Chapter 32 commands for static route, 1 ip route, Chapter 32 commands for static route -135 – PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 496: Ip route
32-135
Chapter 32 Commands for Static Route
32.1 ip route
Command:
ip route {<ip-prefix> <mask> | <ip-prefix>/<prefix-length>} {<gateway-address> |
<gateway-interface>} [<distance>]
no ip route {<ip-prefix> <mask> | <ip-prefix>/<prefix-length>} [<gateway-address> |
<gateway-interface>] [<distance>]
Function:
Configure the static route. The “no ip route {<ip-prefix> <mask> | <ip-prefix>/<prefix-length>}
[<gateway-address> | <gateway-interface>] [<distance>]” command deletes the static route.
Parameter:
The <ip-prefix> and <mask> are respectively destination IP address and subnet mask, shown in
dotted decimal notation; <ip-prefix> and <prefix-length> are respectively the destination IP
address and the length of prefix; <gateway-address> is the next-hop IP address shown in dotted
decimal notation; <gateway-interface> is the next-hop interface, < distance > is the manage
distance of route management, ranging between 1~255.
Default:
The management distance of static routing is defaulted at 1.
Command Mode:
Global Mode.
Usage Guide:
When configuring the next-hop of static routing, both by specifying the next-hop IP address of the
route data packet and the exit interface are available.
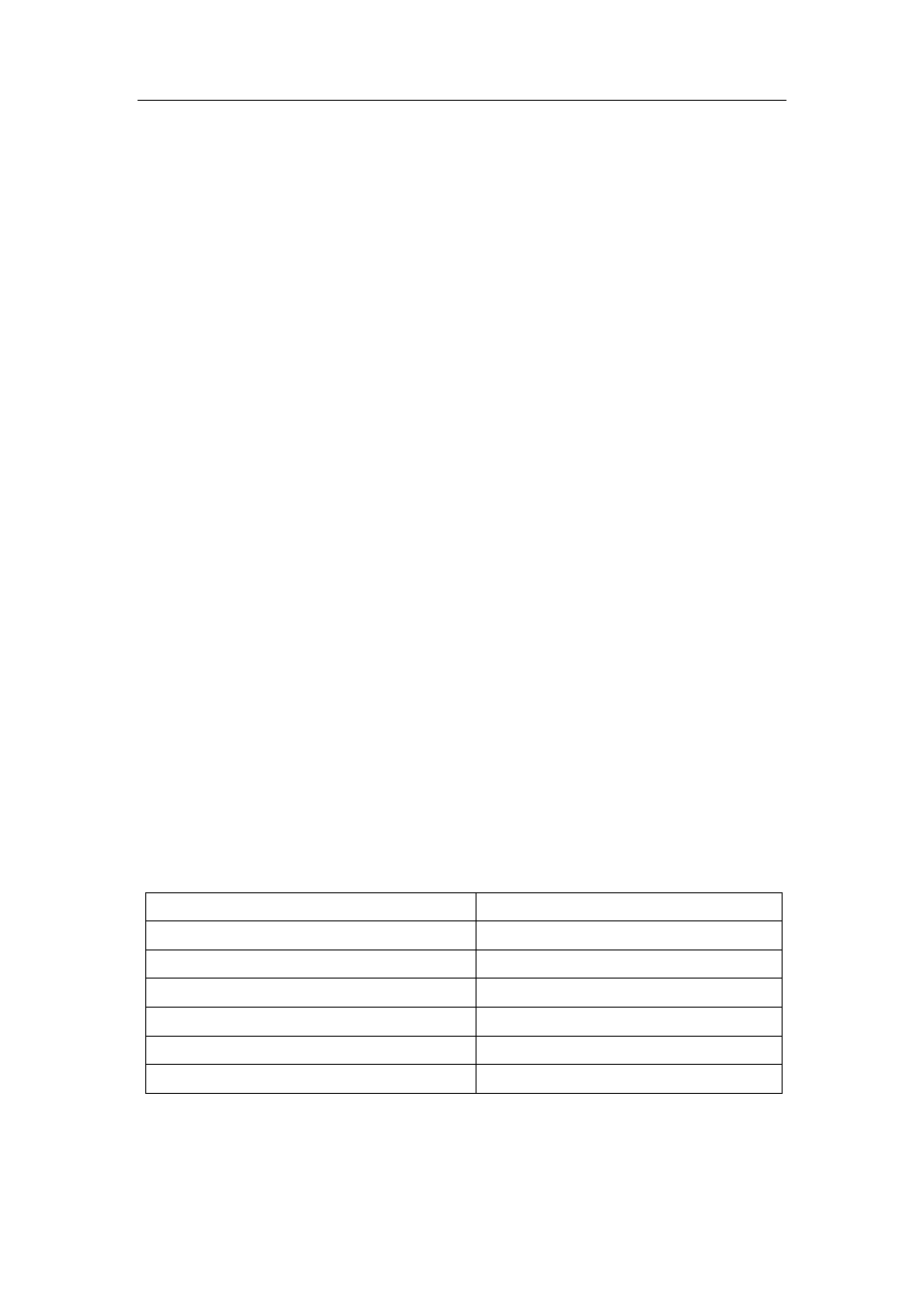
The default distance values of each route type in the layer 3 switch of our company are listed below:
Route Type
Distance Value
Direct Route
0
Static Route
1
OSPF
110
RIP
120
IBGP
200
EBGP
20
The direct route has the highest priority when each route management distance value remain
unchanged and followed by static route, EBGP、OSPF、RIP、IBGP.
Example: