CIRCUTOR PowerStudio Series User Manual
Page 217
PowerStudio
User Manual 217
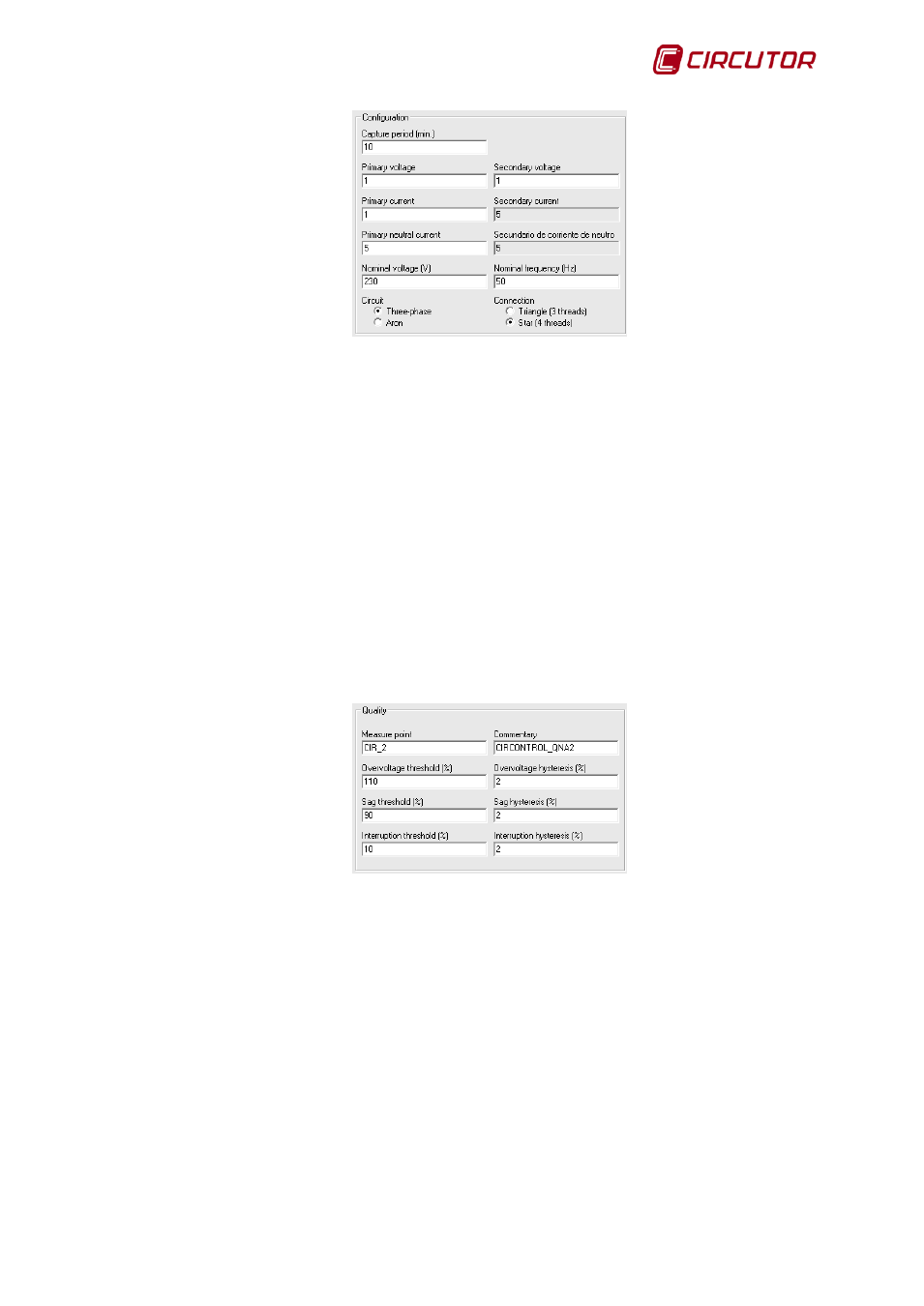
• Capture period: Configuration in minutes between records stored on the device.
• Primary voltage: Device primary voltage value.
• Secondary voltage: Device secondary voltage value.
• Primary current: Device primary current value.
• Secondary current: Device secondary current value.
• Neutral primary current: Device neutral primary current value.
• Neutral secondary current: Device neutral secondary voltage value.
• Rated voltage: Rated voltage of the equipment, with a 3-wire configuration the composite
voltage should be programd and the single voltage on four wires. If the measurement is carried
out through voltage transformers, the programd value must refer to the secondary.
• Nominal frequency: Nominal frequency of the device.
• Circuit: Enables the type of circuit to which it is connected to carry out the measurement to be
chosen, whether it is connected to a three-phase device or if it only uses two current
connectors for the measurement (Aron).
• Connection: Enables the type of connection to which it is connected to carry out the
measurement to be chosen, whether delta (connection between phases, without neutral) or
star (3-phase connection and neutral)
• Measurement point: Brief description of the measurement point where the QNA is situated
• Comments: Brief description of the measurement point.
• Overvoltage threshold: Serves to program the overvoltage percentage. Each semi-cycle with
an rms value exceeding this value will be understood as over voltage.
• Overvoltage hysteresis: Overvoltage hysteresis is where the start-up voltage is different from
the end voltage of overvoltage. An overvoltage will start when the voltage threshold value is
exceeded and will finish when it is lower than the value defined by the difference between the
threshold and the hysteresis.
• Gap threshold: Serves to program the gap detection. Each semi-cycle with an rms value not
reaching this defined value will be understood as a gap.
• Gap Hysteresis: Will define a gap hysteresis so that the initial voltage is different to the end of
gap voltage. A gap will start when the voltage does not exceed the threshold value and will
finish when this is lower than the value defined by the sum of the threshold and the hysteresis.
• Interruption threshold: defined as power off (absence of tension, interruption) the voltage
drop below the value set.