Altera Arria 10 Avalon-MM User Manual
Page 144
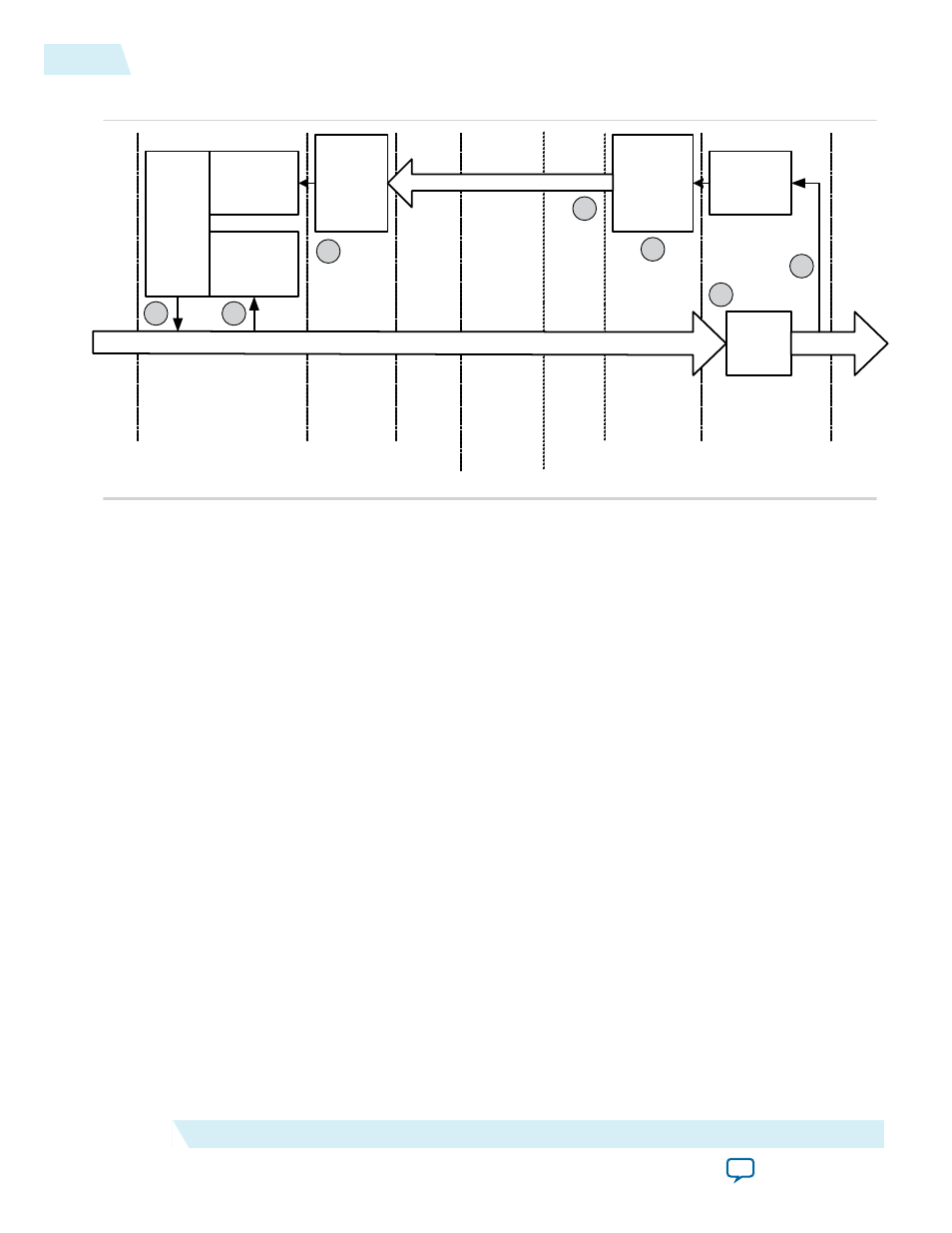
Figure 12-1: Flow Control Update Loop
Credits
Consumed
Counter
Credit
Limit
Data Packet
Flow
Control
Gating
Logic
(Credit
Check)
Allow
Incr
Rx
Buffer
Data Packet
Credit
Allocated
FC
Update
DLLP
Generate
FC
Update
DLLP
Decode
FC Update DLLP
App
Layer
Transaction
Layer
Data Link
Layer
Physical
Layer
Incr
Physical
Layer
Data Link
Layer
Transaction
Layer
App
Layer
Data Source
PCI
Express
Link
Data Sink
1
2
7
6
5
3
4
The following numbered steps describe each step in the Flow Control Update loop. The corresponding
numbers in the figure show the general area to which they correspond.
1. When the Application Layer has a packet to transmit, the number of credits required is calculated. If
the current value of the credit limit minus credits consumed is greater than or equal to the required
credits, then the packet can be transmitted immediately. However, if the credit limit minus credits
consumed is less than the required credits, then the packet must be held until the credit limit is
increased to a sufficient value by an FC Update DLLP. This check is performed separately for the
header and data credits; a single packet consumes only a single header credit.
2. After the packet is selected for transmission the
credits
consumed
register is incremented by the
number of credits consumed by this packet. This increment happens for both the header and data
credit
consumed
registers.
3. The packet is received at the other end of the link and placed in the RX buffer.
4. At some point the packet is read out of the RX buffer by the Application Layer. After the entire packet
is read out of the RX buffer, the
credit
allocated
register can be incremented by the number of
credits the packet has used. There are separate
credit
allocated
registers for the header and data
credits.
5. The value in the
credit
allocated
register is used to create an FC Update DLLP.
6. After an FC Update DLLP is created, it arbitrates for access to the PCI Express link. The FC Update
DLLPs are typically scheduled with a low priority; consequently, a continuous stream of Application
Layer TLPs or other DLLPs (such as ACKs) can delay the FC Update DLLP for a long time. To prevent
starving the attached transmitter, FC Update DLLPs are raised to a high priority under the following
three circumstances:
a. When the last sent
credit allocated
counter minus the amount of received data is less than
MAX_PAYLOAD
and the current
credit allocated
counter is greater than the last sent credit
12-2
Throughput Optimization
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Throughput Optimization