Totally) stub area, Nssa area – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 240
25-6
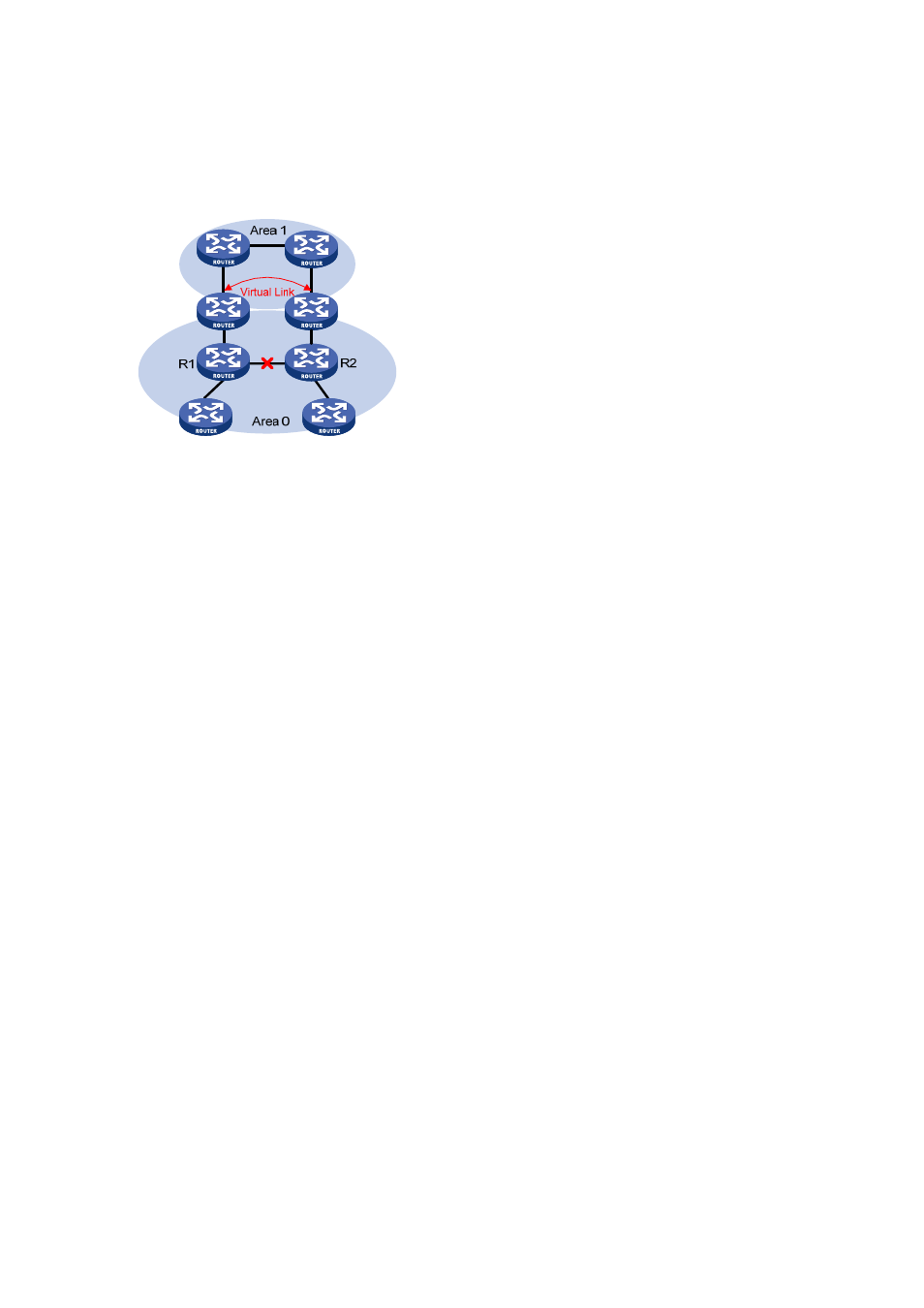
Another application of virtual links is to provide redundant links. If the backbone area cannot maintain
internal connectivity due to a physical link failure, configuring a virtual link can guarantee logical
connectivity in the backbone area, as shown below.
Figure 25-4
Virtual link application 2
The virtual link between the two ABRs acts as a point-to-point connection. Therefore, you can configure
interface parameters such as hello packet interval on the virtual link as they are configured on physical
interfaces.
The two ABRs on the virtual link exchange OSPF packets with each other directly, and the OSPF
routers in between simply convey these OSPF packets as normal IP packets.
(Totally) Stub area
The ABR in a stub area does not distribute Type-5 LSAs into the area, so the routing table size and
amount of routing information in this area are reduced significantly.
You can configure the stub area as a totally stub area, where the ABR advertises neither the
destinations in other areas nor the external routes.
Stub area configuration is optional, and not every area is eligible to be a stub area. In general, a stub
area resides on the border of the AS.
The ABR in a stub area generates a default route into the area.
Note the following when configuring a (totally) stub area:
z
The backbone area cannot be a (totally) stub area.
z
The stub command must be configured on routers in a (totally) stub area.
z
A (totally) stub area cannot have an ASBR because AS external routes cannot be distributed into
the stub area.
z
Virtual links cannot transit (totally) stub areas.
NSSA area
Similar to a stub area, an NSSA area imports no AS external LSA (Type-5 LSA) but can import Type-7
LSAs that are generated by the ASBR and distributed throughout the NSSA area. When traveling to the
NSSA ABR, Type-7 LSAs are translated into Type-5 LSAs by the ABR for advertisement to other areas.
In the following figure, the OSPF AS contains three areas: Area 1, Area 2 and Area 0. The other two
ASs employ the RIP protocol. Area 1 is an NSSA area, and the ASBR in it translates RIP routes into
Type-7 LSAs and advertises them throughout Area 1. When these LSAs travel to the NSSA ABR, the
ABR translates Type-7 LSAs to Type-5 LSAs for advertisement to Area 0 and Area 2.