Appendix c mw+ camming 101 – Yaskawa MotionWorks+ Windows Software User Manual
Page 207
MotionWorks+™
Appendix C MW+ Camming 101
201
Appendix C
MW+ Camming 101
1. What is a cam profile?
A cam profile is simply a list of number pairs that describe the relationship of two axes.
The simplest cam table consists of two pairs of points, the beginning, and the end. This
would make a “straight line” relationship, identical to a gearing relationship, where the
gear ratio is the last pair of numbers. A cam profile can be much more complex. It can
consist of thousands of pairs of numbers, describing a mathematical formula, such as a
sine wave, or any arbitrary relationship that best applies to the process. With a cam table
in place, the servo can be precisely positioned at every step along the machine cycle. The
possibilities are almost limitless, the slave can match speed, accelerate ahead of the mas-
ter, remain motionless for a time, or move backwards; all speeds dictated by the speed of
the master. Most importantly, the cam profile contains position data that synchronizes two
axes, regardless of speed.
2. How are cam profiles created in MW+?
Two ways: either with Cam Tool, or calculated within MW+ blocks.
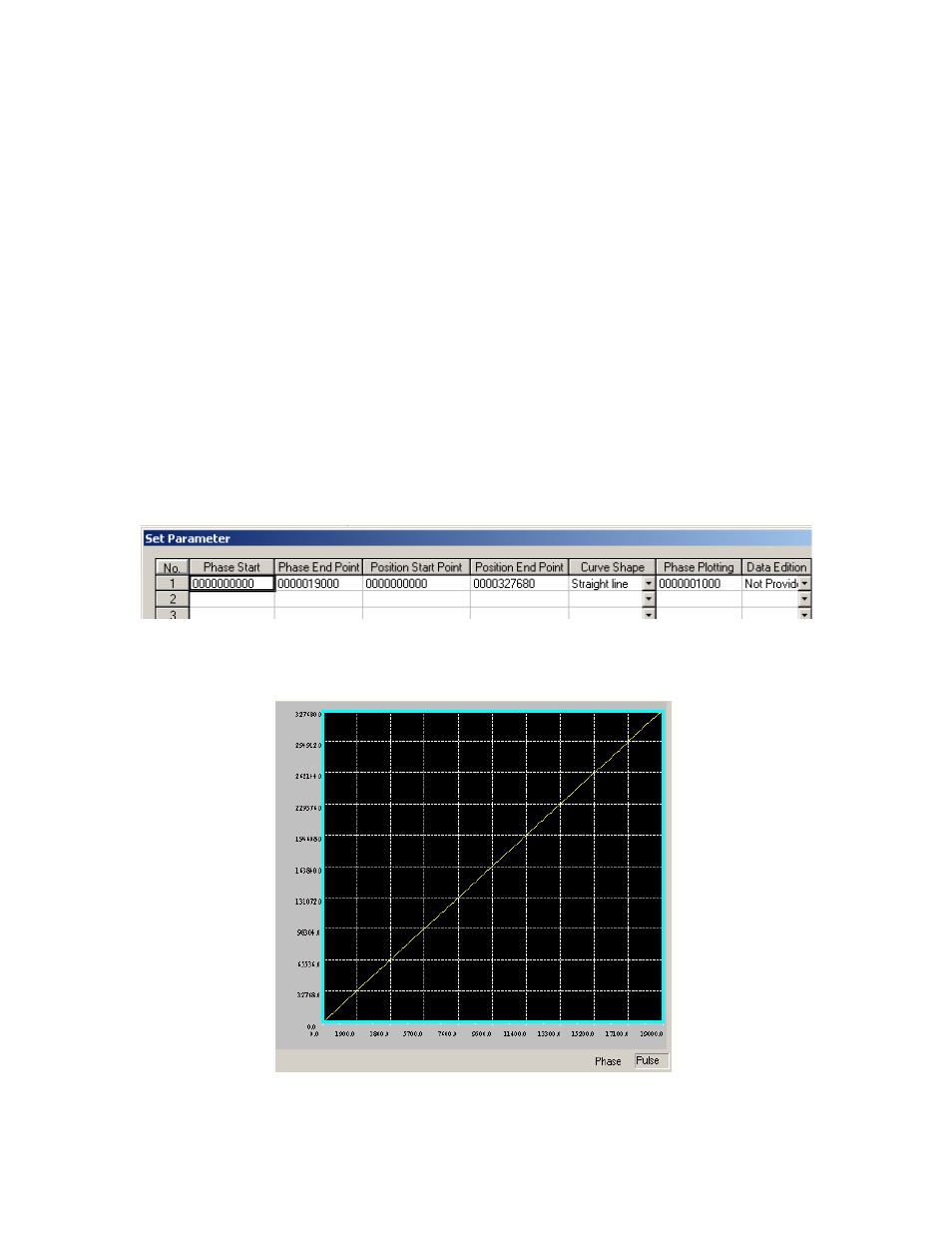
Figure 1: This is a simple profile, with only a straight-line segment.
Figure 2: Cam Tool graph showing the master / slave relationship