H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 315
28-9
As defined by IANA, the high-order 24 bits of an IPv4 multicast MAC address are 0x01005e, bit 25 is
0x0, and the low-order 23 bits are the low-order 23 bits of a multicast IPv4 address. The IPv4-to-MAC
mapping relation is shown in
Figure 28-5
IPv4-to-MAC address mapping
XXXX X
X
XXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
1110 XXXX
0XXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
XXXX XXXX
0000 0001
0000 0000
0101 1110
32-bit IPv4 address
48-bit MAC address
5 bits lost
25-bit MAC address prefix
…
23 bits
mapped
…
The high-order four bits of a multicast IPv4 address are 1110, indicating that this address is a multicast
address, and only 23 bits of the remaining 28 bits are mapped to a MAC address, so five bits of the
multicast IPv4 address are lost. As a result, 32 multicast IPv4 addresses map to the same MAC address.
Therefore, in Layer 2 multicast forwarding, a device may receive some multicast data addressed for
other IPv4 multicast groups, and such redundant data needs to be filtered by the upper layer.
2) IPv6 multicast MAC addresses
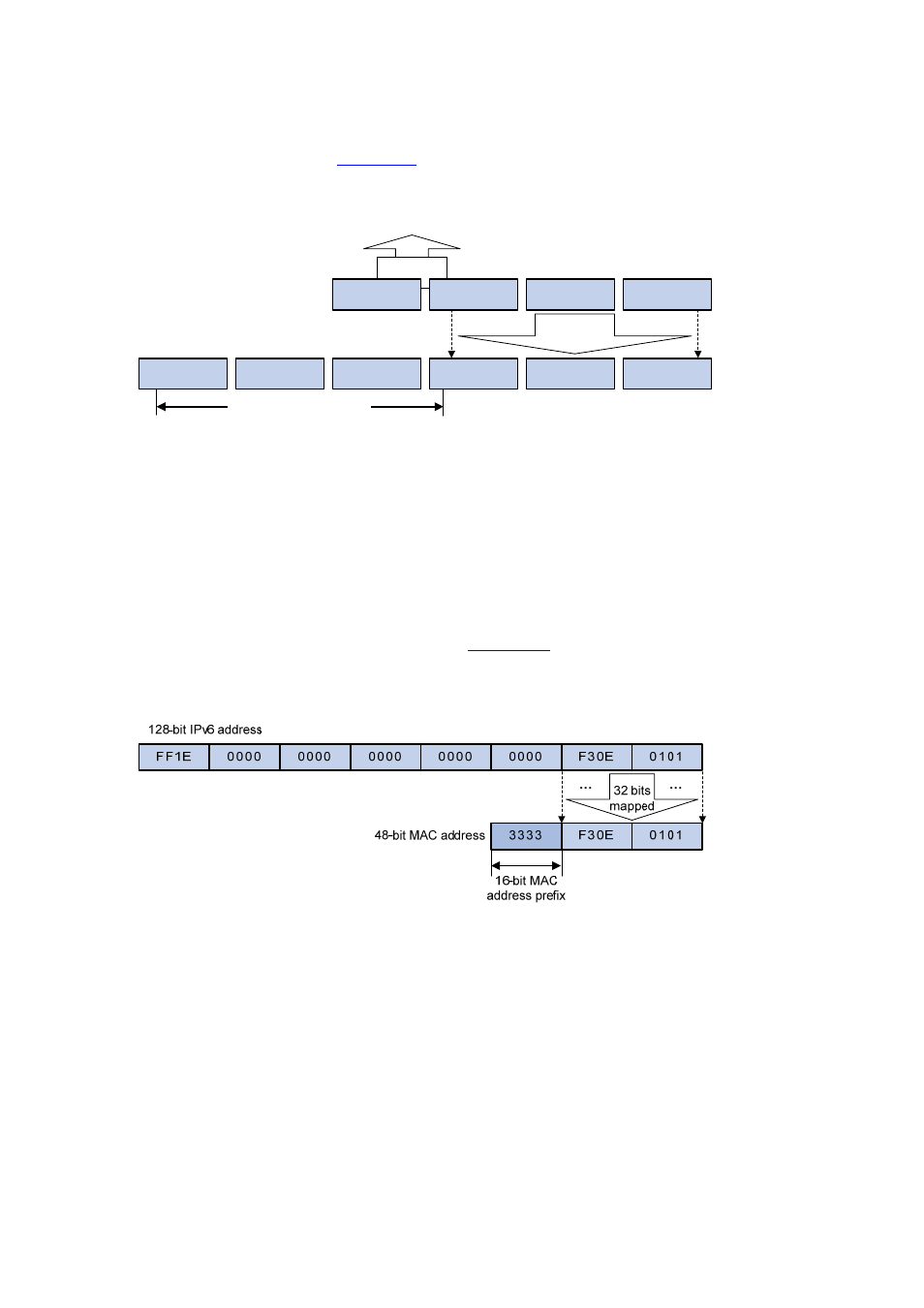
The high-order 16 bits of an IPv6 multicast MAC address are 0x3333, and the low-order 32 bits are the
low-order 32 bits of a multicast IPv6 address.
shows an example of mapping an IPv6
multicast address, FF1E::F30E:0101, to a MAC address.
Figure 28-6
An example of IPv6-to-MAC address mapping