Dldp implementation – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 298
27-6
DLDP implementation
1) On a DLDP-enabled link that is in up state, DLDP sends DLDP packets to the peer device and
processes the DLDP packets received from the peer device. DLDP packets sent vary with DLDP
states.
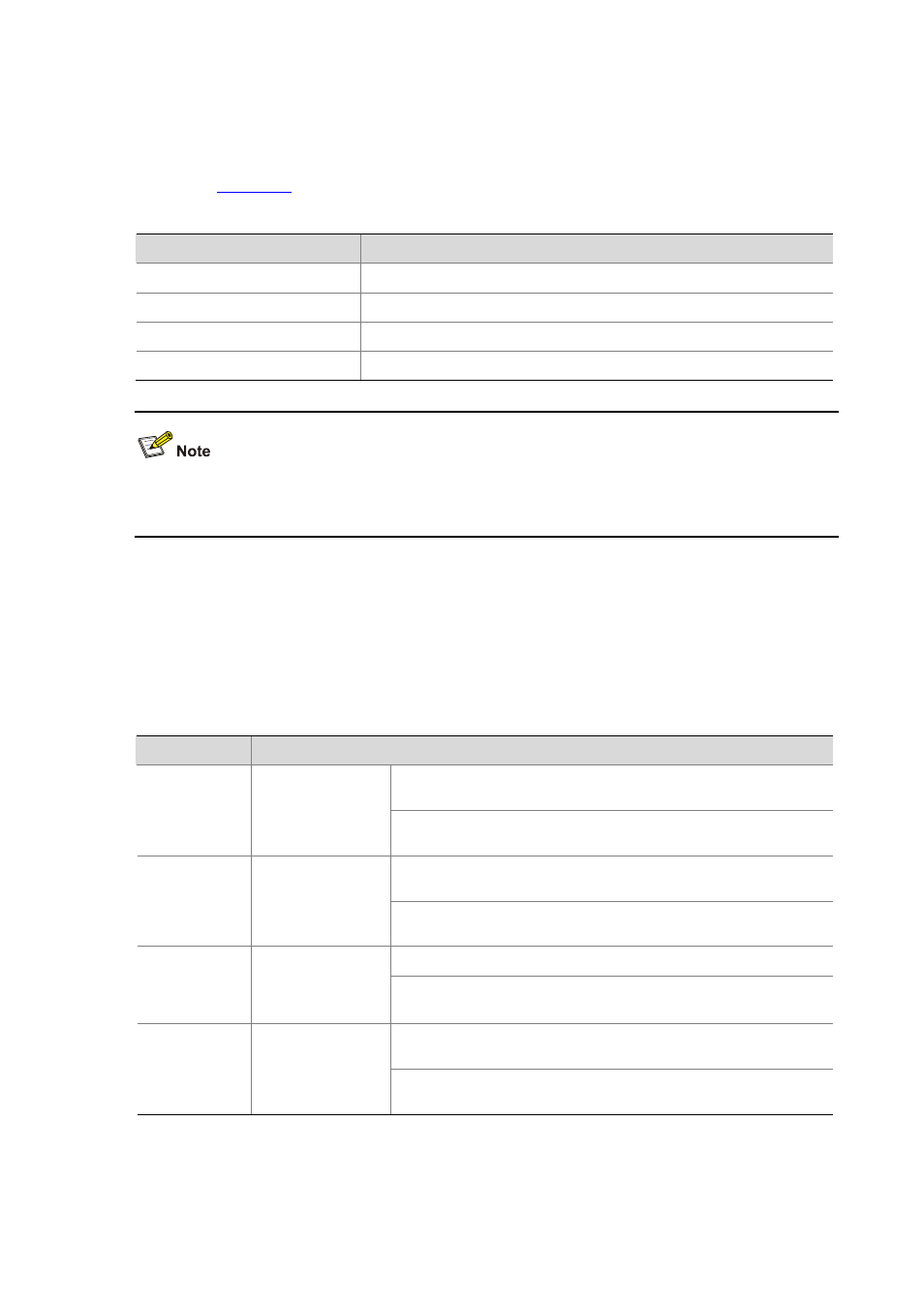
lists DLDP states and the corresponding packets.
Table 27-4
DLDP packet types and DLDP states
DLDP state
Type of DLDP packets sent
Active
Advertisement packet with RSY tag
Advertisement
Normal Advertisement packet
Probe Probe
packet
Disable
Disable packet and RecoverProbe packet
When a device transits from a DLDP state other than Inactive state or Disable state to Initial state, it
sends Flush packets.
2) A received DLDP packet is processed as follows.
z
In any of the three authentication modes, the packet is dropped if it fails to pass the authentication.
z
The packet is dropped if the setting of the interval for sending Advertisement packets it carries
conflicts with the corresponding local setting.
z
Other processes.
Table 27-5
Procedures for processing different types of DLDP packets
Packet type
Processing procedure
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the
neighbor entry, triggers the Entry timer, and transits to Probe state.
Advertisement
packet with
RSY tag
Retrieving the
neighbor
information.
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry
timer and transits to Probe state.
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the
neighbor entry, triggers the Entry timer, and transits to Probe state.
Normal
Advertisement
packet
Retrieves the
neighbor
information.
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry
timer.
If yes, no process is performed.
Flush packet
Determines
whether or not the
local port is in
Disable state.
If not, removes the corresponding neighbor entry (if any).
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the
neighbor entry, transits to Probe state, and returns Echo packets.
Probe packet
Retrieves the
neighbor
information.
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry
timer and returns Echo packets.