Wireless sniffer, Band navigation – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 582
566
Tag messages by copying all the information (message header and payload inclusive) except the
multicast address, and adding the BSSID, channel, timestamp, data rate, RSSI, SNR and radio
mode of the radio on which the relevant Tag messages were received.
•
Upon receiving MU messages (suppose that the MUs mode has been configured on the AC, and
the location server has notified the AP to report MU messages), the AP checks the messages,
encapsulates those that pass the check and reports the messages to the location server. The AP
encapsulates an MU message by copying its source address, Frame Control field and Sequence
Control field, and adding the BSSID, channel, timestamp, data rate, RSSI, SNR and radio mode of
the radio on which the relevant Tag messages were received.
3.
Calculate the locations of Tags or MUs
After receiving Tag and MU messages from APs, the location server uses an algorithm to calculate
the locations of the Tag and MU devices according to the RSSI, SNR, radio mode and data rate
carried in the messages, and displays the locations on the imported map. Typically, a location
server can calculate the locations as long as more than 3 APs operating in monitor or hybrid report
Tag or MU messages.
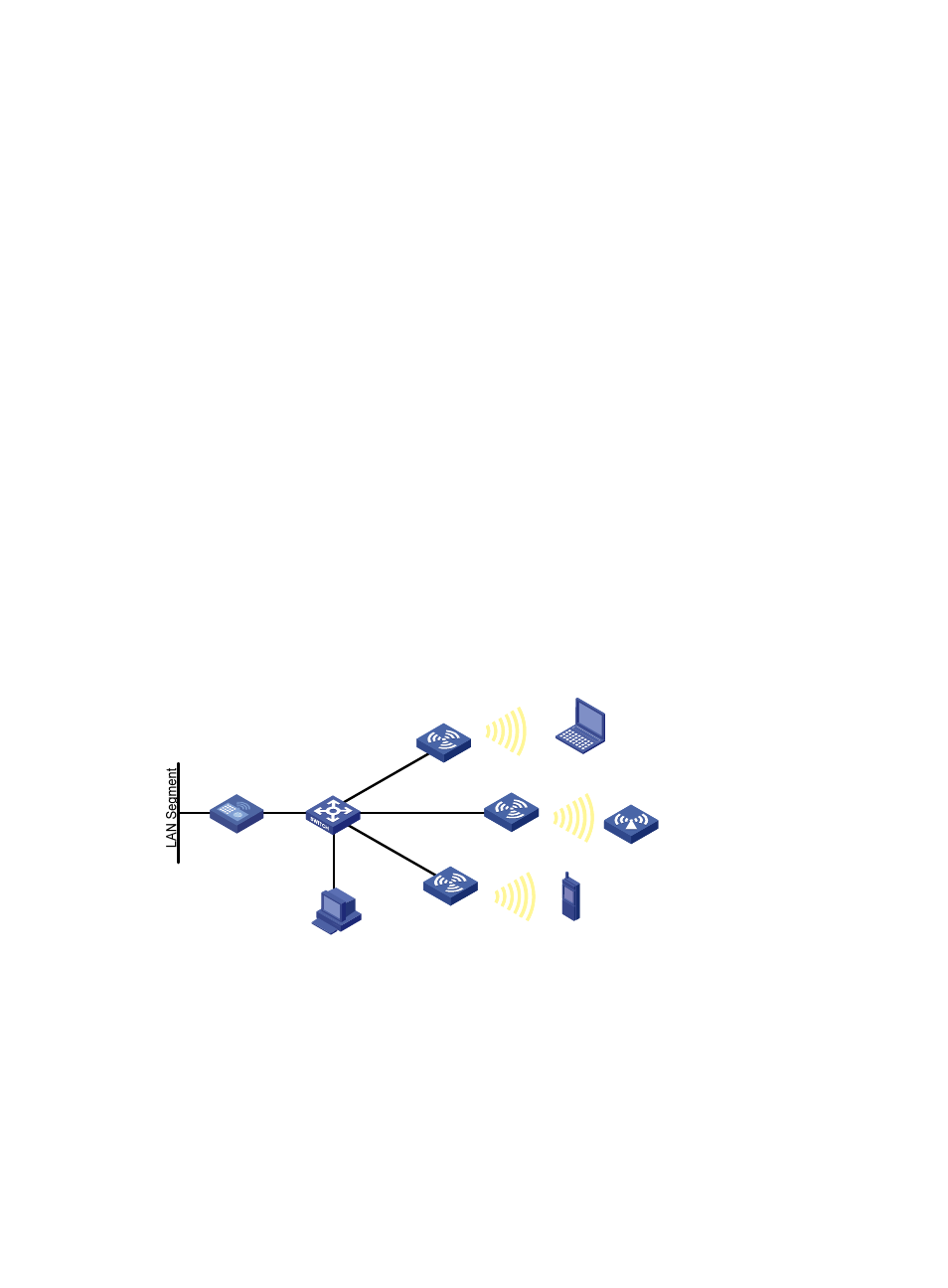
Wireless sniffer
In a wireless network, it is difficult to locate signal interference or packet collision by debugging
information or terminal display information of WLAN devices. To facilitate the troubleshooting, configure
an AP as a packet sniffer to listen to, capture, and record wireless packets. The sniffed packets are
recorded in the .dmp file for troubleshooting.
As shown in
, enable wireless sniffer on the Capture AP. The Capture AP is able to listen to the
wireless packets in the network, including the packets from other APs, rouge APs, and clients.
Administrators can download the .dmp file to the PC and make further analysis.
Figure 596 Network diagram
Band navigation
The 2.4 GHz band is often congested. Band navigation enables APs to accept dual-band (2.4 GHz and
5 GHz) clients on their 5 GHz radio, increasing overall network performance.
When band navigation is enabled, the AP directs clients to its 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio by following
these principles:
•
For a 2.4 GHz client, the AP associates to the client after rejecting it several times.
Switch
Capture AP
AP 1
AP 2
Client
Rogue AP
AC
PDA
PC