H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 166
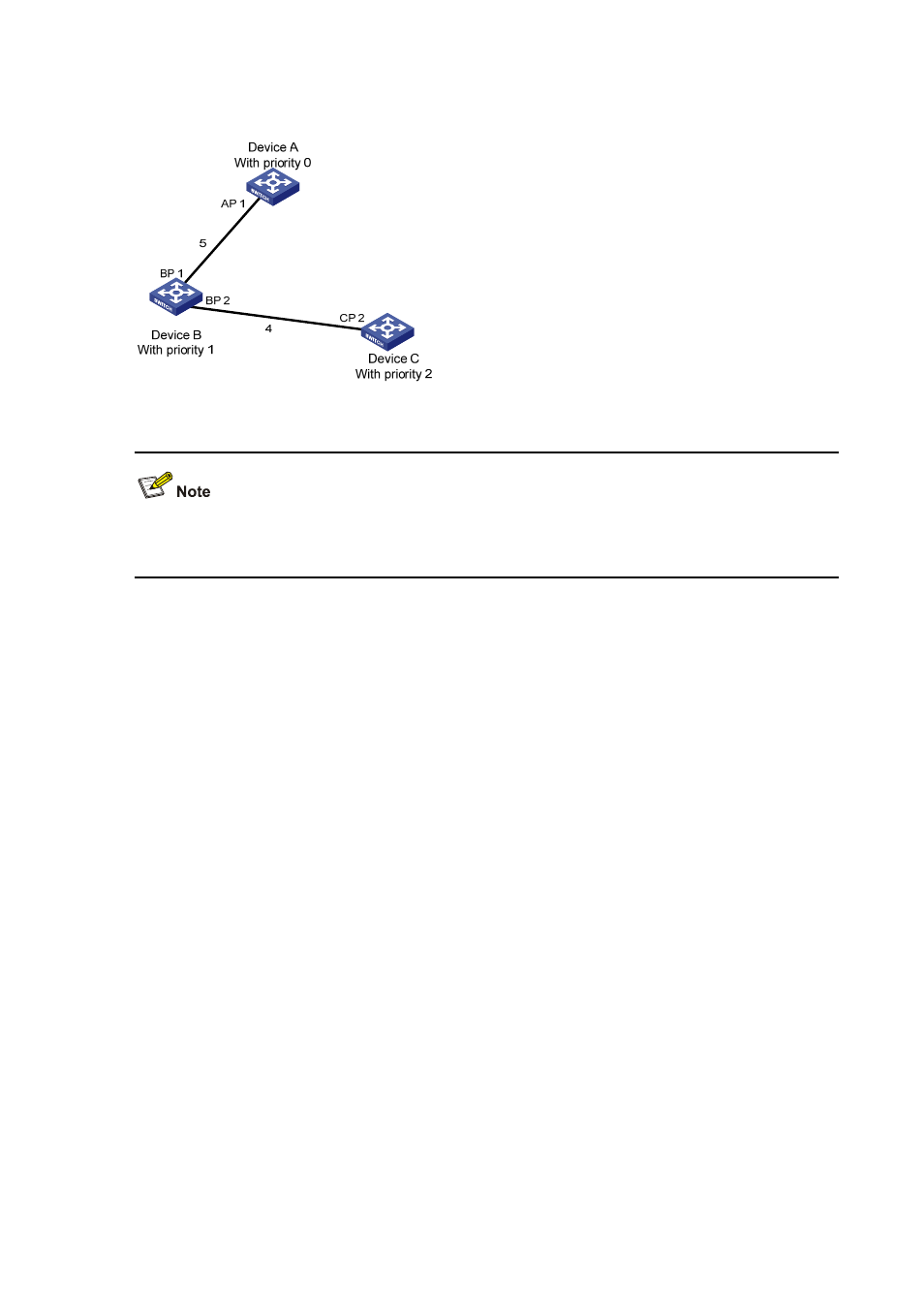
20-8
Figure 20-3
The final calculated spanning tree
To facilitate description, the spanning tree calculation process in this example is simplified, while the
actual process is more complicated.
2) The BPDU forwarding mechanism in STP
z
Upon network initiation, every switch regards itself as the root bridge, generates configuration
BPDUs with itself as the root, and sends the configuration BPDUs at a regular interval of hello time.
z
If it is the root port that received the configuration BPDU and the received configuration BPDU is
superior to the configuration BPDU of the port, the device will increase message age carried in the
configuration BPDU by a certain rule and start a timer to time the configuration BPDU while it sends
out this configuration BPDU through the designated port.
z
If the configuration BPDU received on the designated port has a lower priority than the
configuration BPDU of the local port, the port will immediately send out its better configuration
BPDU in response.
z
If a path becomes faulty, the root port on this path will no longer receive new configuration BPDUs
and the old configuration BPDUs will be discarded due to timeout. In this case, the device will
generate a configuration BPDU with itself as the root and sends out the BPDU. This triggers a new
spanning tree calculation process so that a new path is established to restore the network
connectivity.
However, the newly calculated configuration BPDU will not be propagated throughout the network
immediately, so the old root ports and designated ports that have not detected the topology change
continue forwarding data along the old path. If the new root port and designated port begin to forward
data as soon as they are elected, a temporary loop may occur.
3) STP
timers
STP calculations need three important timing parameters: forward delay, hello time, and max age.