5 pd control (pd), 1 ) operation – Yaskawa MP900 Series Ladder Programming Manual User Manual
Page 219
5.8 DDC Instructions
5.8.5 PD Control (PD)
5-150
5.8.5 PD Control (PD)
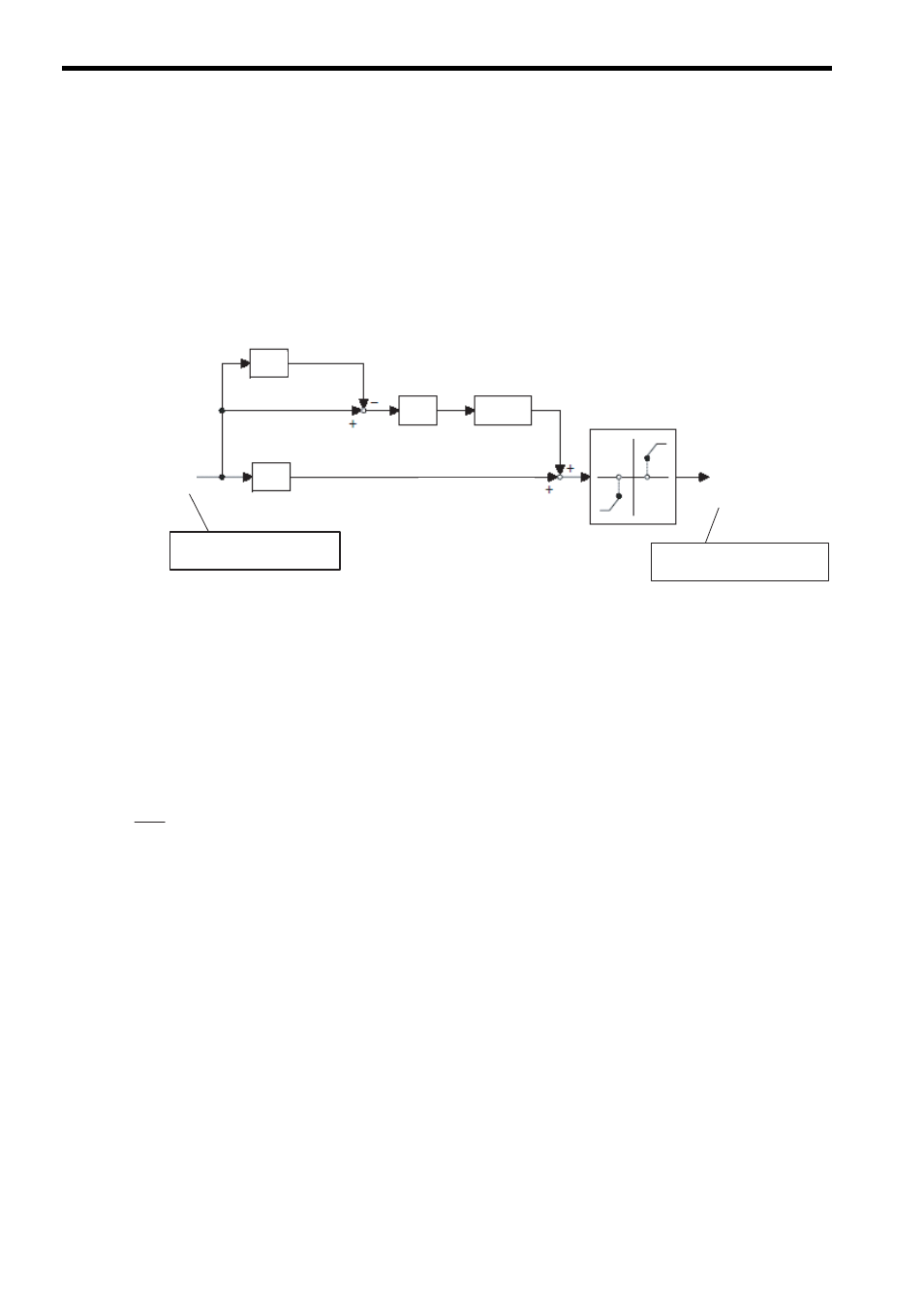
( 1 ) Operation
When deviation X is input, the PD instruction performs P and D operations and a range operation based on predefined
parameters in a parameter table, and outputs the result as compensation Y.
The input value to the PD instruction can be an integer or a real number. Double-length integers cannot be used.
The structure of the parameter table is different for integers and real numbers.
∗ The differential time (Td) changes based on the relationship between the change in the deviation input (X – X’)
and the previous deviation input (X’) as follows:
If the change in the deviation input (X – X’) and the previous deviation input (X’) have the same sign
(divergence)
→ Td = Td1 (differential time for divergence)
If the change in the deviation input (X – X’) and the previous deviation input (X’) have different signs (con-
vergence)
→ Td = Td2 (differential time for convergence)
The operation of the PD instruction can be expressed by the following formula, where X (s) is the input value and Y (s)
is the output value.
= Kp + Kd
× Td × S
Deviation X
Compensation Y
(PD output)
PD Compensation Value Range Operation
(Upper/Lower Limit + Dead Zone A)
P compensation
D compensation
RCHK
+ DZA
Previous input value
X'
Kp
Kd
Td/Ts
Differential (D) operation*
Input value for PD instruction
Output value for PD instruction
Kp: P (proportional) gain
Kd: D (differential) gain
Ts: Scan time
Td: Differential time
Y(s)
X(s)