How vlan works – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 148
21-2
A VLAN is logically divided on an organizational basis rather than on a physical basis. For example, all
workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup can be connected to the same LAN,
regardless of their physical locations.
VLAN technology delivers the following benefits:
Confining broadcast traffic within individual VLANs. This reduces bandwidth waste and improves
network performance.
Improving LAN security. By assigning user groups to different VLANs, you can isolate them at
Layer 2. For hosts in different VLANs to communicate, routers or Layer 3 switches are required.
Flexible virtual workgroup creation. As users from the same workgroup can be assigned to the
same VLAN regardless of their physical locations, network construction and maintenance is much
easier and more flexible.
How VLAN Works
To enable a network device to identify frames of different VLANs, a VLAN tag field is inserted into the
data link layer encapsulation.
The format of VLAN-tagged frames is defined in IEEE 802.1Q-1999.
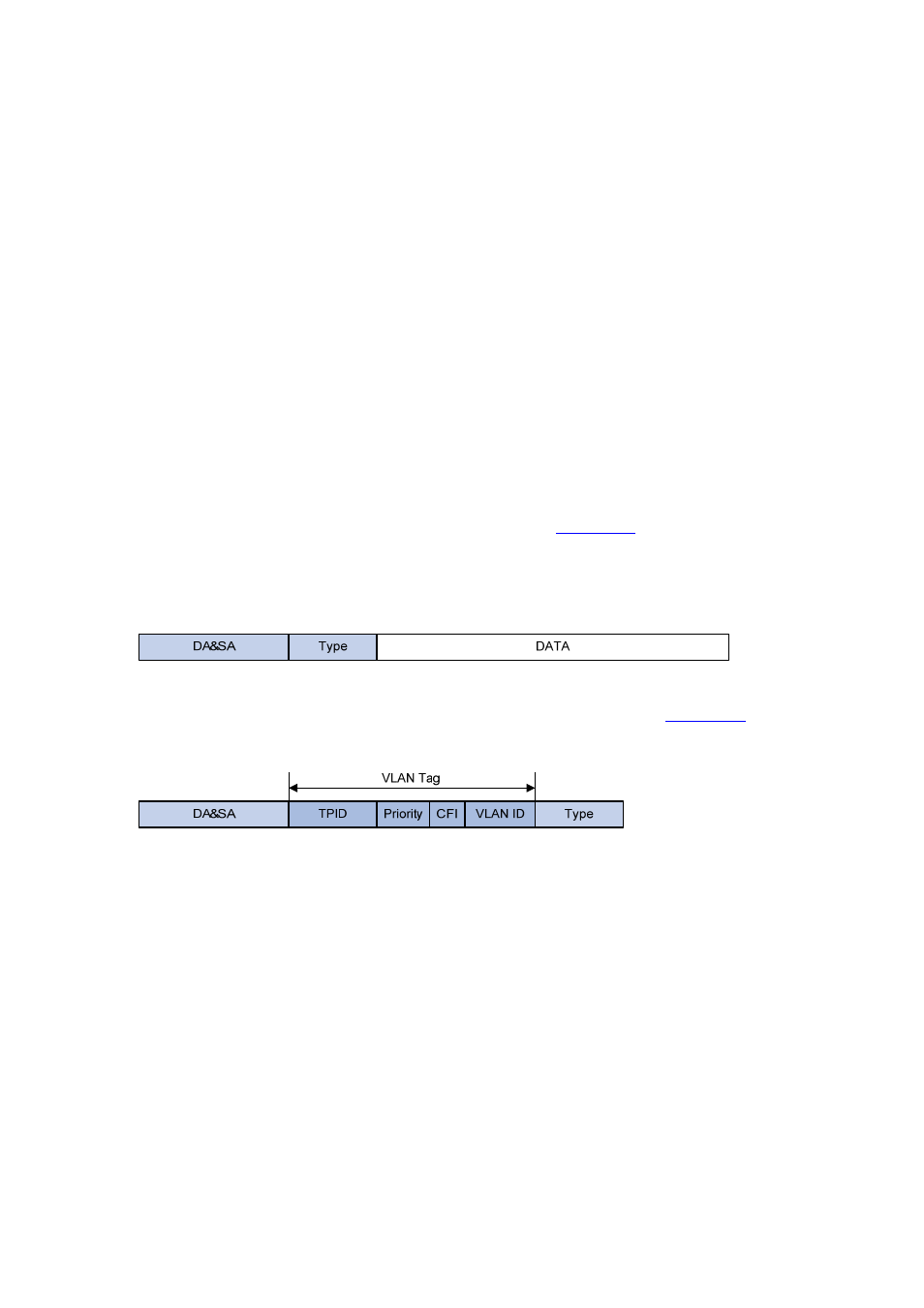
In the header of a traditional Ethernet data frame as shown in
, the field after the destination
MAC address and the source MAC address fields (DA&SA in the figure) is the Type field indicating the
upper layer protocol type.
Figure 21-2 The format of a traditional Ethernet frame
IEEE 802.1Q inserts a four-byte VLAN tag before the Type field, as shown in
Figure 21-3 The position and format of VLAN tag
A VLAN tag comprises four fields: tag protocol identifier (TPID), priority, canonical format indicator (CFI),
and VLAN ID.
The 16-bit TPID field with a value of 0x8100 indicates that the frame is VLAN tagged.
The 3-bit priority field indicates the 802.1p priority of the frame.
The 1-bit CFI field specifies whether the MAC addresses are encapsulated in the canonical format
for the receiving device to correctly interpret the MAC addresses. Value 0 indicates that the MAC
addresses are encapsulated in canonical format; value 1 indicates that the MAC addresses are
encapsulated in non-canonical format. The field is set to 0 by default.
The 12-bit VLAN ID field identifies the VLAN the frame belongs to. The VLAN ID range is 0 to 4095.
As 0 and 4095 are reserved by the protocol, the VLAN ID range available for assignment is 1 to
4094.
When receiving a frame, a network device looks at its VLAN tag to decide how to handle the frame.