Arp process, Table 1-3 – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 487
1-3
Table 1-3 ARP entries
ARP entry
Generation Method
Maintenance Mode
Static ARP entry
Manually configured
Manual maintenance
Dynamic ARP entry
Dynamically generated
ARP entries of this type age with time.
The aging period is set by the ARP aging
timer.
ARP Process
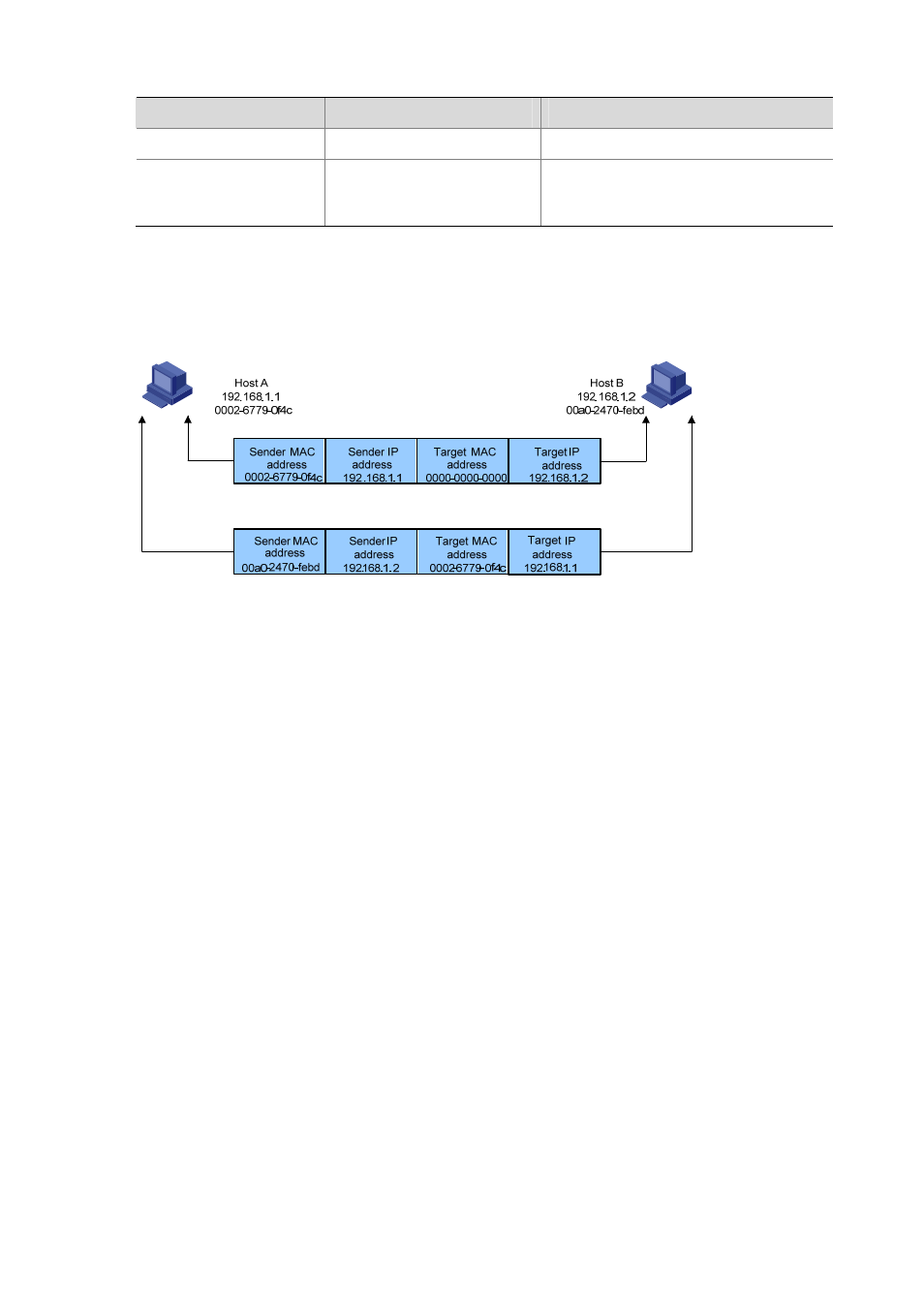
Figure 1-2 ARP process
Suppose that Host A and Host B are on the same subnet and that Host A sends a message to Host B.
The resolution process is as follows:
1) Host A looks in its ARP mapping table to see whether there is an ARP entry for Host B. If Host A
finds it, Host A uses the MAC address in the entry to encapsulate the IP packet into a data link layer
frame and sends the frame to Host B.
2) If Host A finds no entry for Host B, Host A buffers the packet and broadcasts an ARP request, in
which the source IP address and source MAC address are respectively the IP address and MAC
address of Host A and the destination IP address and MAC address are respectively the IP
address of Host B and an all-zero MAC address. Because the ARP request is sent in broadcast
mode, all hosts on this subnet can receive the request, but only the requested host (namely, Host B)
will process the request.
3) Host B compares its own IP address with the destination IP address in the ARP request. If they are
the same, Host B saves the source IP address and source MAC address into its ARP mapping
table, encapsulates its MAC address into an ARP reply, and unicasts the reply to Host A.
4) After receiving the ARP reply, Host A adds the MAC address of Host B into its ARP mapping table
for subsequent packet forwarding. Meanwhile, Host A encapsulates the IP packet and sends it out.
Usually ARP dynamically implements and automatically seeks mappings from IP addresses to MAC
addresses, without manual intervention.