Watson-Marlow MM440 User Manual
Page 252
3 Functions
Issue 10/06
MICROMASTER 440 Operating Instructions
252
6SE6400-5AW00-0BP0
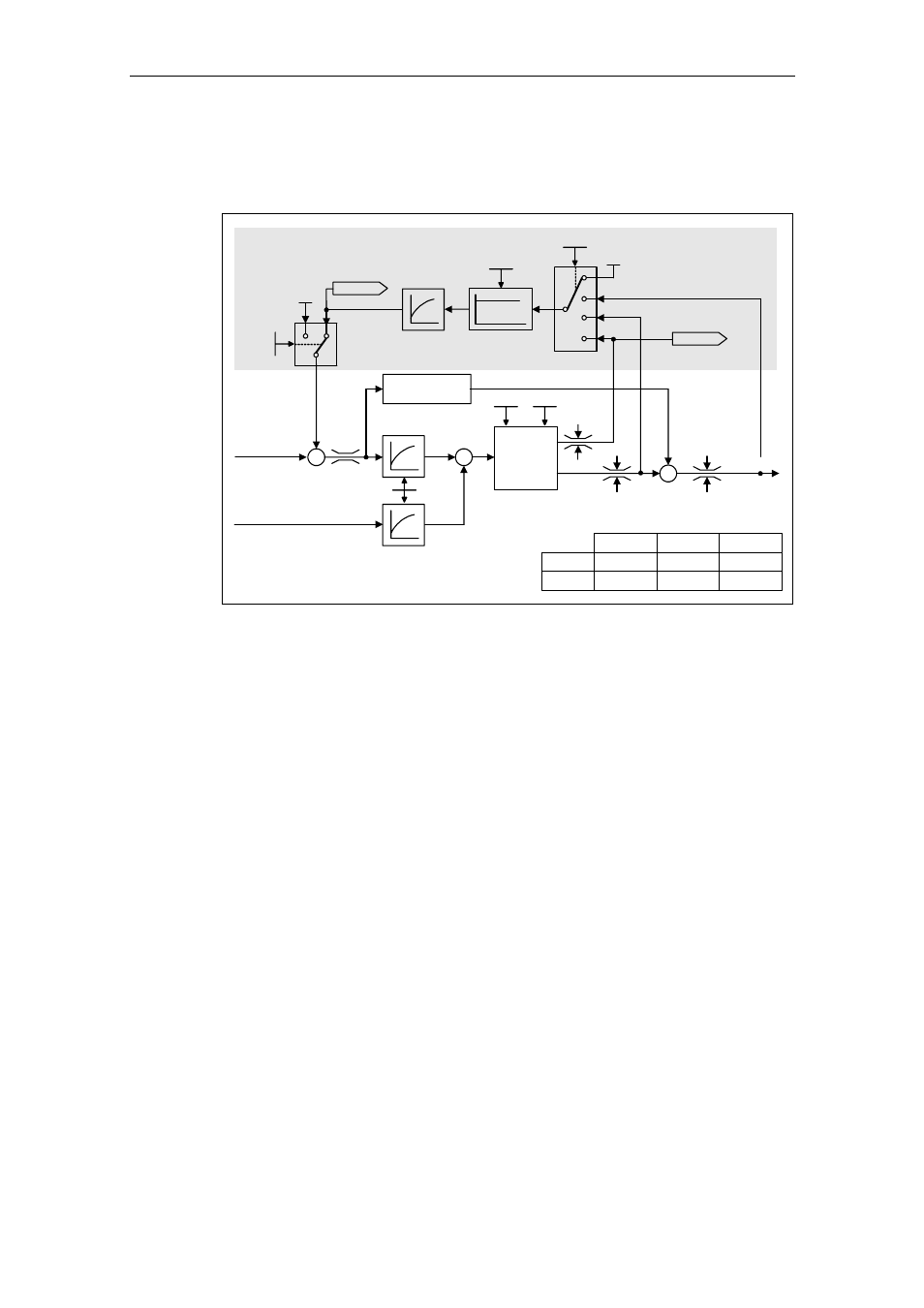
Droop (P1488 – P1492)
The droop (enabled using P1488) means that with increasing load torque, the
speed setpoint is proportionally reduced.
–
–
Pre-
control
PI
Speed
controller
r1538
r1539
0
2
1
3
0
0
1
0
r1538
r1539
r1538
r1539
Torque
setpoint
P1492
P1489
P1488
r1482
r1490
Droop
150 ms
SLVC:
VC:
P1452
P1442
P1470
P1460
P1472
P1462
T
i
K
p
T
n
T
i
K
p
T
n
Act. frequency
Freq. setpoint
*)
*) only active if the pre-control is activated
(P1496 > 0)
Fig. 3-107
Speed controller with droop
Droop is the simplest method to implement load sharing control. However, this load
sharing control can only be used if the drives only motor and are operated more or
less under steady-state conditions (i.e. at constant speed). For drives, which are
frequently accelerated and braked with high speed changes, this technique is only
conditionally suitable.
The most simple load sharing control is, e.g., used for applications where two or
several motors are mechanically coupled or operate on a common shaft and which
have to fulfill the requirements above. In this case, the droop controls torsional
stressing associated with the mechanical coupling by changing the speeds of the
individual motors (excessive torques are reduced for an individual drive).
Prerequisite
¾
All of the drives must be operated with closed-loop Vector speed control (with or
without speed actual value encoder)
¾
The ramp-up and ramp-down times of the ramp-function generator must be
identical for all of the drives.