Pixel aspect ratio, Capturing or adding various aspect ratios – Adobe Premiere Elements 8 User Manual
Page 73
68
USING ADOBE PREMIERE ELEMENTS 8 EDITOR
Importing and adding media
Last updated 8/12/2010
Pixel aspect ratio
Pixel aspect ratio describes the ratio of width to height in a single pixel of a frame. Pixel aspect ratios vary because
different video systems make different assumptions about the number of pixels required to fill a frame. For example,
many computer video standards define a frame that has a 4:3 aspect ratio as 640 x 480 pixels. Pixels that are square,
which have an aspect ratio themselves of 1:1, perfectly fill the horizontal and vertical space defined by that frame.
However, video standards such as DV NTSC, which is the standard followed by most consumer DV camcorders (sold
in the U.S.), define a 4:3 aspect ratio frame as 720 x 480 pixels. Consequently, to fit all of these pixels in the frame, the
pixels must be narrower than the square pixels. These narrow pixels are called rectangular pixels, and they have an
aspect ratio of 0.9:1, or 0.9 as they are commonly called. DV pixels are vertically oriented in systems producing NTSC
video and horizontally oriented in systems producing PAL video. Adobe Premiere Elements displays a clip’s pixel
aspect ratio next to the clip’s image thumbnail in the Project view.
If you display rectangular pixels on a square-pixel monitor, images appear distorted, for example, circles distort into
ovals. However, when displayed on a broadcast monitor, the images appear correctly proportioned because broadcast
monitors use rectangular pixels. Adobe Premiere Elements can display and output clips of various pixel aspect ratios
without distortion because it attempts to automatically display them with the pixel aspect ratio of your project. You
may occasionally encounter a distorted clip if Adobe Premiere Elements interprets pixel aspect ratio incorrectly; if this
happens, you can correct the distortion by manually specifying the source clip’s pixel aspect ratio.
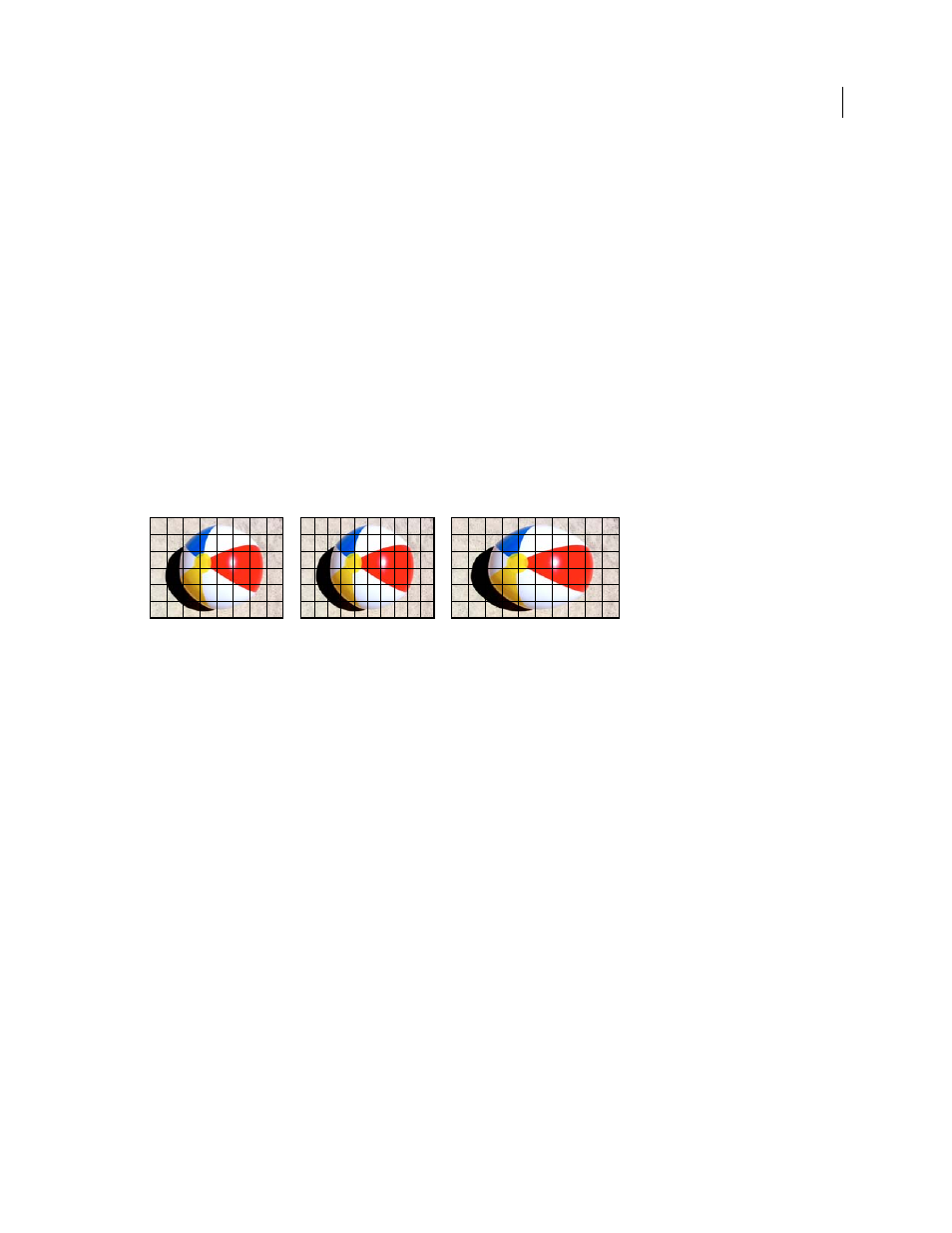
Pixel and frame aspect ratios
A. Square pixels and 4:3 frame aspect ratio B. Nonsquare pixels and 4:3 frame aspect ratio C. Nonsquare pixels displayed uncorrected on a
square-pixel monitor
Capturing or adding various aspect ratios
Adobe Premiere Elements attempts to automatically compensate for pixel aspect ratios and preserve the frame size of
added images. Images that you add are treated in the following ways:
•
When you capture or add video at either the D1 resolution of 720 x 486 or the DV resolution of 720 x 480,
Adobe Premiere Elements automatically sets the pixel aspect ratio for that file to D1/DV NTSC (0.9). When you
add footage at the D1 or DV resolution of 720 x 576, Adobe Premiere Elements automatically sets the pixel aspect
ratio for that file to D1/DV PAL (1.067). However, it is always a good idea to make sure that all files are interpreted
correctly by looking in the Media view or the Interpret Footage dialog box.
•
Adobe Premiere Elements automatically assigns pixel aspect ratios to files by using the entries in the Interpretation
Rules.txt file, which is located in the Adobe Premiere Elements/Plug-ins folder. If a specific type of image is
consistently misinterpreted (distorted) when you add it, you can add or change the entries in the Interpretation
Rules.txt file by using a text editor, such as Notepad. If you want to override the pixel aspect ratio interpretation for
files already in a project, use the Interpret Footage command.
•
If you want to change the size of a clip in Adobe Premiere Elements and its pixel aspect ratio is correct, select the
clip and change the Scale property of the Motion effect. The Motion effect is available in the Properties view with
the clip selected in the Timeline or Sceneline.
A B
C