Example – Yaskawa SMC–4000 User Manual
Page 338
328
SMC–4000 User Manual
Example:
An array element number can also be a variable. This allows array entries to be assigned sequentially
using a counter.
Example:
The above example records 10 position values at a rate of one value per 10 msec. The values are stored in
an array named POS. The variable, COUNT, is used to increment the array element counter. The above
example can also be executed with the automatic data capture feature described as follows.
Arrays may be uploaded and downloaded using the QU and QD commands.
QU array[ ],start,end,comma
QD array[ ],start,end
where array is an array name such as A[ ].
Start is the first element of array (default=0)
End is the last element of array (default=last element)
Comma -- if comma is a 1, then the array elements are separated by a comma. If not a 1, then the elements
are separated by a carriage return.
The file is terminated using <control>Z, <control>Q, <control>D or \.
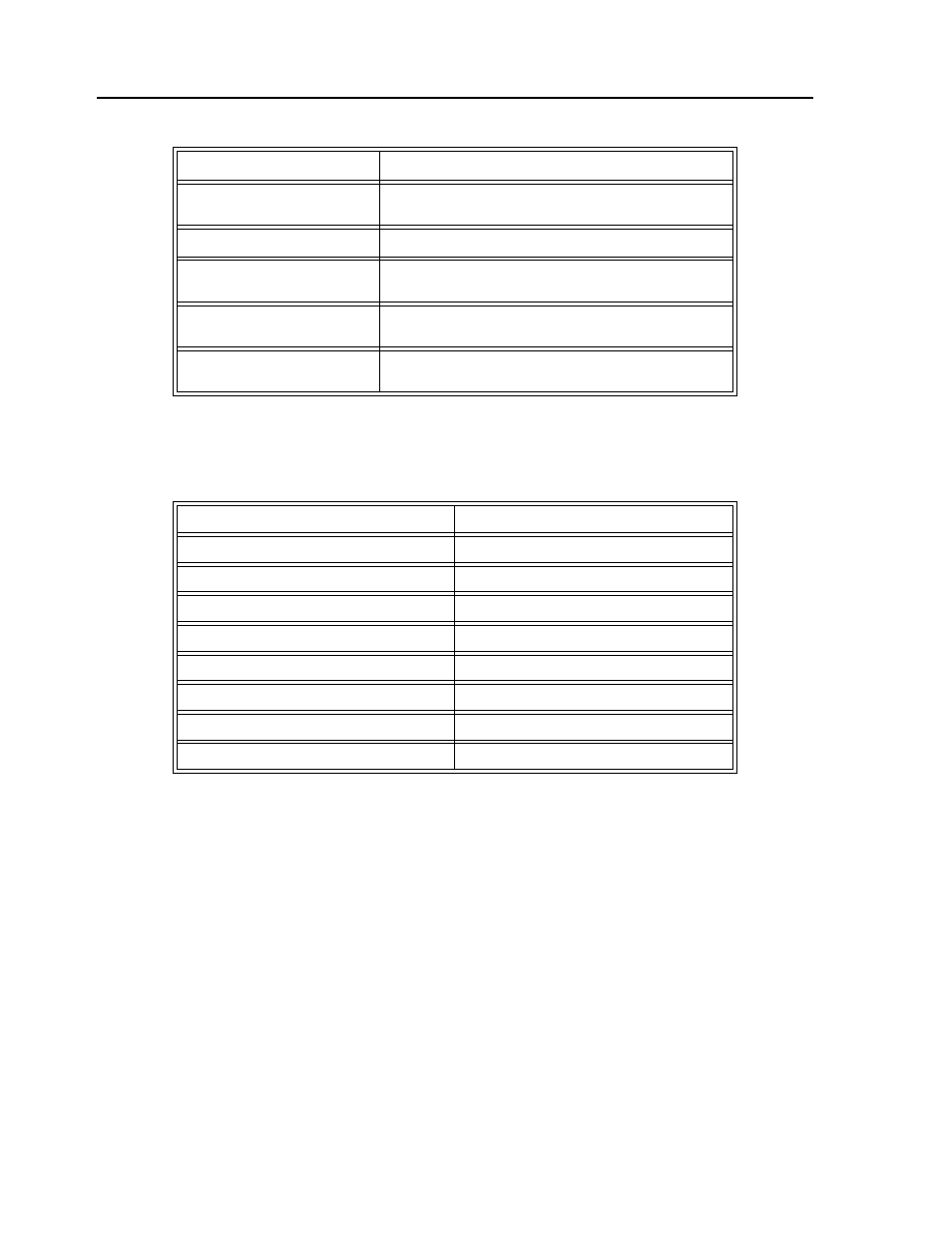
DM SPEED[10]
Dimension Speed Array
SPEED[1]=7650.2
Assigns the first element of the array, SPEED the value
7650.2
SPEED[1]=
Returns array element value
POSX[10]=_TPX
Assigns the 10th element of the array POSX the returned
value from the tell position command.
CON[2]=@COS[POS]*2
Assigns the second element of the array CON the cosine of
the variable POS multiplied by 2.
TIMER[1]=TIME
Assigns the first element of the array timer the returned
value of the TIME keyword.
#A
Begin Program
COUNT=0;DM POS[10]
Initialize counter and define array
#LOOP
Begin loop
WT 10
Wait 10 msec
POS[COUNT]=_TPX
Record position into array element
POS[COUNT]=
Report position
COUNT=COUNT+1
Increment counter
JP #LOOP,COUNT<10
Loop until 10 elements have been stored
EN
End Program