Rstp (rapid spanning tree protocol), Port state of rstp – ATL Telecom R1-SW Ethernet Switch User Manual
Page 265
Configuring STP/RSTP
13-7
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
While STP is enabled, and BPDU is spread, topology is changed continuously on other parts of
the network. It takes a lot of time that the changed topology is applied to spanning tree. RSTP
802.1W improve disadvantage of STP.
The key difference between STP and RSTP is the transition states of a port. STP moves a port
from the blocking state to the forwarding state after the listening and the learning state. RSTP
reduces the transition steps by moving directly a port from the blocking state to the forwarding
state. This allows rapid reconfiguration capability when the topology has changed.
Port State of RSTP
There are three port states - discarding, learning, forwarding - in RSTP 802.1W. The learning
state and the forwarding state are the same as the states of STP, and the discarding state
includes the disable state, the blocking state and the listening state of STP. The following table
provides a comparison of STP and RSTP port states.
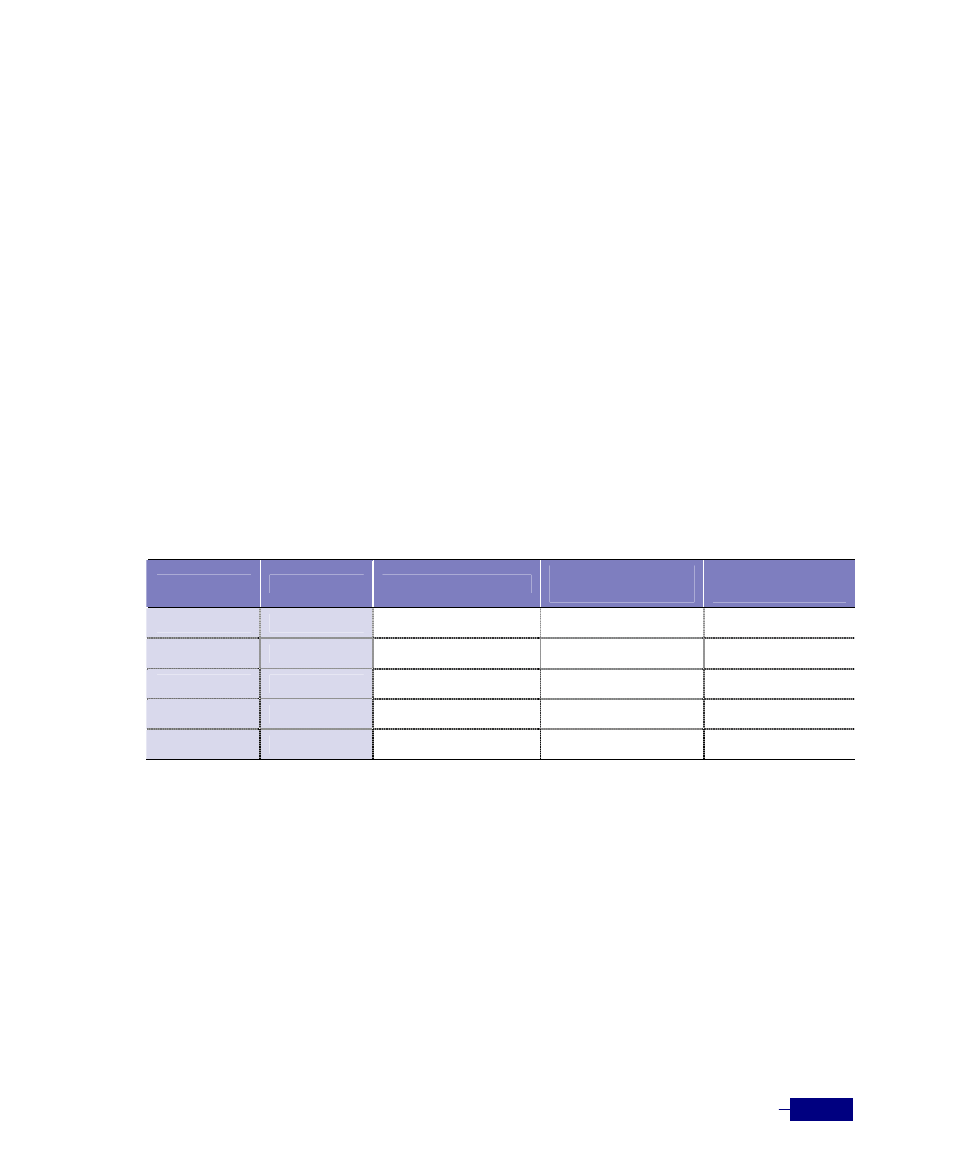
Table 13-2 Comparison of STP and RSTP port states
STP Port State
RSTP Port State
Operational Status
Is Port Included in the
Active Topology?
Is port learning MAC
Addresses?
Blocking
Discarding
Enabled No No
Listening
Discarding
Enabled No No
Learning
Learning
Enabled No Yes
Forwarding
Forwarding
Enabled Yes Yes
Disabled
Discarding
Disabled No No