3 basic qos model, 3 basic qos model -132 – PLANET WGSW-52040 User Manual
Page 210
transmission bandwidth, IP provide bandwidth service by the best effort. This is acceptable for
services like Mail and FTP, but for increasing multimedia business data and e-business data
transmission, this best effort method cannot satisfy the bandwidth and low-lag requirement.
Based on differentiated service, QoS specifies a priority for each packet at the ingress. The
classification information is carried in Layer 3 IP packet header or Layer 2 802.1Q frame
header. QoS provides same service to packets of the same priority, while offers different
operations for packets of different priority. QoS-enabled switch or router can provide different
bandwidth according to the packet classification information, and can remark on the
classification information according to the policing policies configured, and may discard some
low priority packets in case of bandwidth shortage.
If devices of each hop in a network support differentiated service, an end-to-end QoS solution
can be created. QoS configuration is flexible, the complexity or simplicity depends on the
network topology and devices and analysis to incoming/outgoing traffic.
23.1.3 Basic QoS Model
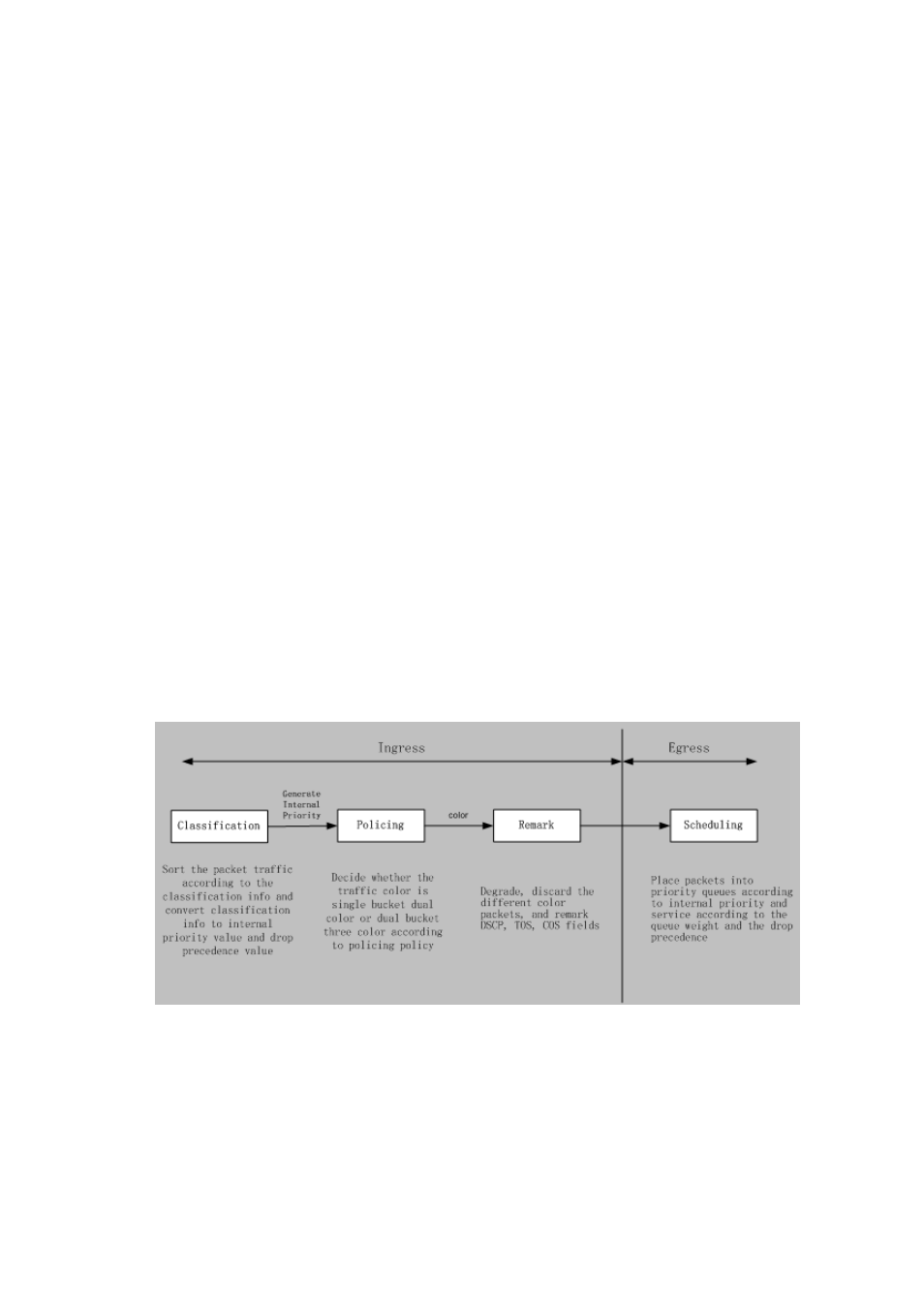
The basic QoS consists of four parts: Classification, Policing, Remark and Scheduling, where
classification, policing and remark are sequential ingress actions, and Queuing and
Scheduling are QoS egress actions.
Figure 23-3: Basic QoS Model
Classification: Classify traffic according to packet classification information and generate
internal priority and drop precedence based the classification information. For different packet
types and switch configurations, classification is performed differently; the flowchart below
explains this in detail.
23-132