Figure 285: mvr concept – Microsens MS453490M Management Guide User Manual
Page 464
C
HAPTER
18
| Multicast Filtering
Multicast VLAN Registration
– 464 –
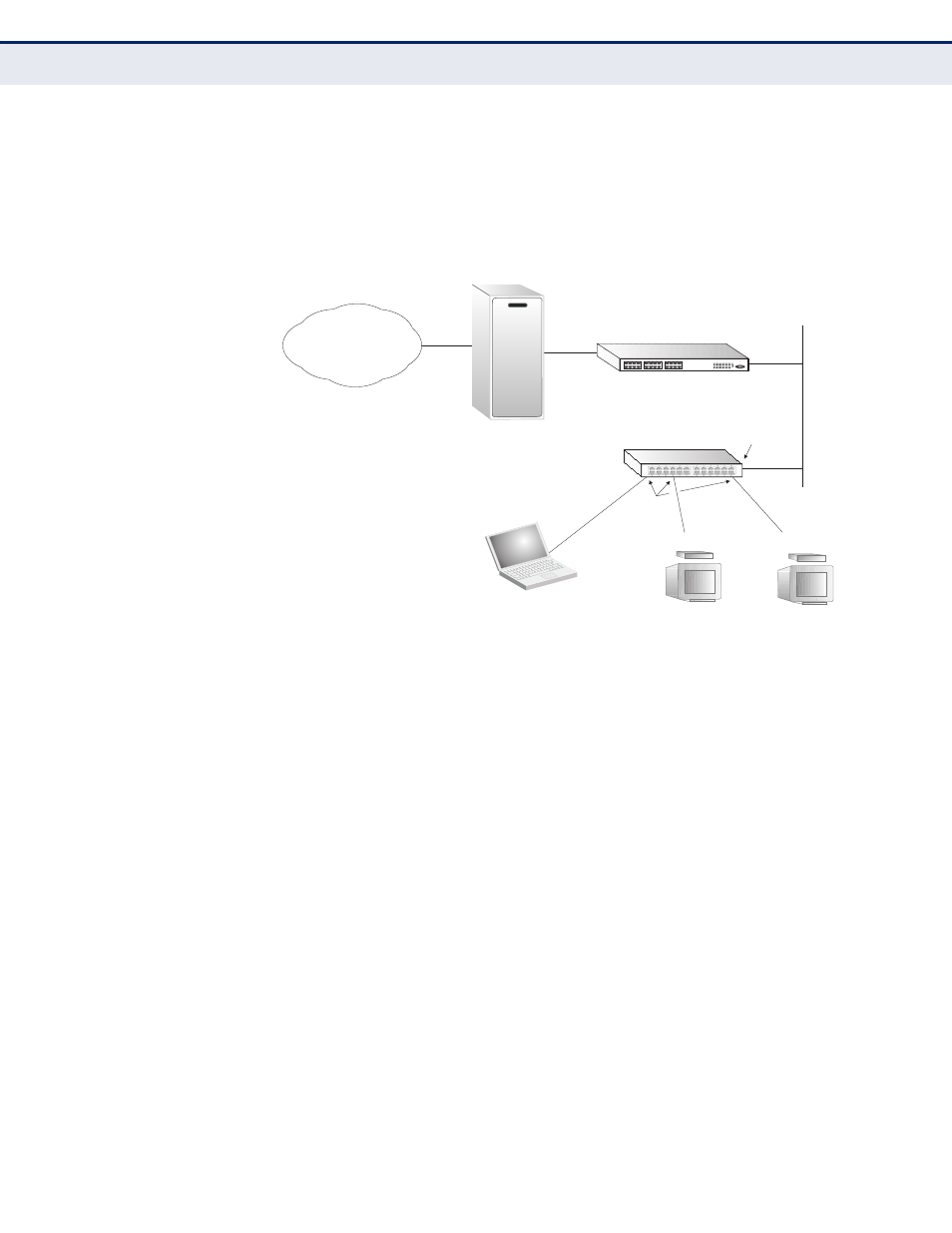
MVR maintains the user isolation and data security provided by VLAN
segregation by passing only multicast traffic into other VLANs to which the
subscribers belong. Even though common multicast streams are passed
onto different VLAN groups from the MVR VLAN, users in different IEEE
802.1Q or private VLANs cannot exchange any information (except through
upper-level routing services).
Figure 285: MVR Concept
C
OMMAND
U
SAGE
◆
General Configuration Guidelines for MVR:
1.
Enable MVR globally on the switch, select the MVR VLAN, and add
the multicast groups that will stream traffic to attached hosts (see
"Configuring Global MVR Settings" on page 465
2.
Set the interfaces that will join the MVR as source ports or receiver
ports (see
"Configuring MVR Interface Status" on page 466
3.
For multicast streams that will run for a long term and be associated
with a stable set of hosts, you can statically bind the multicast
group to the participating interfaces (see
Groups to Interfaces" on page 468
◆
Although MVR operates on the underlying mechanism of IGMP
snooping, the two features operate independently of each other. One
can be enabled or disabled without affecting the behavior of the other.
However, if IGMP snooping and MVR are both enabled, MVR reacts only
to join and leave messages from multicast groups configured under
MVR. Join and leave messages from all other multicast groups are
managed by IGMP snooping. Also, note that only IGMP version 2 or 3
hosts can issue multicast join or leave messages.
Multicast Router
Layer 2 Switch
Multicast Server
PC
TV
Set-top Box
TV
Set-top Box
Satellite Services
Service
Network
Source
Port
Receiver
Ports