Multicast address, Interface identifier in ieee eui-64 format – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 907
1-4
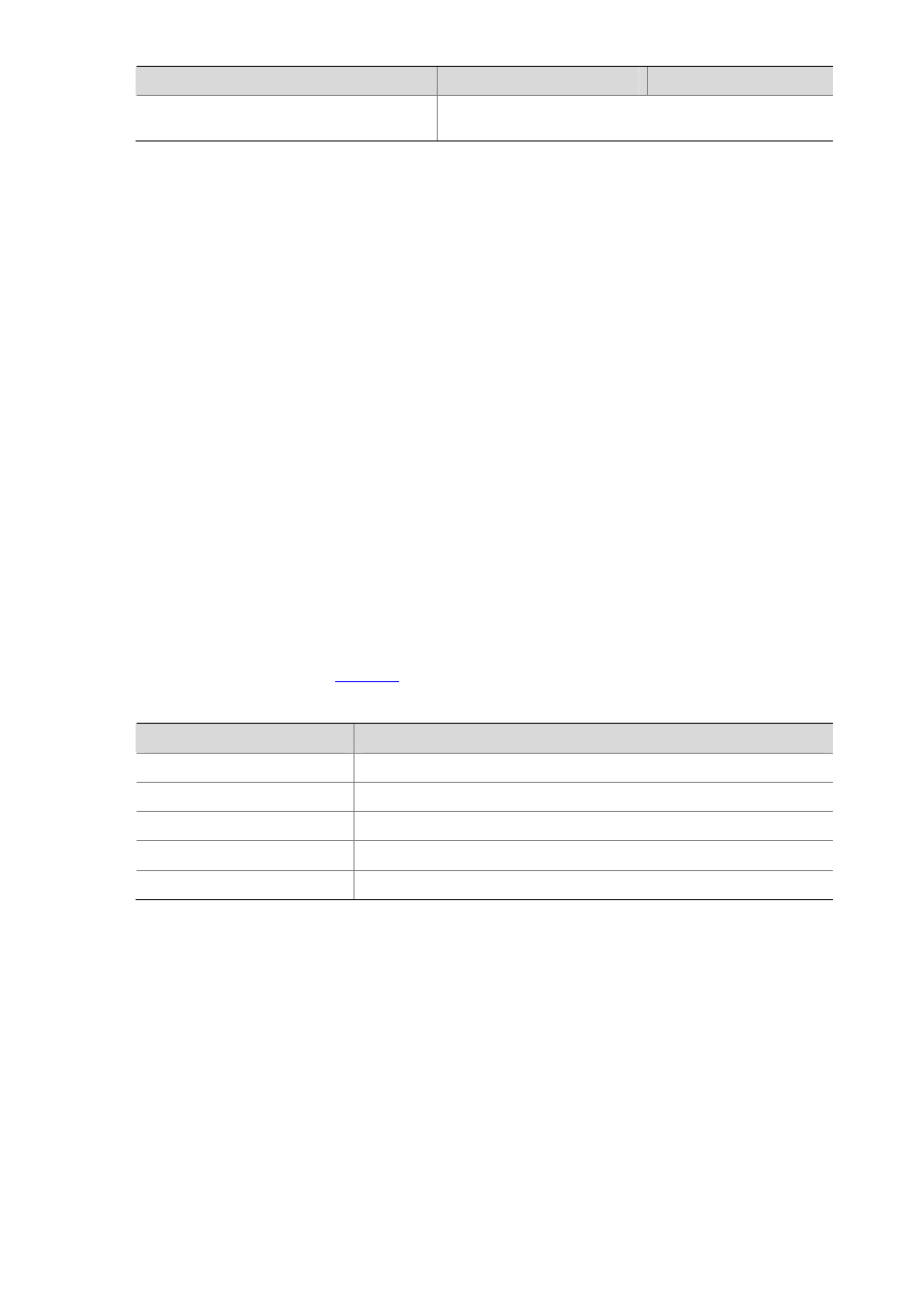
Type
Format prefix (binary)
IPv6 prefix ID
Anycast address
Anycast addresses are taken from unicast address space and
are not syntactically distinguishable from unicast addresses.
Unicast address
There are several forms of unicast address assignment in IPv6, including global unicast address,
link-local address, and site-local address.
z
The global unicast address, equivalent to an IPv4 public address, is used for aggregatable links
and provided for network service providers. This type of address allows efficient routing
aggregation to restrict the number of global routing entries.
z
The link-local address is used in the neighbor discovery protocol and the stateless
autoconfiguration process. Routers must not forward any packets with link-local source or
destination addresses to other links.
z
IPv6 unicast site-local addresses are similar to private IPv4 addresses. Routers must not forward
any packets with site-local source or destination addresses outside of the site (equivalent to a
private network).
z
Loopback address: The unicast address 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 (represented in shorter format as ::1) is
called the loopback address and may never be assigned to any physical interface. Like the
loopback address in IPv4, it may be used by a node to send an IPv6 packet to itself.
z
Unassigned address: The unicast address :: is called the unassigned address and may not be
assigned to any node. Before acquiring a valid IPv6 address, a node may fill this address in the
source address field of an IPv6 packet, but may not use it as a destination IPv6 address.
Multicast address
Multicast addresses listed in
Table 1-2
are reserved for special purpose.
Table 1-2 Reserved IPv6 multicast addresses
Address
Application
FF01::1
Node-local scope all-nodes multicast address
FF02::1
Link-local scope all-nodes multicast address
FF01::2
Node-local scope all-routers multicast address
FF02::2
Link-local scope all-routers multicast address
FF05::2
Site-local scope all-routers multicast address
Besides, there is another type of multicast address: solicited-node address. The solicited-node
multicast address is used to acquire the link-layer addresses of neighbor nodes on the same link and is
also used for duplicate address detection. Each IPv6 unicast or anycast address has one
corresponding solicited-node address. The format of a solicited-node multicast address is as follows:
FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FFXX:XXXX
Where, FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF is permanent and consists of 104 bits, and XX:XXXX is the last 24 bits of an
IPv6 address.
Interface identifier in IEEE EUI-64 format
Interface identifiers in IPv6 unicast addresses are used to identify interfaces on a link and they are
required to be unique on that link. Interface identifiers in IPv6 unicast addresses are currently required
to be 64 bits long. An interface identifier is derived from the link-layer address of that interface. Interface
identifiers in IPv6 addresses are 64 bits long, while MAC addresses are 48 bits long. Therefore, the