Mlsp advantages, Operation of mlsp, Formation of dormant links – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 325
309
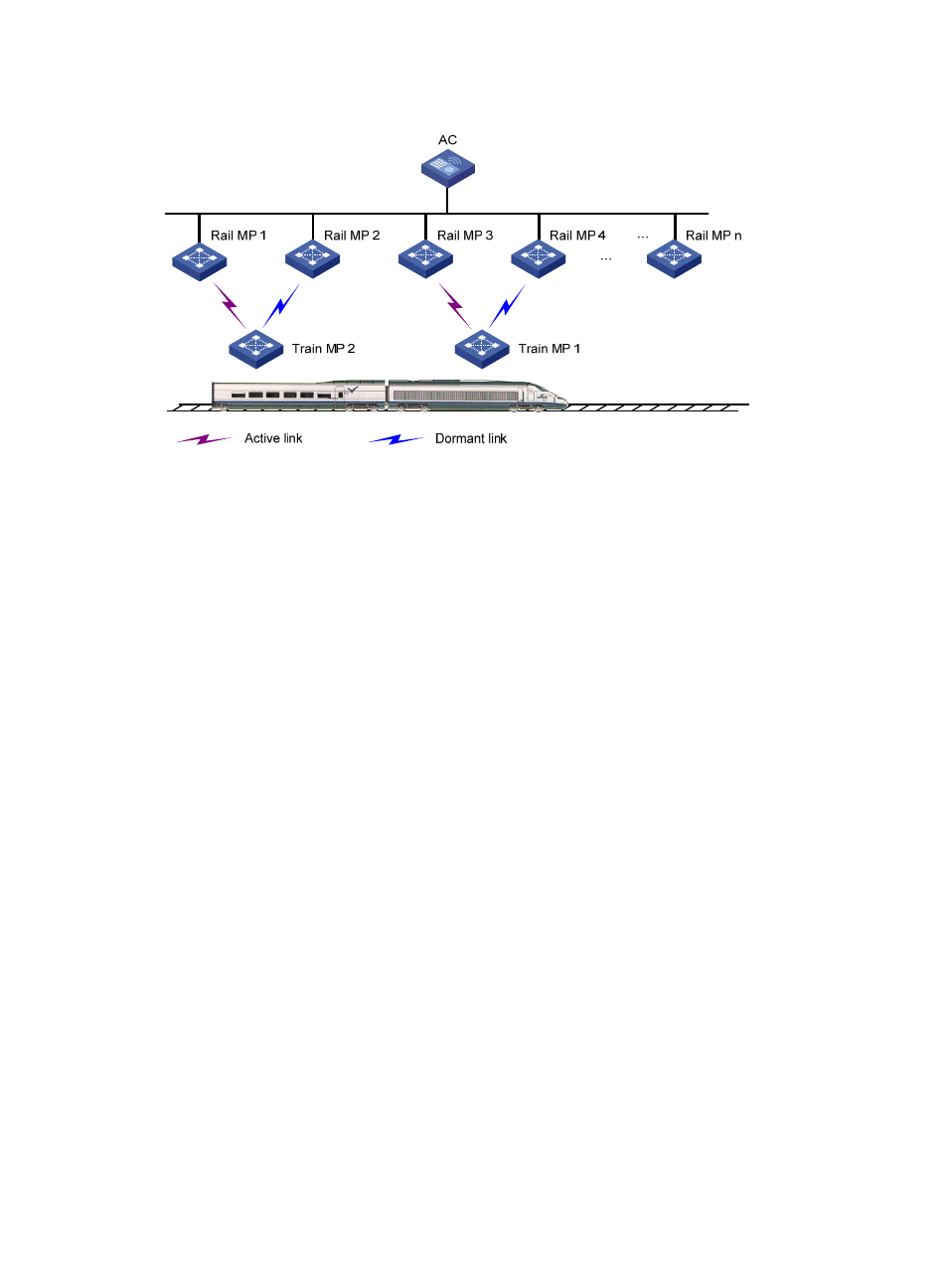
Figure 327 Diagram for MLSP
•
Active Link: Logical link through which all data communication from/to a train MP happens.
•
Dormant Link: Logical link over which no data transfer happens, but it satisfies all the criteria for
becoming an active link.
MLSP advantages
•
MLSP ensures that the link switch time is less than 30 ms.
•
MLSP works well even if the devices get saturated at high power level.
•
MLSP achieves zero packet loss during link switch.
Operation of MLSP
MLSP establishes multiple links at any given time between a train MP and multiple rail MPs to provide link
redundancy, thus ensuring high performance and good robustness for the network.
The following parameters are considered by MLSP for link switch. Based on the deployment, all these
parameters are tunable to achieve best results.
•
Link formation RSSI/link hold RSSI—This is the minimum RSSI to allow a link to be formed and held.
Therefore, the minimum RSSI must be ensured at any given point in the tunnel. Otherwise, the error
rate can be very high.
•
Link switch margin—If the RSSI of the new link is greater than that of the current active link by the
link switch margin, active link switch occurs. This mechanism is used to avoid frequent link switch.
•
Link hold time—An active link remains up within the link hold time, even if the link switch margin is
reached. This mechanism is used to avoid frequent link switch.
•
Link saturation RSSI—This is the upper limit of RSSI on the active link. If the value is reached, link
switch occurs.
Formation of dormant links
A train MP performs active scanning to find neighboring rail MPs by sending probe requests at a very
high rate. Based on probe responses received, the train MP forms a neighbor table.
After that, the train MP creates dormant links with rail MPs that have an RSSI value greater than the link
formation RSSI.