Chapter 14 802.1x configuration, 1 introduction to 802.1x – Amer Networks SS2R48G4i V2 User Manual
Page 128
SS2R24G4i/SS2R48G4i
117
Chapter 14 802.1x Configuration
14.1 Introduction to 802.1x
IEEE 802.1x is a port-based network access management method, which authenticates and
manages the accessing devices on the physical access level of the LAN device. The physical access
level here are the ports of the switch. If the users’ devices connected to such ports can be authenticated,
access to resources in the LAN is allowed; otherwise, access will be denied, which is essentially the
same as disconnecting physically.
IEEE 802.1x defines a port-based network access management protocol. It should be noted that
the protocol applies to point-to-point connection between the accessing device and the access port,
where the port can be either a logical port or a physical port. Typically, one physical port of the switch
connects with one terminal device (physical port-based) only.
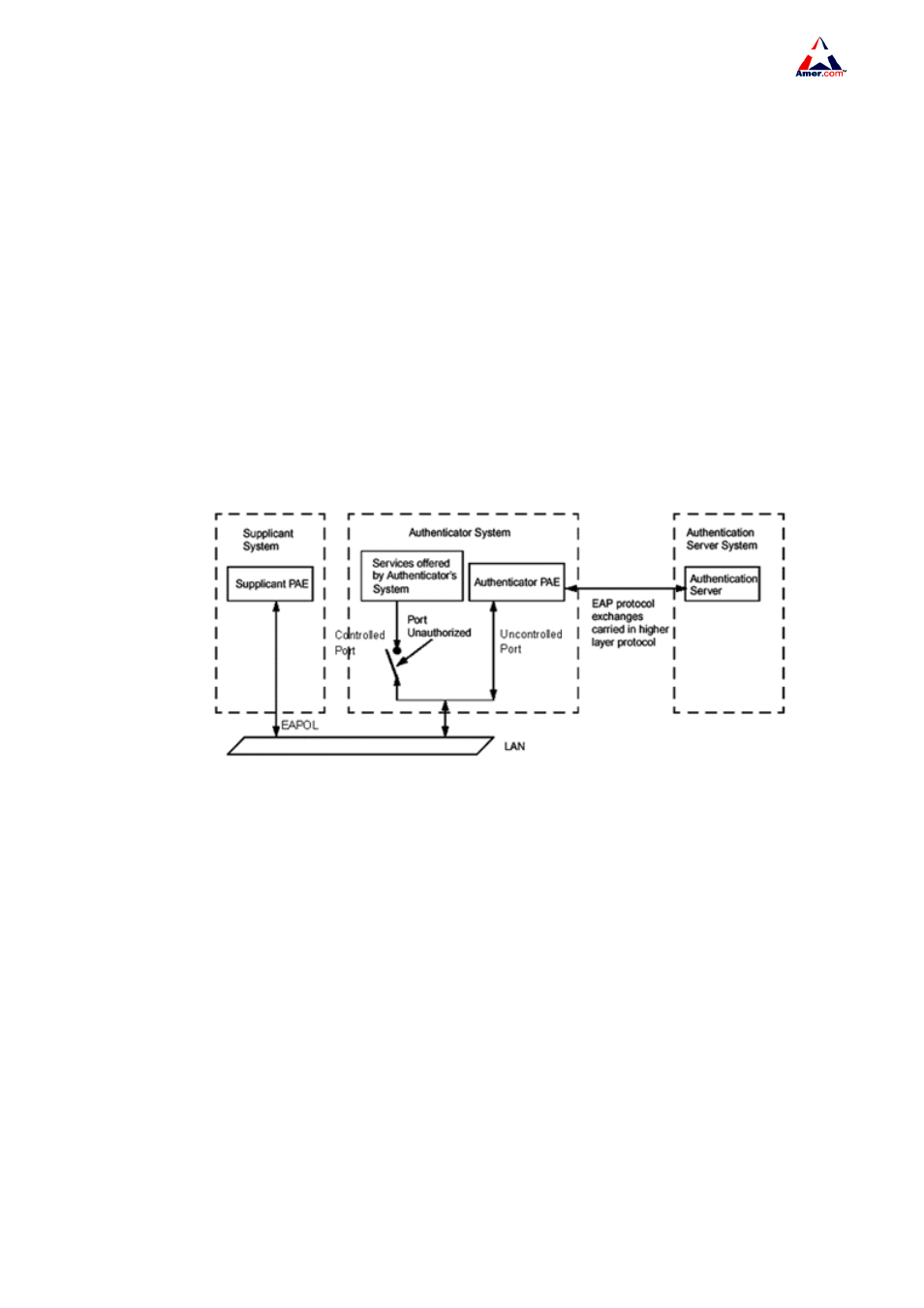
The architecture of IEEE 802.1x is shown below
Fig 14-1 802.1x architecture
As shown in the above figure, the IEEE 802.1x architecture consists of three parts
Supplicant System (user access devices)
Authenticator System (access management unit)
Authentication Server System (the authenticating server)
EAPOL protocol defined by IEEE 802.1x runs between the user access device (PC) and access
management unit (access switch); and EAP protocol is also used between the access management
unit and authenticating server. EAP packets encapsulates the authenticating data. The EAP packet is
conveyed in the packets of the higher layer protocols such as RADIUS to pass through complex
network to the authenticating server.
The ports provided by the port-based network access management device end are divided into two
virtual port types managed port and non-managed port. A non-managed port is always in the
connected status for both in and out directions to transfer EAP authenticating packets. A managed port
will be in the connected status when authorized to transfer commutation packets; and is shutdown when
not authorized, and cannot transfer any packets.