Scrambling types, Differential encoder, Bpsk bit ordering – Comtech EF Data SDM-300A User Manual
Page 364: Interleaver (reed-solomon codec), 3 scrambling types, 4 differential encoder, 5 bpsk bit ordering, 6 interleaver (reed-solomon codec)
SDM-300A Satellite Modem
Revision 6
Specifications
MN/SDM300A.IOM
19–8
19.4.3 Scrambling
Types
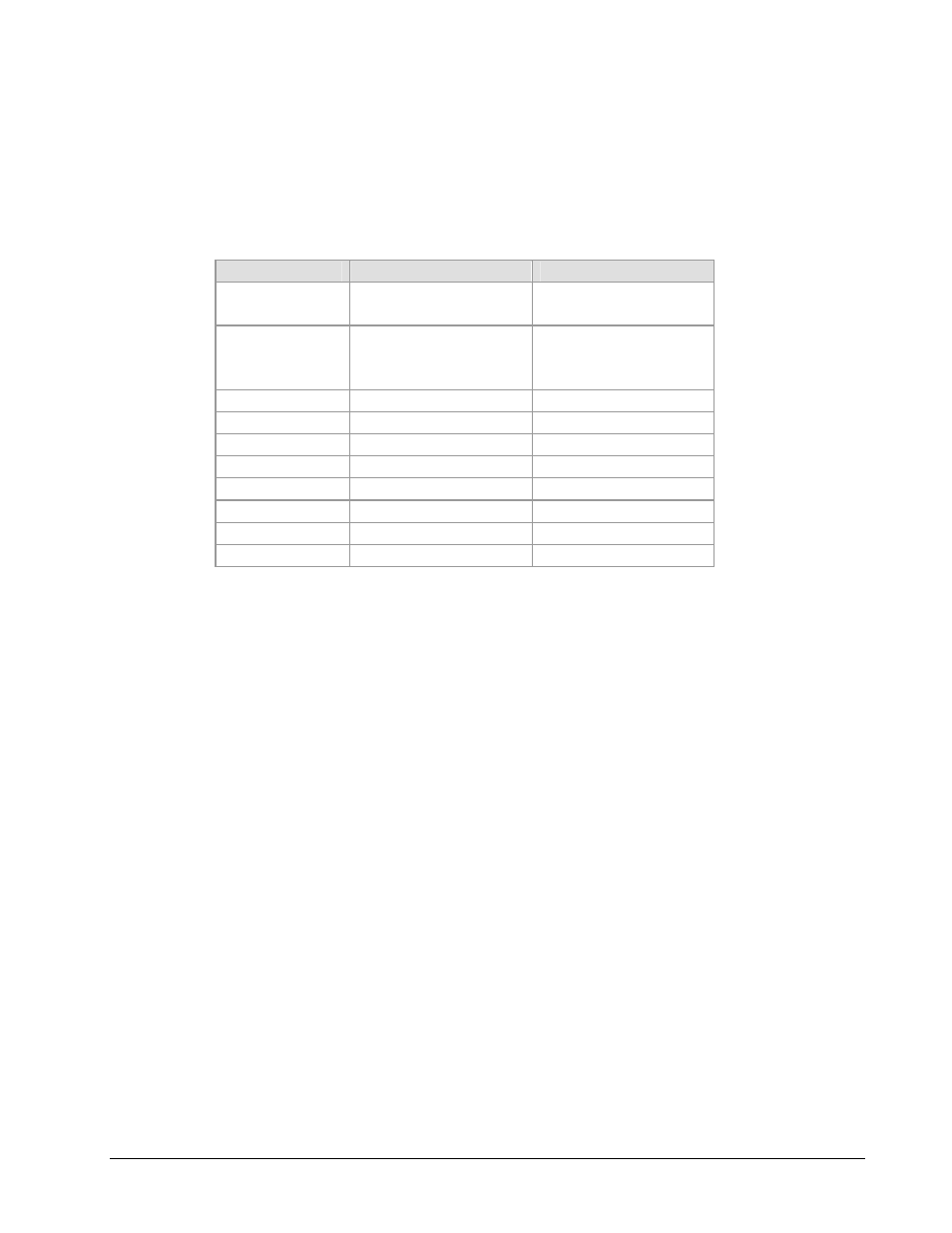
The operator can select one of the following scrambling types.
Modulation Type
FEC or Framing
Scrambling
EFD Closed,
CSC Closed
Sequential ITU
V.35
EFD Closed,
CSC Closed,
FDC Closed
Viterbi
ITU V.35 Intelsat Modified
EFD Closed
Viterbi/RS Concatenated
EFD Modified V.35
EFD Closed
Turbo
2
12-1
Synchronous
EFD Closed
Turbo
IESS-315 Mode
EFD Closed
ASYNC
2
15-1
Synchronous
FDC Closed
Sequential
FDC Modified V.35
Intelsat Open
Viterbi IDR
ITU V.35 Intelsat Modified
Intelsat Open
Viterbi IDR with RS
ITU V.35 Intelsat Modified
Intelsat Open
IBS, D&I, IESS-310
2
15-1
Synchronous
19.4.4 Differential
Encoder
The differential encoder (On or Off) takes care of one set of ambiguities due the error
correction codes being transparent.
19.4.5 BPSK
Bit
Ordering
The encoder has the ability to select whether I is the first bit or Q is the first bit in the symbol
word grouping for compatibility with any system. For standard operation Q is the first bit.
• Viterbi (Standard/Non-Standard)
• Sequential (Standard/Non-Standard)
• Turbo (Not Supported)
19.4.6
Interleaver (Reed-Solomon Codec)
• QPSK – Depth 4 (IBS, IDR, D&I)
• 8-PSK – Depth 4 (No Overhead, IBS, D&I) (IESS-310)
• QPSK/OPSK – Depth 4, 8, 16 (Closed Network, ASYNC)
• 8-PSK – Depth 8 (IDR) (IESS-310)