Mac address replication configuration, Overview – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 208
1-5
MAC Address Replication Configuration
The contents of this section are only applicable to the S3100-EI series among S3100 series switches.
Overview
The MAC address replication feature allows you to copy the MAC address table entries of one or
multiple VLANs to the MAC address table of another VLAN. This feature effectively reduces the
broadcasts and improves network security when you use the VLAN marking function with the
traffic-remark-vlanid command.
Using MAC Address Replication Together with VLAN Marking
By default, a port with the VLAN marking function configured adds the source MAC addresses of
incoming packets to the MAC address table of the original VLAN, replaces the original VLAN tag of the
packets with the marked VLAN tag, and forwards the packets to the marked VLAN. When the response
packets enter the switch through the marked VLAN, the switch, however, cannot find the MAC
addresses of the response packets in the MAC address table of the marked VLAN, and have to
broadcast the packets in the VLAN.
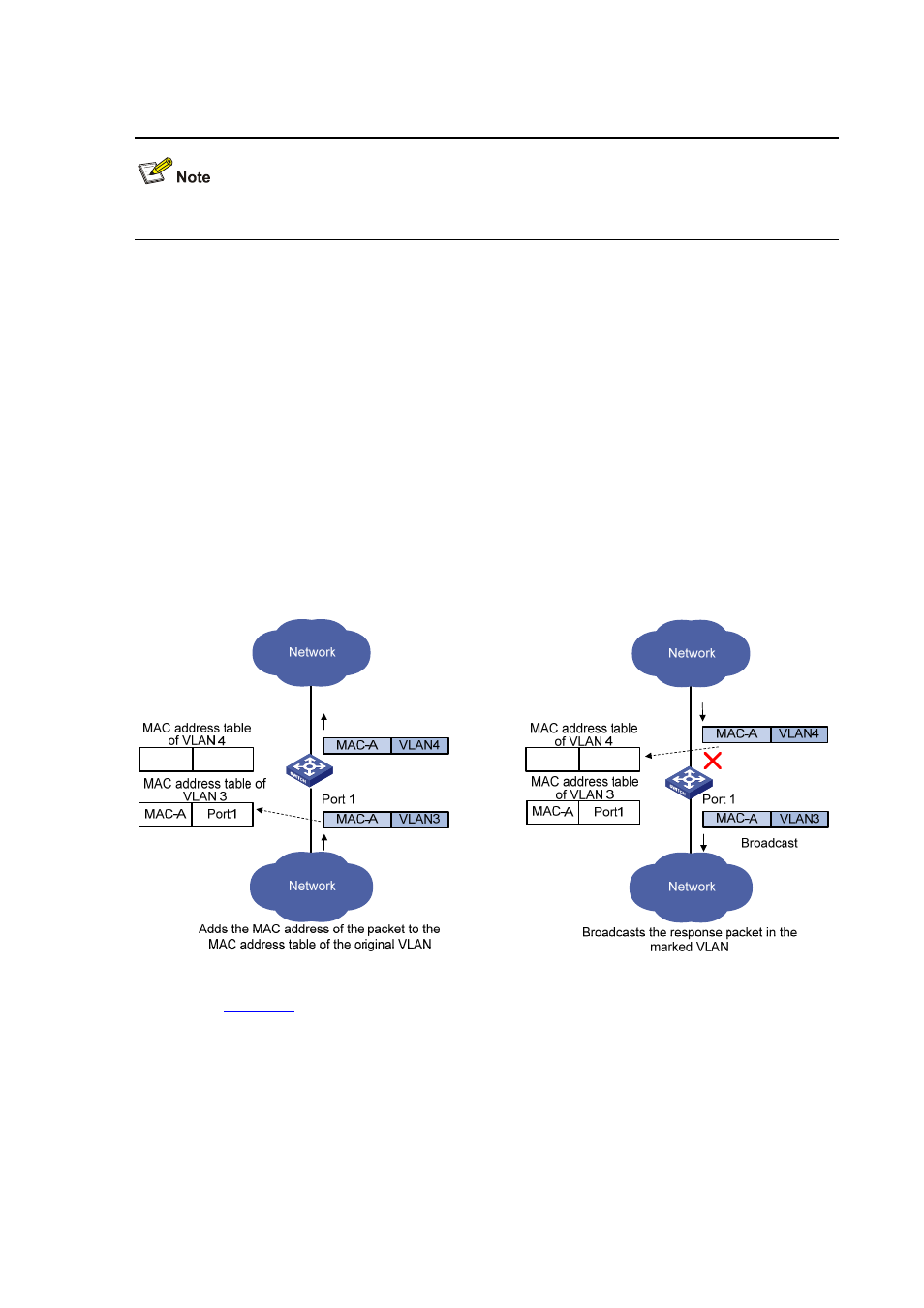
Figure 1-6 How a VLAN marking-enabled port learns MAC addresses
As shown in
, VLAN marking is configured on Port 1 to replace the VLAN tag of packets from
VLAN 3 with VLAN tag 4. When Port 1 receives a packet from VLAN 3, it adds the source MAC address
(MAC-A) of the packet to the MAC address table of VLAN 3 (also called the original VLAN).
When a response packet enters the switch through VLAN 4, the switch searches the outbound port for
MAC-A in the MAC address table of VLAN 4. The switch considers this packet as a unicast packet with
an unknown destination MAC address and broadcasts it to all the ports in VLAN 4 because the switch
cannot find the corresponding MAC address entry in the MAC address table of VLAN 4. Broadcasting
packets wastes the network resources and might cause security problems.