Chapter 11 vhdl tutorials, Verifying a slave dut – Altera Mentor Verification IP Altera Edition AMBA AXI4-Lite User Manual
Page 335
Mentor Verification IP AE AXI4-Lite User Guide, V10.3
335
April 2014
Chapter 11
VHDL Tutorials
This chapter discusses how to use the Mentor Verification IP Altera Edition master and slave
BFMs to verify slave and master components, respectively.
In the
tutorial, the slave is an on-chip RAM model that is verified using
a master BFM and test program. In the
tutorial, the master issues
simple write and read transactions that are verified using a slave BFM and test program.
Following this top-level discussion of how you verify a master and a slave component using the
Mentor Verification IP Altera Edition is a brief example of how to run Qsys, the powerful
system integration tool in the Quartus II software. This procedure shows you how to use Qsys to
create a top-level DUT environment. For more details on this example, refer to “
Note
Parameters to configure any optional signals, master BFM transaction issuing, and slave
BFM acceptance capability, are set with the Qsys Parameter Editor. See “
” on page 356 for details of the Qsys Parameter Editor.
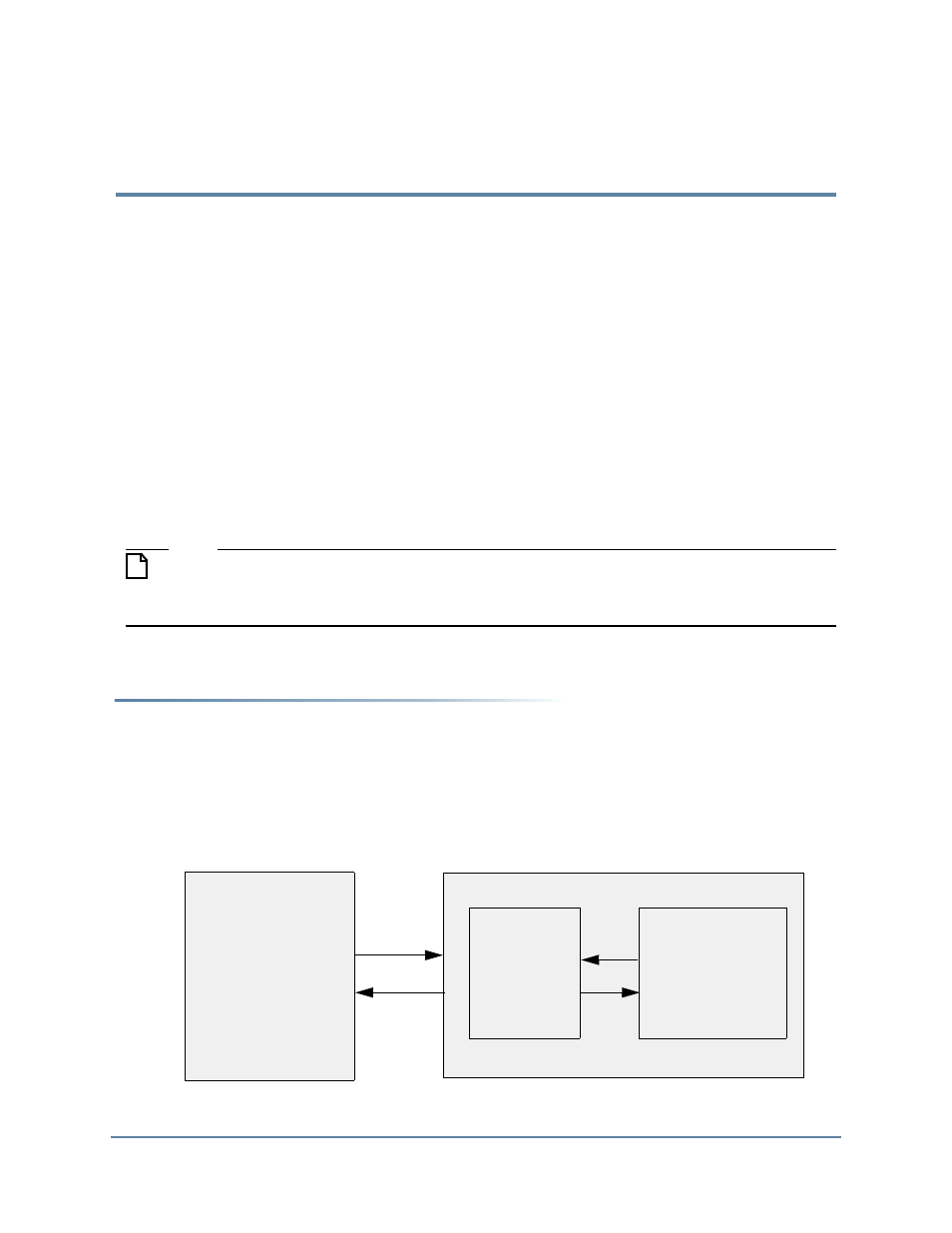
Verifying a Slave DUT
A slave DUT component is connected to a master BFM at the signal-level. A master test
program, written at the transaction-level, generates stimulus via the master BFM to verify the
slave DUT.
illustrates a typical top-level test bench environment.
Figure 11-1. Slave DUT Top-Level Test Bench Environment
Master
BFM
On-chip
RAM slave
Master test program
Top-level file