Priority trust mode – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 585
1-6
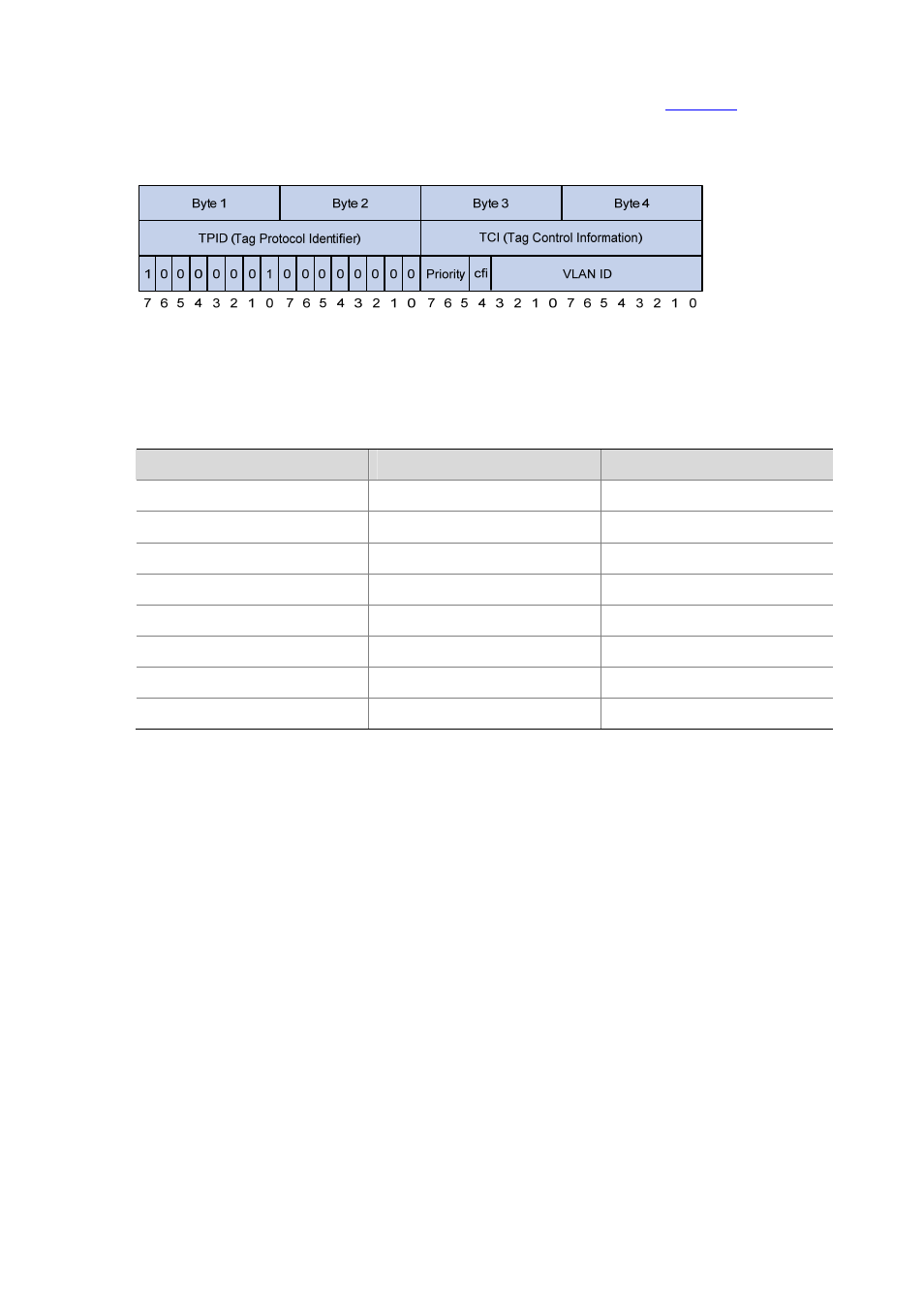
The 4-byte 802.1Q tag header consists of the tag protocol identifier (TPID, two bytes in length), whose
value is 0x8100, and the tag control information (TCI, two bytes in length).
describes the
detailed contents of an 802.1Q tag header.
Figure 1-4 802.1Q tag headers
In the figure above, the priority field (three bits in length) in TCI is 802.1p priority (also known as CoS
precedence), which ranges from 0 to 7.
Table 1-4 Description on 802.1p priority
802.1p priority (decimal)
802.1p priority (binary)
Description
0 000
best-effort
1 001
background
2 010
spare
3 011
excellent-effort
4 100
controlled-load
5 101
video
6 110
voice
7 111
network-management
The precedence is called 802.1p priority because the related applications of this precedence are
defined in detail in the 802.1p specifications.
3) Local
precedence
Local precedence is a locally significant precedence that the device assigns to a packet. A local
precedence value corresponds to one of the eight hardware output queues. Packets with the highest
local precedence are processed preferentially. As local precedence is used only for internal queuing, a
packet does not carry it after leaving the queue.
Priority trust mode
After a packet enters a switch, the switch sets the 802.1p priority and local precedence for the packet
according to its own capability and the corresponding rules.
1) For a packet carrying no 802.1q tag
When a packet carrying no 802.1q tag reaches a port, the switch uses the port priority as the 802.1p
precedence value of the received packet, searches for the local precedence corresponding to the port
priority of the receiving port in the 802.1p-to-local precedence mapping table, and assigns the local
precedence to the packet.
2) For an 802.1q tagged packet