Example – Watson-Marlow MM440 User Manual
Page 69
Issue 10/06
3 Functions
MICROMASTER 440 Operating Instructions
6SE6400-5AW00-0BP0
69
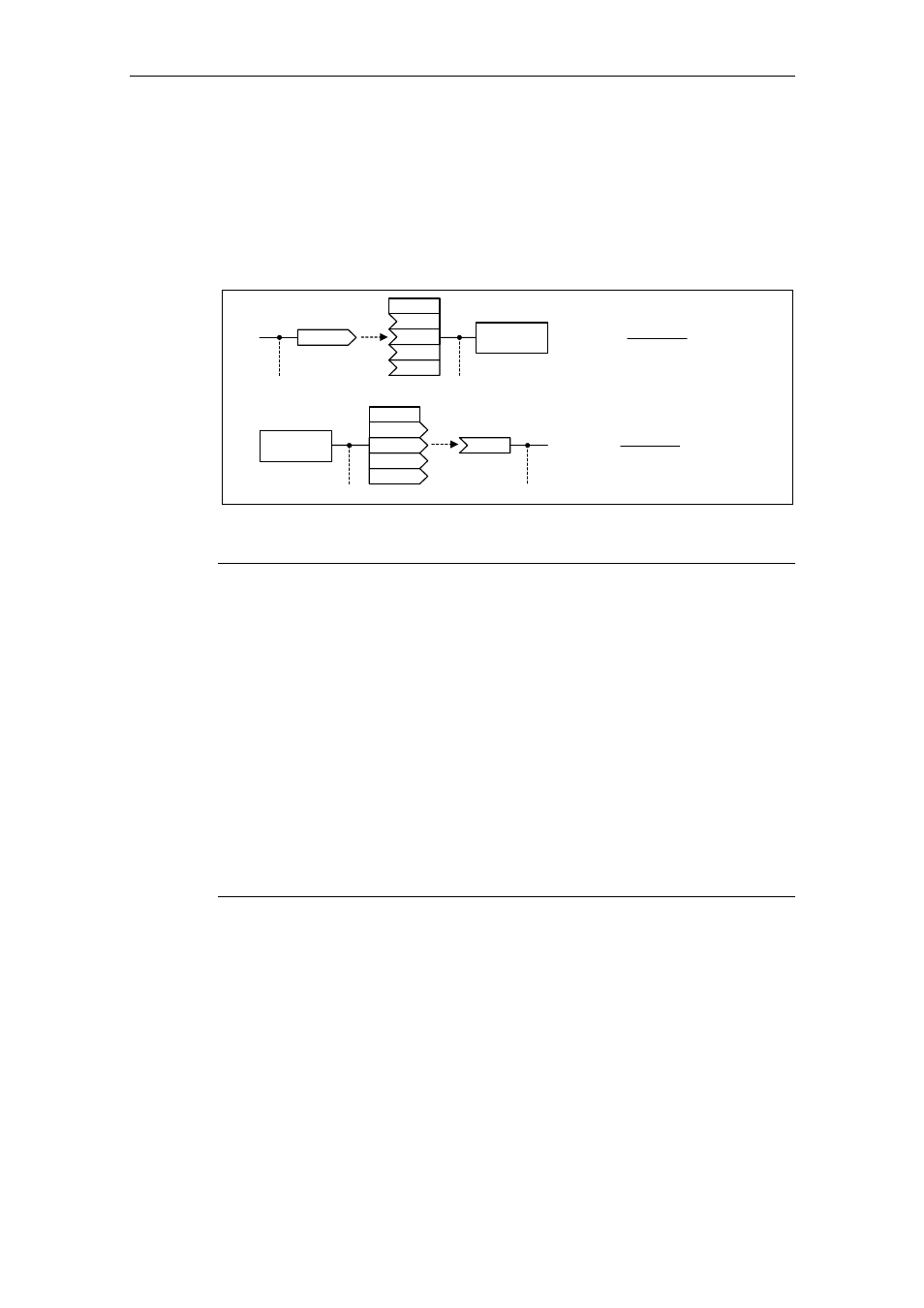
Example
Using the reference frequency P2000 as example, normalization / de-normalization
is demonstrated via the serial interface "USS at BOP link".
If the connection between two BICO parameters is closed (directly using the BICO
parameters or indirectly using P0719 or P1000), that have different representation
types (normalized representation (hex) or physical representation (Hz)), then in the
frequency inverter, the following normalization is made to the target value:
P1070
y[Hz]
2000
P
4000[Hex]
r2015[1]
y[Hz]
⋅
=
r2015
[0]
[1]
[2]
[3]
P2016
[0]
[1]
[2]
[3]
r0021
x[Hz]
y[Hex]
x[Hex]
]
Hex
[
4000
P2000[Hz]
r0021[Hz]
y[Hex]
⋅
=
USS-PZD
BOP link
USS-PZD
BOP link
Fig. 3-13
Normalization / de-normalization
Note
¾
Analog values are limited to 10 V or 20 mA. A maximum of 100 % referred to
the corresponding reference values can be output / entered as long as no
DAC/ADC scaling is made (factory setting).
¾
Setpoints and actual value signals via serial interface:
♦ When transferring using the PZD part, they are limited to the value 7FFF h.
This is the reason that the maximum value is 200 % referred to the reference
value.
♦ When transferring data using the PKW part, they are transferred dependant
on the data type and the units.
¾
Parameter P1082 (max. frequency) limits the frequency in the frequency
inverter independent of the reference frequency. When changing P1082
(factory setting: 50 Hz), this is the reason that P2000 should always be
adapted (factory setting: 50 Hz). If, e.g. for a NEMA motor, the parameter is set
to 60 Hz, and no changes are made regarding P2000, then the analog setpoint
/ actual value is limited to 100 % or a setpoint / actual value signal at 4000 h is
limited to 50 Hz!