4 the encapsulation of eap attributes, 4 the encapsulation of eap attributes -140 – PLANET WGSW-52040 User Manual
Page 361
Identifier: to assist matching the Request and Response messages.
Length: the length of the EAP packet, covering the domains of Code, Identifier, Length and
Data, in byte.
Data: the content of the EAP packet, depending on the Code type.
42.1.4 The Encapsulation of EAP Attributes
RADIUS adds two attribute to support EAP authentication: EAP-Message and
Message-Authenticator. Please refer to the Introduction of RADIUS protocol in
“AAA-RADIUS-HWTACACS operation” to check the format of RADIUS messages.
1. EAP-Message
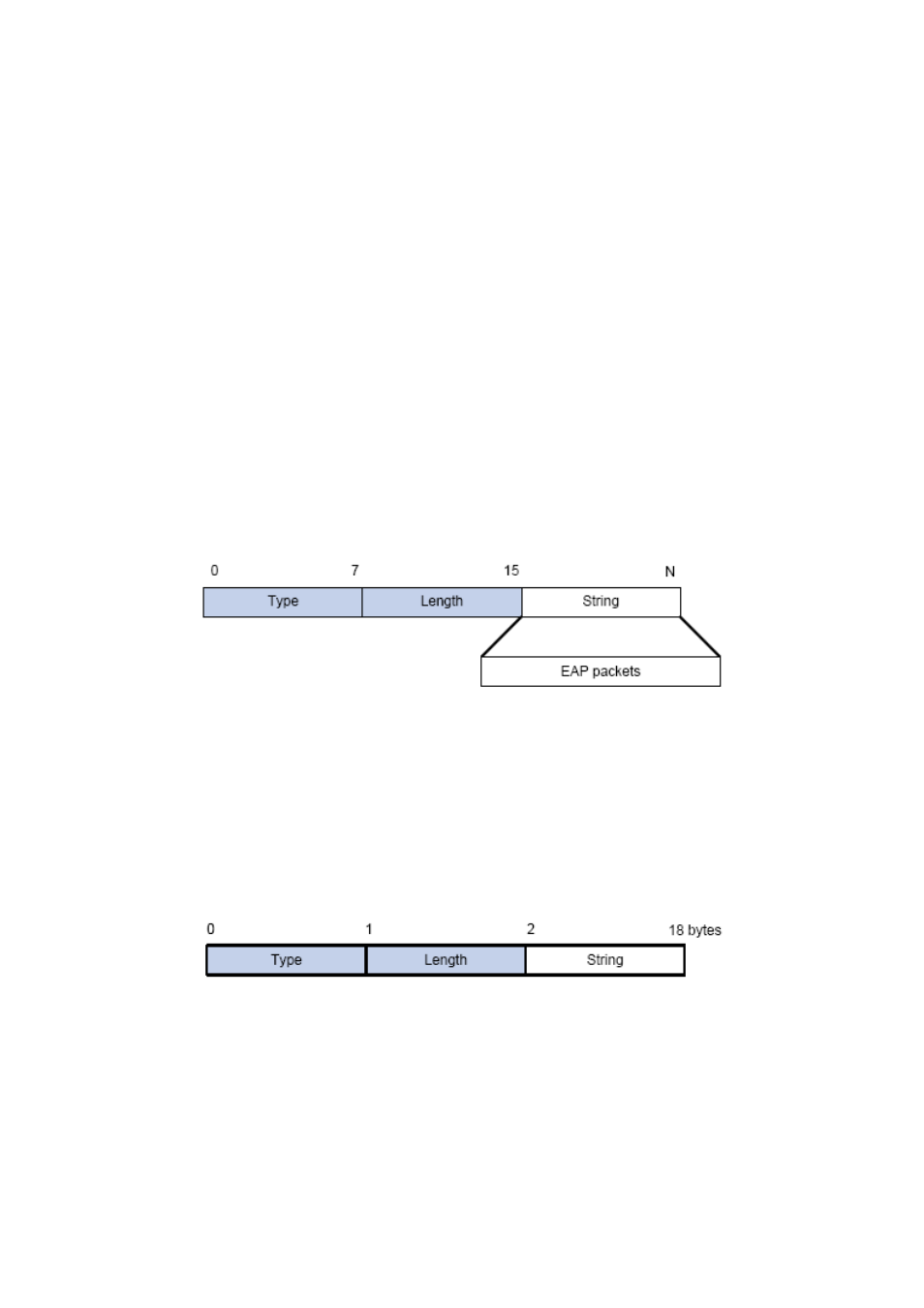
As illustrated in the next figure, this attribute is used to encapsulate EAP packet, the type code
is 79, String domain should be no longer than 253 bytes. If the data length in an EAP packet is
larger than 253 bytes, the packet can be divided into fragments, which then will be
encapsulated in several EAP-Messages attributes in their original order.
Figure 42-6: the Encapsulation of EAP-Message Attribute
2. Message-Authenticator
As illustrated in the next figure, this attribute is used in the process of using authentication
methods like EAP and CHAP to prevent the access request packets from being eavesdropped.
Message-Authenticator should be included in the packets containing the EAP-Message
attribute, or the packet will be dropped as an invalid one.
Figure 42-7: Message-Authenticator Attribute
42-140