Congestion, Causes, Impacts – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 531
46-2
Video-on-Demand (VoD). The enterprise users expect to connect their regional branches together
through VPN technologies to carry out operational applications, for instance, to access the database of
the company or to monitor remote devices through Telnet.
These new applications have one thing in common, that is, they all have special requirements for
bandwidth, delay, and jitter. For instance, videoconference and VoD need large bandwidth, low delay
and jitter. As for mission-critical applications, such as transactions and Telnet, they may not require
large bandwidth but do require low delay and preferential service during congestion.
The new emerging applications demand higher service performance of IP networks. Better network
services during packets forwarding are required, such as providing dedicated bandwidth, reducing
packet loss ratio, managing and avoiding congestion, regulating network traffic, and setting the
precedence of packets. To meet these requirements, networks must provide more improved services.
Congestion
Congestion occurs on a link or node when traffic size is so large that the processing capability of the link
or node is exceeded. It results in extra delay and even packet drop.
Causes
Congestion is typical of a statistical multiplexing network and can be caused by link failure, insufficient
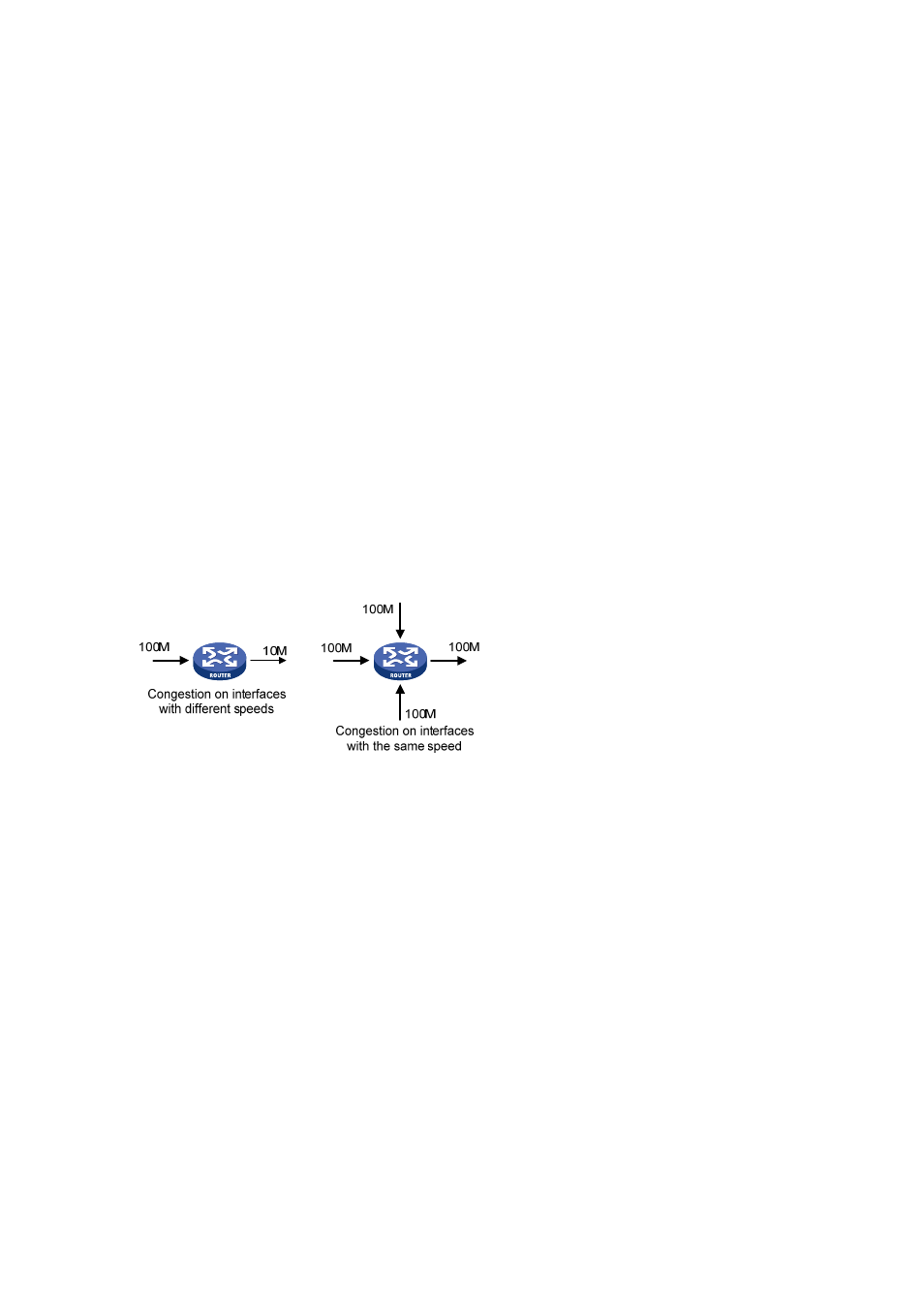
resources, and various other causes. The following figure shows two common congestion scenarios:
Figure 46-1 Traffic congestion causes
The traffic enters a device from a high speed link and is forwarded over a low speed link;
The packet flows enter a device from several interfaces with the same speed and are forwarded
through an interface with the same speed as well.
When traffic arrives at the line speed, congestion may occur due to the network resource bottleneck.
Besides the link bandwidth bottleneck, congestion can also be caused by resource shortage, such as
insufficient processor time, buffer, and memory. In addition, congestion may occur if the arriving traffic is
not managed efficiently, thus resulting in inadequate network resources.
Impacts
Congestion may bring these negative results:
Increased delay and jitter during packet transmission
Decreased network throughput and resource use efficiency
Network resource (memory in particular) exhaustion and even system breakdown
Congestion is unavoidable in switched networks or multi-user application environments. To improve the
service performance of your network, you must take measures to manage and control it.
One major issue that congestion management deals with is how to define a resource dispatching policy
to prioritize packets for forwarding when congestion occurs.