Subway wlan mesh deployment, Wlan mesh security, Mesh link metric – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 184
172
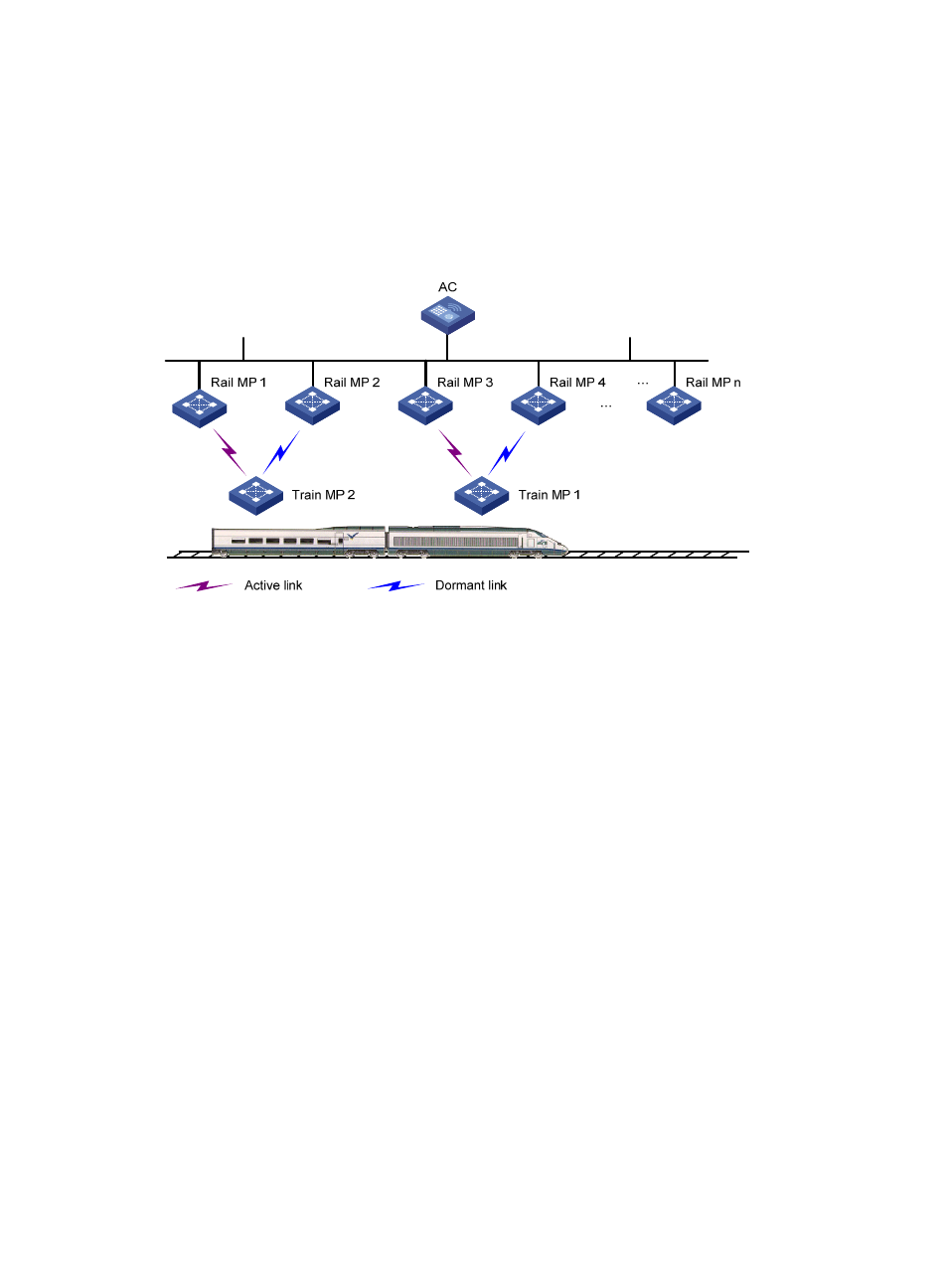
Subway WLAN mesh deployment
In a subway system, the control and data information must be sent to fast-moving trains in real time to
provide Internet access service for customers in the trains and provide control information for train
operation. As shown in
, a subway WLAN mesh solution adopts the AC + Rail MP (in fit mode)
+ Train MP (fat mode) networking mode. Rail MPs are deployed along the railway and connected to the
AC through wired connections.
Figure 89 Subway deployment of mesh
The train MPs connect to rail MPs based on the radio signal strength indicator (RSSI) values. A train MP
establishes with rail MPs two types of links (active and dormant), in which, one link is the active and all
the other links are dormant. Data is transferred through the active link only. The active link changes
during the movement of the train MP.
The subway WLAN mesh deployment uses the Mobile Link Switch Protocol (MLSP), a proprietary
protocol developed by H3C for obtaining high-speed link switch with zero packet loss during train
movement. H3C has adopted new IEEE standard 802.11s as the underlying protocol for link formation
and communication between mobile radio (MR) and wayside AP. Train MPs are not required to act as
authenticators.
WLAN mesh security
WLAN mesh networks use airwaves as a communication medium, so they are very vulnerable to attacks.
Therefore, security is an essential part of WLAN mesh networks. Security involves encryption algorithms
and key distribution and management.
Mesh link metric
The metric of a mesh link is calculated based on the signal strength indication (RSSI) of the frame received
from the peer MP. The metric or cost of the mesh link is used to select the best route to forward data
frames.