1 overview – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 17
1
1 Overview
As an IMC service component, EAD Security Policy (hereinafter referred to as EAD) works with the IMC
UAM component to provide endpoint security checking and asset management. It plays an essential role
in both the HP EAD solution and BYOD solution.
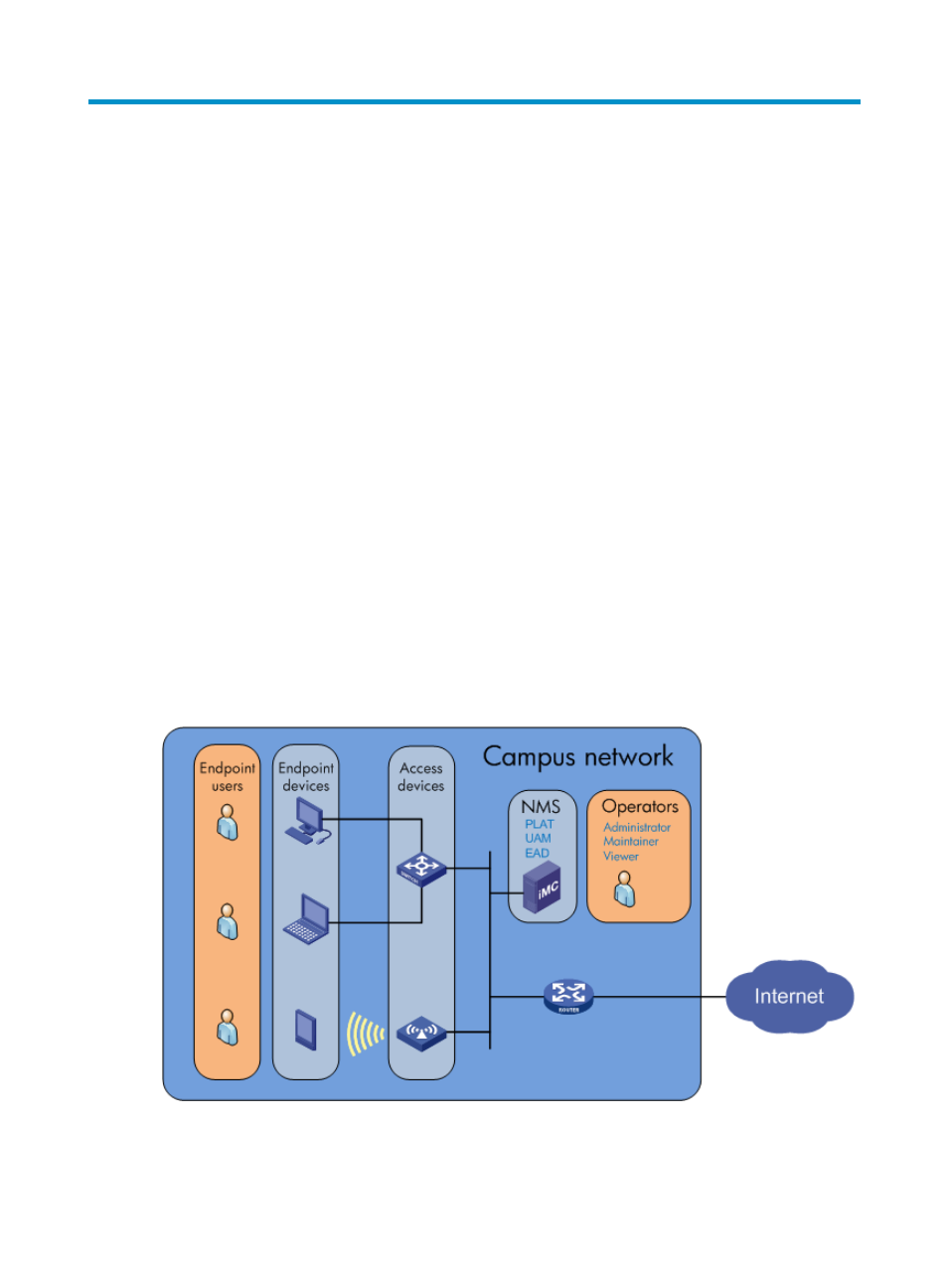
As shown in
, a network deployed with IMC EAD typically has the following elements:
•
UAM server—Server deployed with IMC UAM to provide authentication, authorization, and
accounting services for endpoint users.
•
EAD server—Server deployed with IMC EAD to provide security checking and asset management
for endpoint devices.
•
IMC operator—Depending on the assigned administrative privileges, IMC classifies operators as
administrators, maintainers, and viewers.
•
Access device—Access layer device that works with UAM to provide network access to endpoint
users. Typically, switches with high port density serve as access devices in wired networks, and
access controllers are used as access devices in wireless networks.
•
Endpoint device—Devices used by end user for network access. IMC classifies user endpoints into
PCs and smart devices. PCs include desktop and laptop computers. Smart devices include mobile
phones and tablets.
•
Desktop asset—Windows PC managed as a desktop asset in EAD. Desktop asset management
helps monitor the assets' operating status and usage information.
•
End user—User who accesses the network from an endpoint device by using an access user
account stored in UAM.
Figure 1 Elements involved in a network deployed with EAD