3 starting time and stopping time, 4 overhanging loads – Yaskawa Sigma Mini User Manual
Page 176
SERVO SELECTION AND DATA SHEETS
4.3.3 Starting Time and Stopping Time
— 4-26 —
4.3.3 Starting Time and Stopping Time
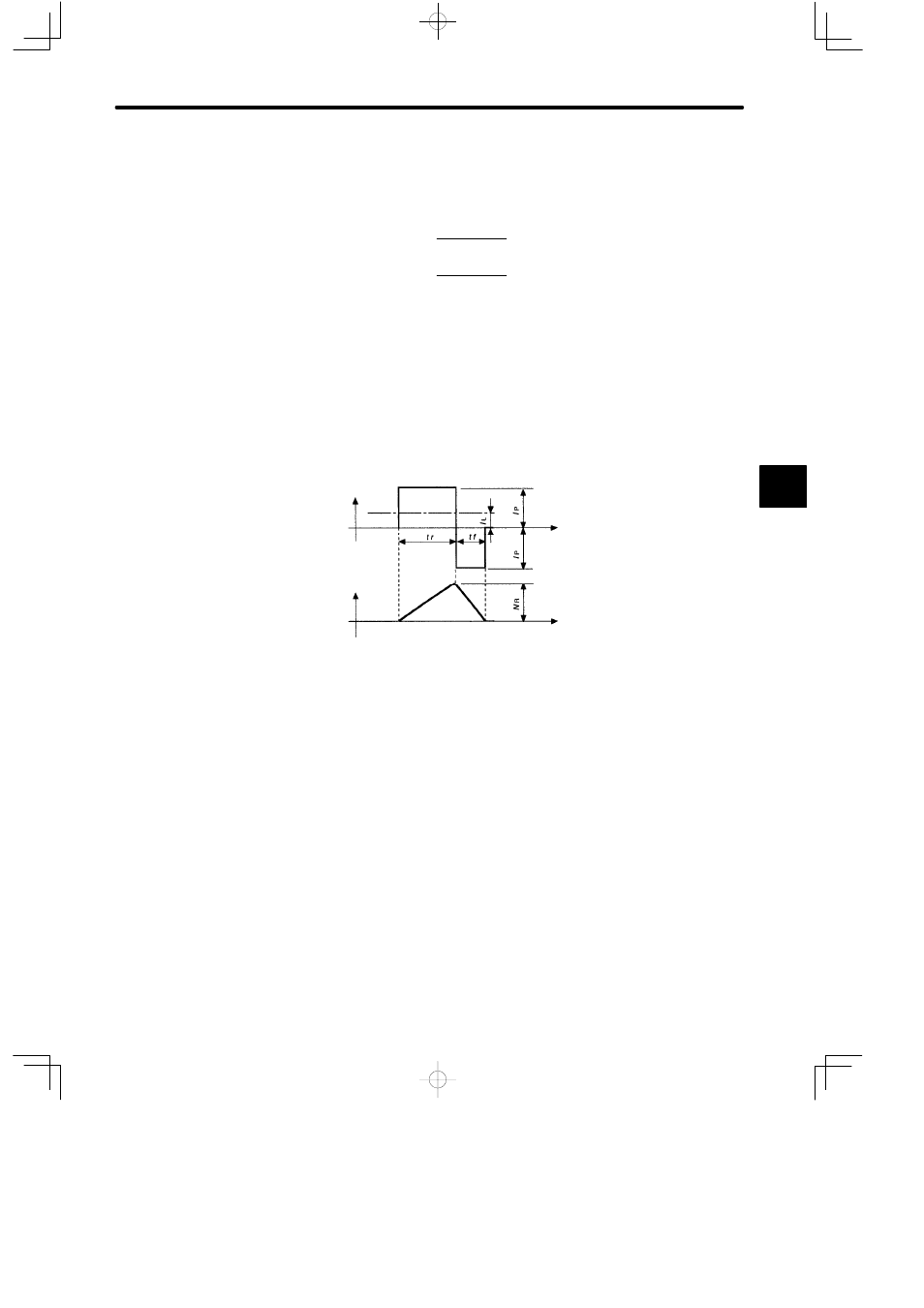
1) The motor starting time (tr) and stopping time (tf) under constant load are calculated by
the following formulas. The motor viscous torque and friction torque are ignored.
Starting Time:
Stopping Time:
tf = 104.7 ×
N
R
(J
M
+ J
L
)
K
t·
I
R
(α–β)
tf = 104.7 ×
N
R
(J
M
+ J
L
)
K
t
·I
R
(α + β)
[ms]
[ms]
N
R
: Motor speed used (min
−1
.)
J
M
: Motor moment of inertia (kg¡m
2
=lb¡in¡s
2
)
(GD
2
M
/4)
. . .
J
L
: Load converted to shaft moment of inertia (kg¡m
2
)
(GD
2
L
/4)
. .
K
t
: Motor torque constant (N¡m/A=lb¡in/A)
I
R
: Motor rated current (A)
α=I
P
/I
R
: Accel/decel current coefficient
[where I
P
is accel/decel current (accel/decel current is α times the motor rated current) (A)]
β=I
L
/I
R
]: Load current coefficient
[I
L
]: Load torque equivalent current (load current is β times the motor rated current) (A)]
Motor Current
Time
Motor Speed
Motor Current (size) - Motor Speed Timing Chart
Time
4.3.4 Overhanging Loads
A Servomotor may not be operated under an overhanging load, that is a load which tends to
continually rotate the motor.
Under an overhanging load (e.g. when the direction of the torque applied by the motor is op-
posite from the direction of shaft rotation), the Servopack regenerative brake is applied con-
tinuously and the regenerative energy of the load may exceed the allowable range and dam-
age the Servopack.
The regenerative brake capacity of the Servopack is rated for short-time operation, approxi-
mately equivalent to the deceleration stopping time.
4