Load-balancing entities, Load-balancing modes – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 580
49-5
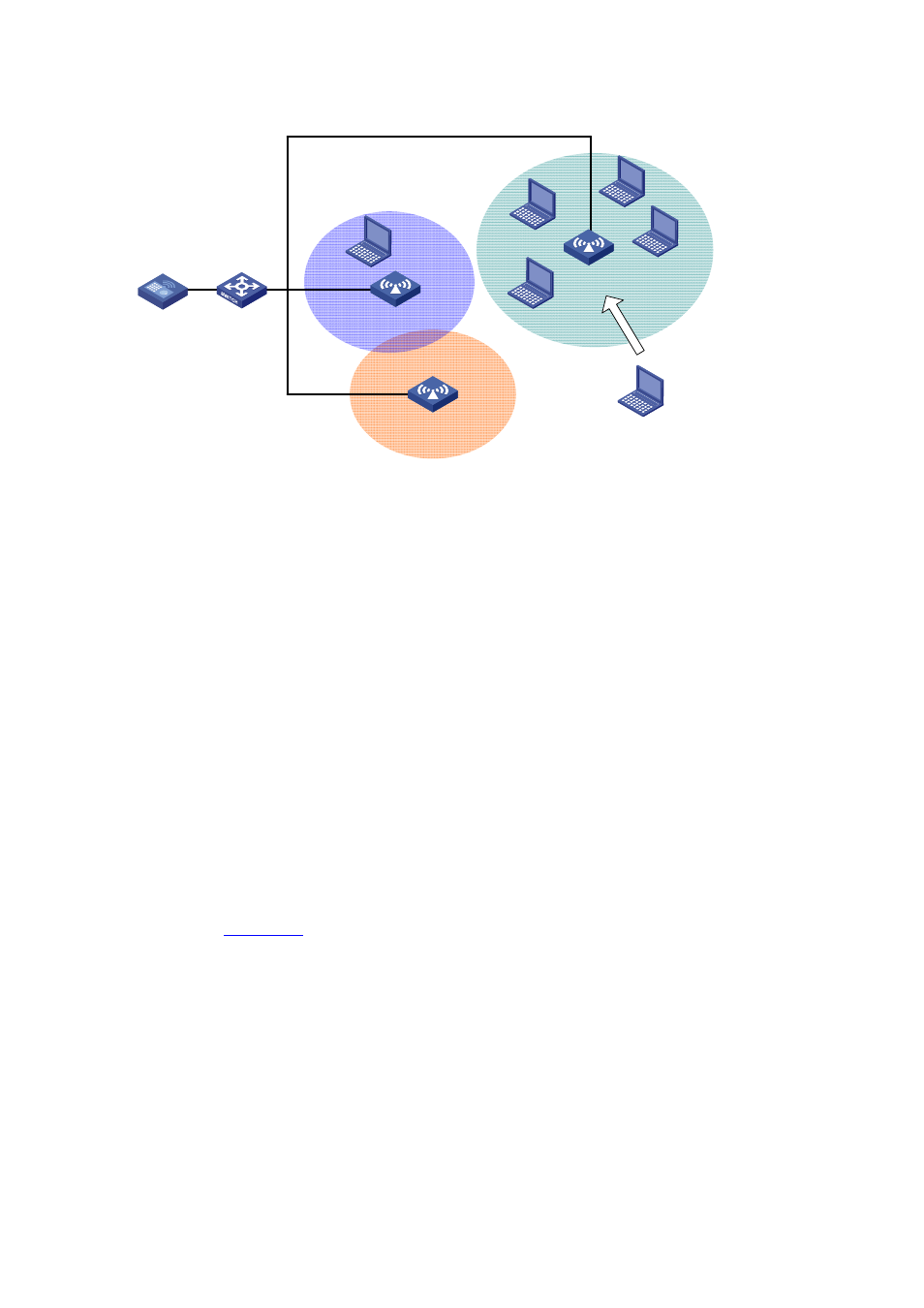
Figure 49-4 Requirement of WLAN load-balancing implementation
AP 1
AP 2
AP 3
Client 1
Client 2
Client 3
Client 4
Client 5
Client 6
AC
L2 switch
Load-balancing entities
Currently, the AC supports AP load balancing and radio load balancing.
AP load balancing
Load balancing is carried out on an AP either based on the number of users connected with it or based
on the traffic load on it. The AP will start load balancing when the threshold and load gap are reached,
and will not accept any further associations unless the load decreases below the threshold, a client is
not able to associate with any other AP, or the load gap is less than the pre-defined limit.
Radio load balancing
Load balancing can be carried out on a radio only when its AP is not overloaded. A radio will start load
balancing when the threshold and maximum load gap are reached and will reject any further
associations unless the load decreases below the threshold, a client is not able to associate with any
other radio, or the load gap is less than the pre-defined limit.
Load-balancing modes
Currently, the AC supports two load balancing modes, session mode and traffic mode.
Session mode load-balancing:
Session-mode load balancing is based on the number of users associated with the AP/radio.
As shown in
, Client 1 is associated with AP 1, and Client 2 through Client 6 are associated
with AP 2. The AC has user-based load balancing configured: the maximum number of sessions is 5
and the maximum load gap is 4. Then, Client 7 sends an association request to AP 2. The session
threshold and load gap have been reached on AP 2, so it rejects the request. At last, Client 7 associates
with AP 1.