Configuring remote snmpv3 users, Figure 226: showing local snmpv3 users, Configuring – Microsens MS453490M Management Guide User Manual
Page 386
C
HAPTER
15
| Basic Administration Protocols
Simple Network Management Protocol
– 386 –
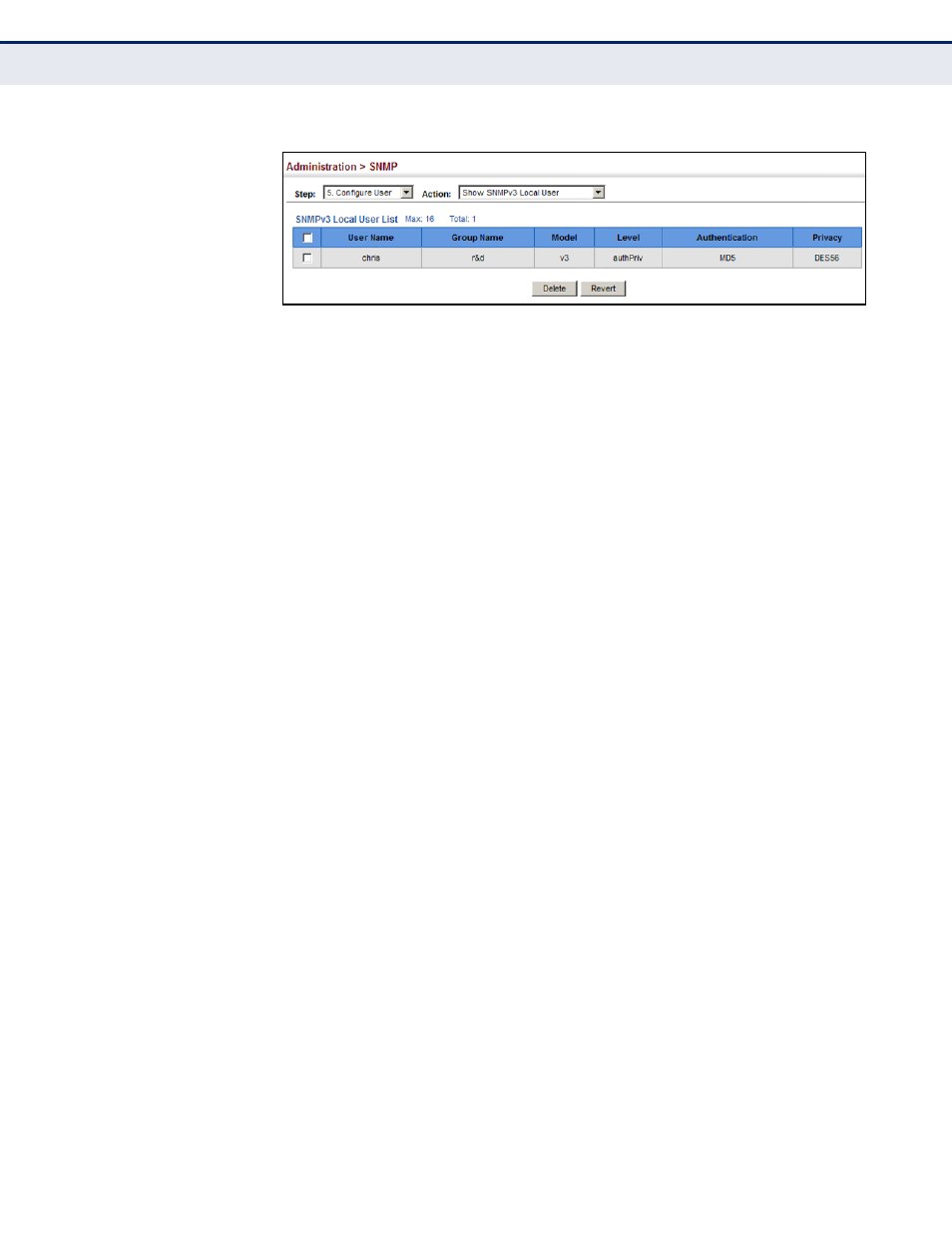
Figure 226: Showing Local SNMPv3 Users
C
ONFIGURING
R
EMOTE
SNMP
V
3 U
SERS
Use the Administration > SNMP (Configure User - Add SNMPv3 Remote
User) page to identify the source of SNMPv3 inform messages sent from
the local switch. Each SNMPv3 user is defined by a unique name. Users
must be configured with a specific security level and assigned to a group.
The SNMPv3 group restricts users to a specific read, write, and notify view.
CLI R
EFERENCES
◆
"snmp-server user" on page 565
C
OMMAND
U
SAGE
◆
To grant management access to an SNMPv3 user on a remote device,
you must first specify the engine identifier for the SNMP agent on the
remote device where the user resides. The remote engine ID is used to
compute the security digest for authentication and encryption of
packets passed between the switch and the remote user. (See
"Specifying Trap Managers" on page 389
and
.)
P
ARAMETERS
These parameters are displayed:
◆
User Name – The name of user connecting to the SNMP agent.
(Range: 1-32 characters)
◆
Group Name – The name of the SNMP group to which the user is
assigned. (Range: 1-32 characters)
◆
Remote IP – The Internet address of the remote device where the
user resides.
◆
Security Model – The user security model; SNMP v1, v2c or v3.
(Default: v3)
◆
Security Level – The following security levels are only used for the
groups assigned to the SNMP security model:
■
noAuthNoPriv – There is no authentication or encryption used in
SNMP communications. (This is the default security level.)
■
AuthNoPriv – SNMP communications use authentication, but the
data is not encrypted.